Content
A distinctive feature of many types of mint is the cooling sensation that occurs in the mouth when eating the leaves of this plant. This is due to the presence of menthol, an organic compound that irritates cold receptors. However, not all plants of this family contain the substance in their composition, and one of these species is spearmint.
Description of spearmint
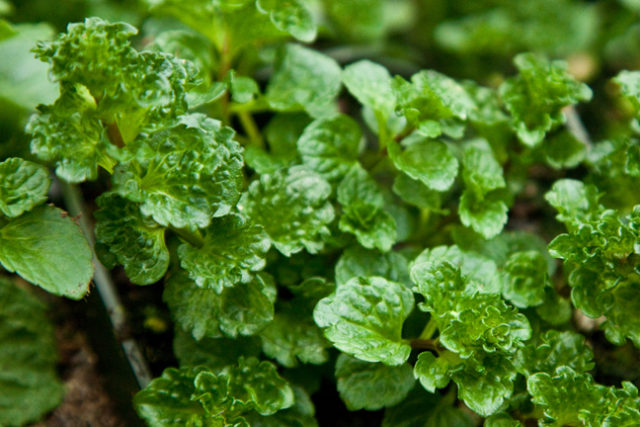
Photos and descriptions of spearmint can be found in many botanical publications. Its main difference from other plants of this family is the shape of the leaves. In this species they are pubescent, with a strongly corrugated leaf plate. Thanks to this, the species got its name - curly or curly mint. Some other plant parameters are shown in the table below:
Parameter | Meaning |
Synonymous names | Mint spearmint, spearmint, curly mint, green |
Plant type | Perennial herbaceous |
General form | Bush 0.5-0.9 m high, multi-stemmed, slightly spreading |
Root | Creeping, tree-like, climbing, superficial, there is a small lobe of adventitious roots |
Stem | Erect, light green, becoming reddish brown with age |
Leaves | Bright green, round-ovate, with short petioles, sessile in the upper part of the stem. The leaf blade has a characteristic bumpy-wrinkled surface, the edge is wavy |
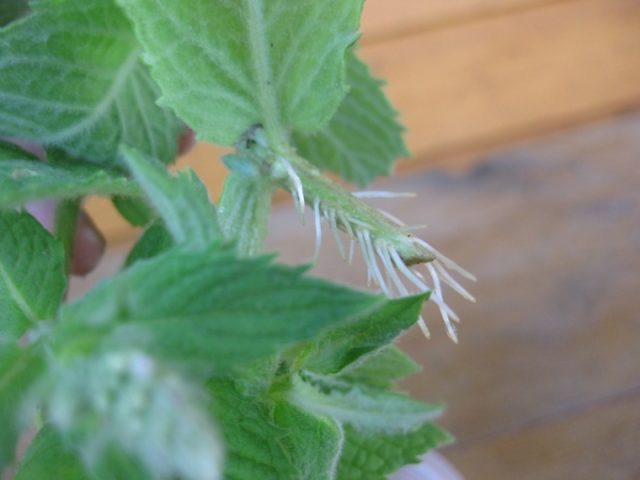
Flowers | Small, mauve, collected in inflorescences, false whorls, at the ends of stems |
Mint in the photo below:
This plant grows wild in North Africa, as well as in Western and South-Eastern Europe.
What is the difference between spearmint and peppermint?
Peppermint contains a large amount of essential oils, one of the components of which is menthol. The refreshing aroma of this plant is strong and quite persistent. Unlike peppermint, spearmint contains virtually no menthol and has a very light, subtle aroma. In addition, differences appear in the biological structure.

Peppermint leaves are more pungent
Peppermint bushes are usually slightly lower and have a pointed end to the leaf blade, while curly mint has a more rounded end.
Use of spearmint in cooking
In cooking, spearmint is used mainly as a spice. In dried form, it is added to spices; fresh herbs are used as a vegetable component in the preparation of a variety of dishes and drinks.
What is the aroma of curly mint?
Curly mint leaves lack the menthol sharpness characteristic of many types in their aroma. Its smell is subtle and delicate. It tastes tender and pleasant, as it has a characteristic mint flavor.
Where can you add mint?
Curly mint leaves are used to prepare meat, fish and poultry dishes, various cocktails and soft drinks. They are widely used for canning vegetables and fruits, added to sauerkraut and soaked apples. Greens are an excellent decoration for dishes; they are often used as one of the components in various salads. Spearmint is brewed into tea and used hot or cold, not only as a refreshing drink, but also as a medicine.

Mint tea is not only tasty, but also healthy
Beneficial properties of spearmint
The essential oils and aromatic compounds contained in spearmint leaves have medicinal properties and are used for a variety of medicinal purposes. And also one of the areas of application of this plant is cosmetology.
Medicinal uses of spearmint
It has long been noted that mint decoction causes a pronounced sedative reaction. Therefore, traditionally this plant was used to calm, normalize sleep, relieve excessive excitement or anxiety. However, the beneficial properties of spearmint do not end there. It can be used for the following medicinal purposes:
- As a choleretic agent that normalizes the digestive process.
- As a vasodilator, lowering blood pressure.
- For inhalation for colds, and also as an analgesic and diaphoretic.
- To relieve swelling, as a local anesthetic for bruises.
- As a mouth rinse to prevent and treat gum disease.
- As a supplement for the treatment of skin rashes and skin cleansing.

A mask of crushed mint leaves will cleanse the skin well.
Restrictions and contraindications
In some cases, the use of spearmint can cause harm rather than benefit. For example, a contraindication to its use is low blood pressure. In this case, using mint will only worsen the situation. This plant should be used with caution for varicose veins, as it reduces the tone of the veins. It should not be used by those people who require increased attention at work, or those suffering from excessive drowsiness. Increased stomach acidity, individual intolerance and childhood (up to 3 years) are also contraindications to the use of spearmint.
Features of reproduction
Due to the ease of propagation, spearmint has long been successfully grown not only in areas of natural growth, but also in many countries of the temperate zone, including Russia. The plant can be propagated in the following ways:
- Seeds.
- Rhizome (root cuttings).
- Air layering.
- Dividing the bush.
- Cuttings.
The seed propagation method is quite long, but it will have to be used if it is not possible to use vegetative methods. Mint seeds can be purchased at many specialty stores or online.In the southern regions, they can be planted directly in open ground, while in more northern regions it is preferable to use the seedling method. In this case, the seeds are germinated at home, and after the weather is suitable outside, the grown seedlings are transferred to a permanent place.

Mint seedlings are very easy to grow at home
If there are already plantings of mint on the site, then it is preferable to use vegetative methods. Here is a brief description of each of them:
- Cuttings. Young apical parts of curly mint shoots 10-15 cm long are used as cuttings. They are cut off and placed in water. Quite quickly, the cuttings begin to form their own root system in the water; after 1.5-2 weeks, the first roots can be seen in the cut areas. After they reach a length of 2-3 cm, they can be transplanted into the ground in a previously prepared place.
Roots on a mint cutting in water appear quite quickly
- Root cuttings. On the climbing rhizomes of curly mint there are a large number of dormant buds. For seedlings, a part of the root 10-12 cm long is used. It is cut off from the common rhizome and planted in moist soil. With regular watering, the buds wake up quite quickly and the plant sprouts.
- Dividing method The bush can be used if its age exceeds 4-5 years. In this case, the plant is completely dug out of the ground and divided into several parts so that each has a sufficient number of roots and a stem with growth buds. Then the divisions are planted in permanent places.
- Air layering. If you bend a side shoot of a bush to the ground and sprinkle it with earth, then each node will quickly begin to form its own root system, and in place of the sprinkled shoot an even row of young seedlings will sprout. They are carefully separated from the mother shoot, separated from each other and dug out of the ground, then replanted in a permanent place.
Landing rules
It is better to dig up the bed for planting curly mint in the fall, this will reduce the likelihood of pests appearing next year. Additionally, you can treat the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate. In the spring, the beds are dug up again, adding mineral and organic fertilizers. At this time, you can use manure and chicken droppings; they enrich the soil with nitrogen and promote the rapid growth of green mass.

Good preparation of beds is the basis for an excellent harvest
After the threat of night frosts has completely passed and the ground has warmed up to + 5-8 ° C, you can begin planting.
Plant mint seedlings in rows, maintaining a distance of 25-30 cm between adjacent plants. The planting holes are pre-prepared so that their volume is sufficient for the root system of the seedlings. Before planting, they are spilled with water, then the seedling is placed in them and the soil is slightly compacted. After this, the root system is sprinkled with soil to the level of the bed, and then watered abundantly with water.
Features of cultivation
After planting, curly mint requires regular moderate watering. When the plants grow older, they will need to be watered less frequently, and if there is sufficient precipitation, additional soil moisture should be abandoned altogether.It is very important to periodically loosen the root zone of the bushes so that the surface roots of the curly mint receive a sufficient amount of oxygen. Weeds must be removed from the garden in a timely manner.

Slurry is an excellent fertilizer for quickly gaining green mass.
From time to time, mint bushes can be fed with mineral fertilizers or organic matter. It is especially important to do this in spring and early summer. For feeding, slurry or diluted chicken droppings are usually used. These components contain a large amount of nitrogen, which stimulates increased growth of green mass. However, it must be remembered that excess nitrogen fertilizers are a risk factor for the development of certain fungal diseases.
Pests and diseases
The juicy and tender leaves of spearmint attract not only people, but also insect pests. Here are some of them most often found on this plant:
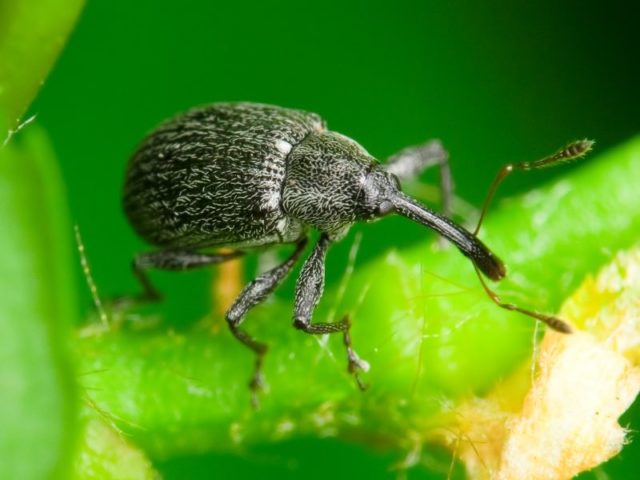
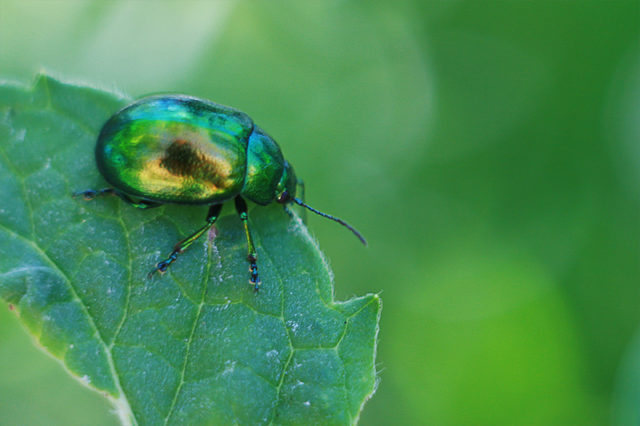
- Weevil. A small bug with a characteristic proboscis that feeds on young green plants.
Can damage not only leaves, but also flower buds
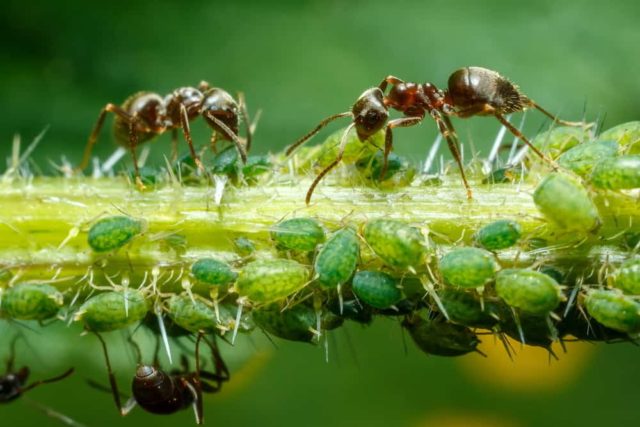
- Aphid. A very small sucking insect of light green color. A feature of aphids is their fertility. They often settle on plants in large colonies, literally sucking all the juices out of it.
Aphids with their inseparable companions - ants
- Peppermint flea. A small greenish-brown bug. It feeds on young greenery and damages leaves and growth buds.
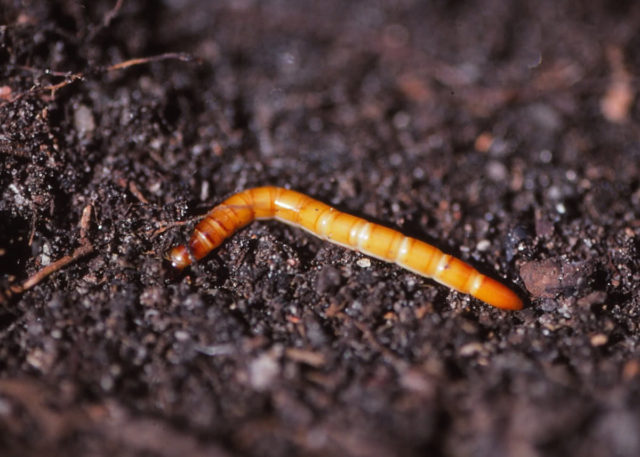
- Wireworm. This is a white, hard click beetle larva that lives in the ground. Damages the roots of many plants, including mint.
Poor care and unfavorable weather conditions can provoke the appearance of various diseases, especially fungal ones, on mint bushes.The most common of them are the following:
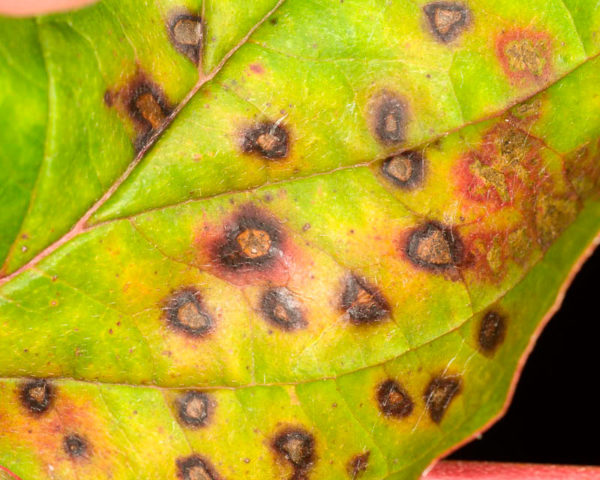
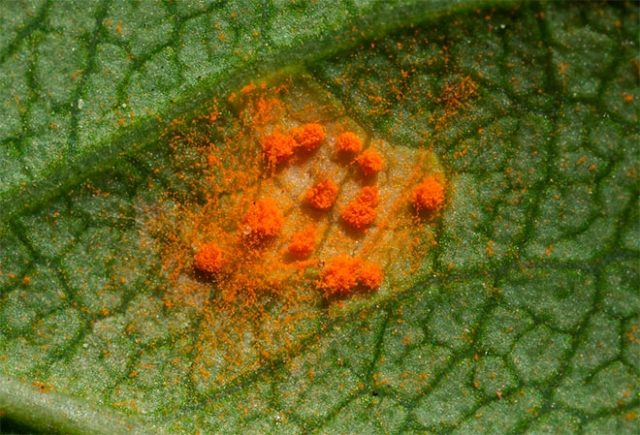
- Rust. The disease can be recognized by the characteristic reddish-brown spore pads of the fungus. Gradually, pockets of rot appear in their place and the plant dies.
- Septoria. It appears in the form of small, clearly defined light spots with a dark border, in place of which pockets of dead tissue then form, which are gradually destroyed. Septoria most often manifests itself in conditions of high temperature and humidity.
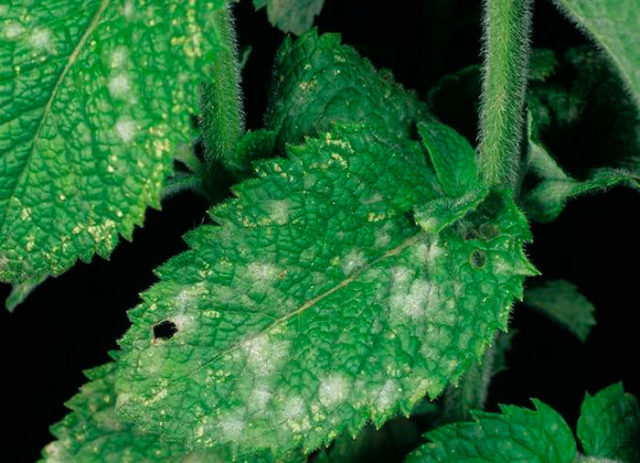
- Powdery mildew. The disease can be recognized by the characteristic thin light coating on the leaves. In such places, plant tissues darken and rot very quickly. A risk factor for powdery mildew is high humidity, as well as sudden drops in temperature.
Prevention of the occurrence of diseases and the appearance of pests is mainly agrotechnical measures, such as deep autumn plowing, removal of plant residues, timely removal of diseased plants, etc.
When and how to collect curly mint
The best time to harvest spearmint is mid-July. At this time, before flowering begins, the leaves of the plant contain the maximum amount of aromatic substances. Mint can be harvested either with individual leaves or with whole plants, cutting them off and tying them into bunches. This should be done on a warm, dry day, making sure to wait until the morning dew has dried on the leaves.
How to properly dry spearmint
The collected leaves of mint are scattered onto baking sheets or plywood boards covered with clean paper, which are placed in a dry, well-ventilated area. At the same time, the grass should not be exposed to direct sunlight. To prevent the leaves from caking, they need to be stirred periodically.After they become brittle, they are crushed and stored.

Completely dried mint leaves become rustling and brittle.
It is best to store dried spearmint leaves in a tightly sealed glass or clay container. It is allowed to place the harvested plant materials in tightly closed canvas or fabric bags, but in this case they must be kept in a cool, dry room, isolated from other spices.
A short video about drying mint can be viewed at the link below.
Conclusion
Spearmint is a beautiful and useful plant. It combines both culinary and medicinal properties and will become an indispensable crop when planting, for example, an apothecary garden. Caring for this plant is simple, and the ease of propagation makes growing spearmint an easy task even for beginners.