Content
Spices are an integral component of many dishes. Spicy additives help make food more aromatic, tastier and more attractive to look at. Another purpose of spices is to improve the absorption of food and activate metabolic processes in the body. At the same time, even chefs often confuse popular herbs. What is the difference between fennel and anise can be found out by their agrotechnical and botanical characteristics.

During the flowering period, fennel and anise are easily distinguishable by the color of their miniature buds
Fennel and anise - the same thing or not
Widely used in cooking, fennel and anise have similar taste and properties. As a result, cooks and consumers often confuse herbs with each other.
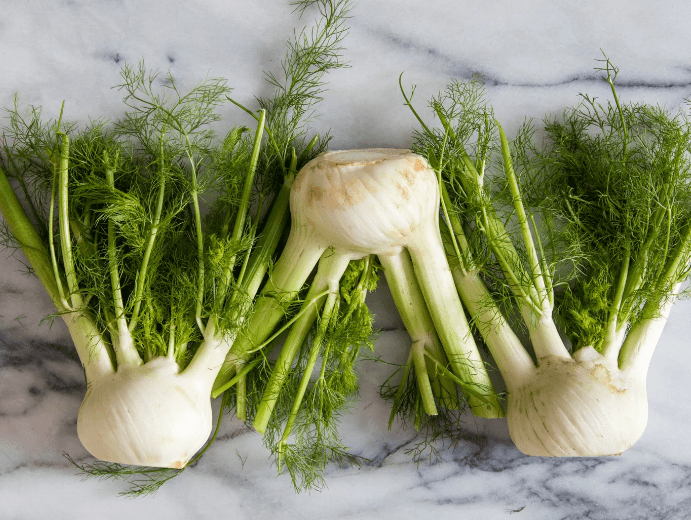

In fact, anise and fennel are different plants, although they belong to the same family - Apiaceae.
What is the difference between fennel and anise?
Related plants have common features. At the same time, each of the spice cultures has characteristics that are characteristic only of them. Upon closer inspection, distinctive qualities are noticeable.
Appearance
The plants are similar in appearance, but knowing the inherent characteristics of each, they can be easily identified. So, annual anise has:
- a taproot that lies deep in the ground, which allows the plant to survive even in extreme conditions;
- straight shoots 0.5 m high and slightly higher;
- stems covered with edges and grooves that begin to branch from the middle;
- carved or serrated foliage of a dim green hue;
- two-seeded fruits of a green-gray hue with small grains inside.
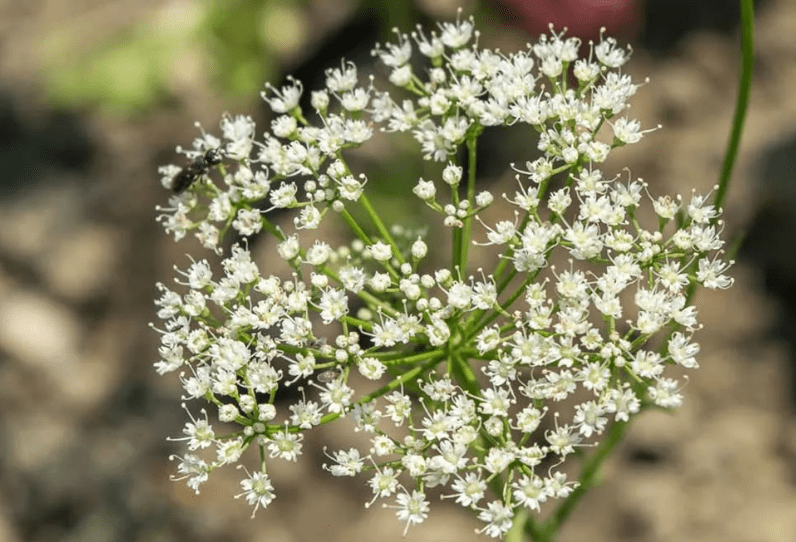
Small white anise buds, collected in inflorescences with a diameter of 6 cm, form on the shoots from the end of June
A relative of anise, fennel belongs to the category of perennials and has its own characteristics. The characteristic features of the plant are:
- fleshy, wrinkled root;
- pinnate leaves with long thread-like lobes;
- yellow flowers collected in flat large umbrellas.
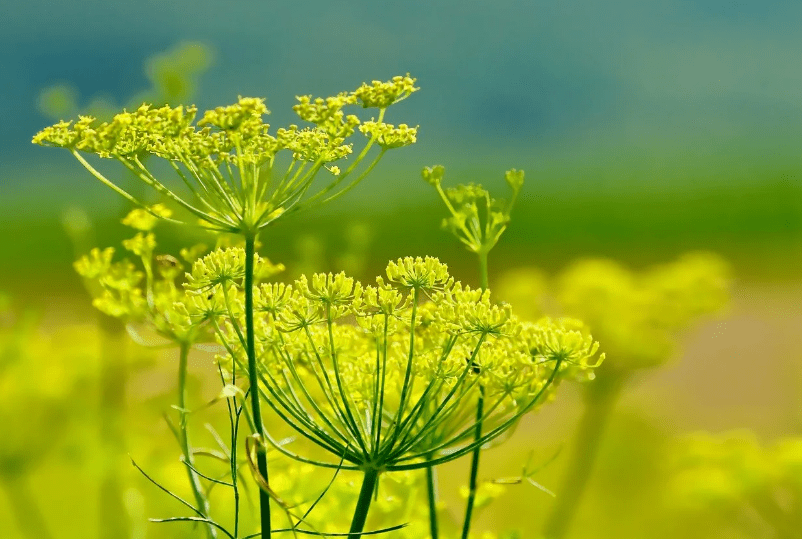

Fennel fruits are also two-seeded.
The stem of the two types of crops is different: the vegetable one is thick and dense, while the ordinary one is noticeably thinner.
Origin
Fennel has been used in the cuisines of different nations for a long time. The historical homeland of the plant is considered to be Southern Europe, the Mediterranean region, from where it came to other countries and continents. The aromatic herb was added to food by the ancient Egyptians, Romans, Greeks, Chinese and Indians.
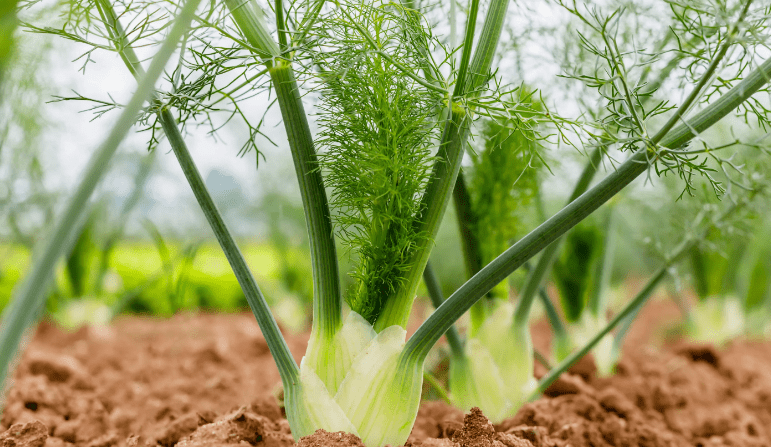

Currently, fennel is cultivated in Europe, North America, and Southeast Asia.
Anise is native to Western Asia and the Mediterranean. It is known that the spice was used by the Egyptians as early as 1000 BC. e. Anise was popular in Ancient Greece and Rome. Later, the spice came to the countries of Northern and Western Europe, where it took its rightful place in national cuisine, medicine and perfumery.
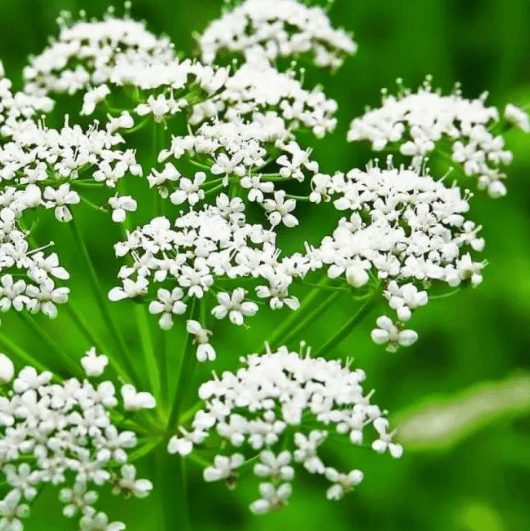

Today, anise is grown in Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia.
Edible parts of the plant
Fennel is completely edible. All parts of the plant are used to prepare various dishes:
- seeds;
- young leaves;
- bulbs (heads of cabbage).
In anise, the seeds are usually used for food. The seeds of the plant have a pleasant aroma. Some gourmets add anise leaves to vegetable and fruit salads.
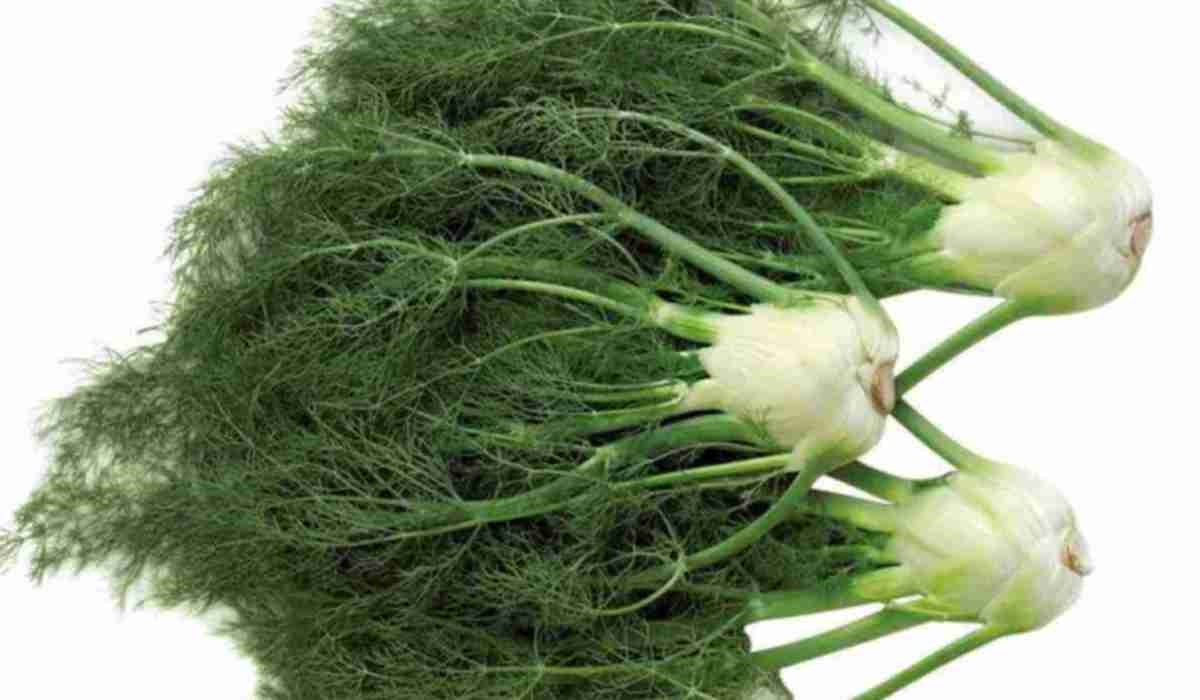

Fennel oil is used as a remedy for toxic liver damage
Fennel and anise seeds are similar, as can be seen in the photo, so they are often confused. The grains of both plants are small, elongated in shape. The taste and aroma are also similar, but the smell emitted by anise seeds is more intense and tart, while that of fennel is not as rich, as if muted.
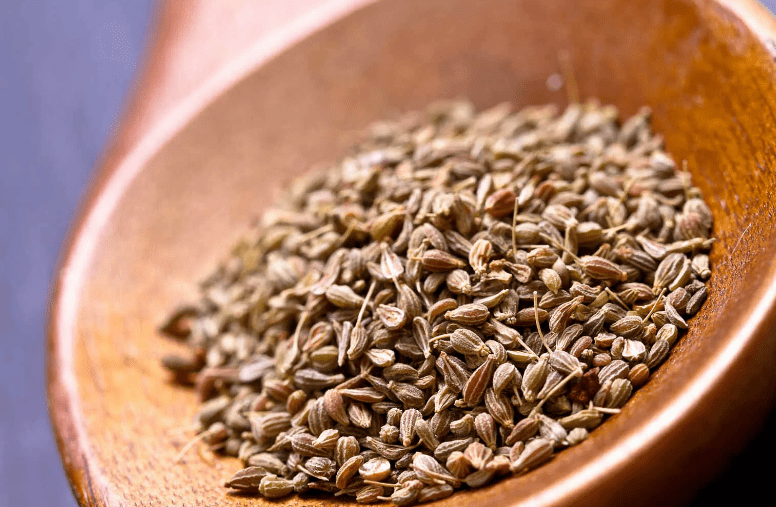

A refreshing licorice aroma is characteristic of the seeds of both plants, but those of anise are smaller.
Methods of application
Connoisseurs note that anise has a special licorice flavor. The reason for this is the organic compound anethole. The key characteristic of a substance is its solubility in alcohol. In this regard, anise seeds are used in the production of some alcoholic beverages (absinthe, sambuca, anise vodka). The plant extract is also added to soft drinks, giving them a light caramel aroma and taste.
Anise is added to dough for baking baked goods or used as a topping for certain types of bread. Spicy seeds are used in preparing meat and poultry dishes, desserts, and marinades.
Fennel is in demand in cooking. The leaves are added to salads, stewed meat and fish dishes. The seeds are used to add spice to broths, soups, marinades, and sauces.Fennel is an essential component of French and Italian cuisine. It is widely used in medicine, as the plant:
- has an antispasmodic effect;
- activates the production of secretions from the digestive glands;
- used as an expectorant.
- has a diuretic effect;
- acts as an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agent.
As a carminative, fennel can even be given to infants for indigestion. Sometimes the herb is added to a sedative mixture.
Features of cultivation
Annual anise is grown exclusively in the southern regions, since in the northern regions the seeds do not have time to ripen. If the plant is planted to produce greenery, then it can be grown in temperate climates. Seeds are sown in the soil directly on the site. The crop requires fertile soil and abundant irrigation.
The growing season for fennel is four months. Therefore, it is advisable to grow the crop as seedlings. The optimal time for planting is the end of April. The first shoots appear only after 20 days. Planting in the open area is planned for the second half of May. Experienced gardeners know the important nuances of caring for fennel:
- The soil must be weeded frequently, as the crop does not respond well to weeds.
- Watering is organized depending on the condition of the soil. Drip irrigation is preferable.
- After each watering, loosening is carried out to a depth of 3-5 cm.
In addition, vegetable varieties of fennel need hilling so that the heads ripen well.The agrotechnical procedure involves the formation of an earthen mound approximately 6 cm high at the stem.
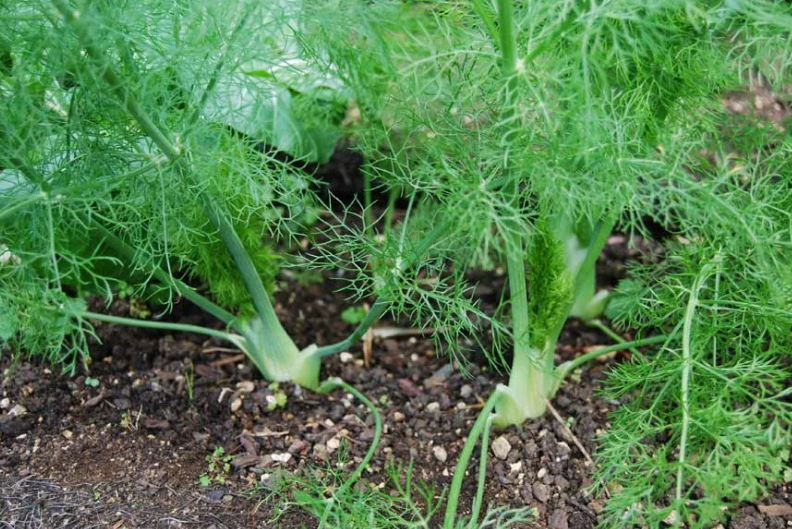

Once during the warm season, the area is fertilized with mineral compounds.
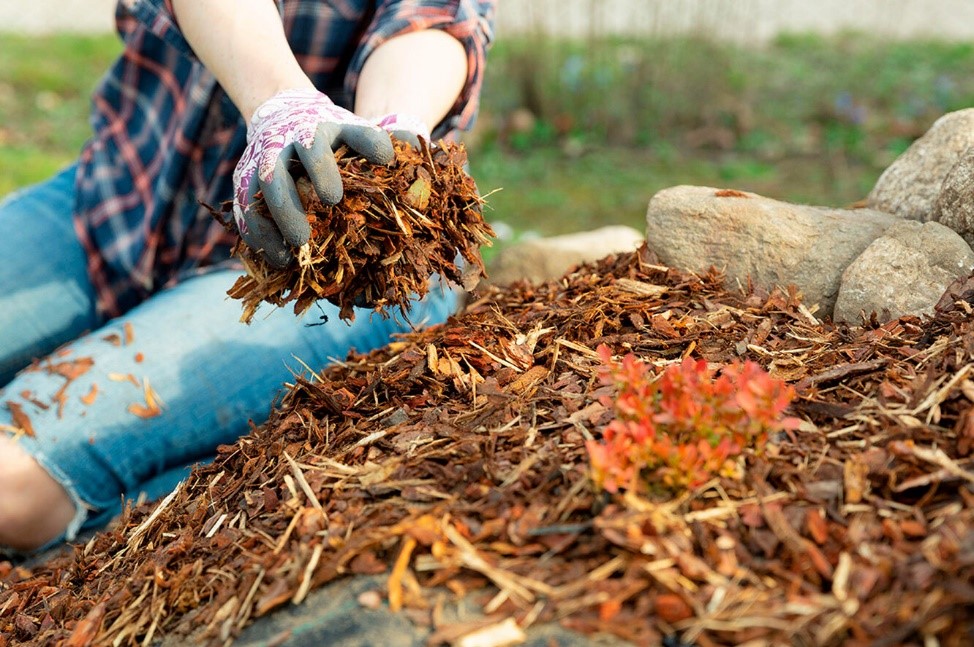

You should not mulch the fennel bed with straw for the winter, as it attracts mice; it is better to choose another natural material
Conclusion
There is a difference between fennel and anise; they are not the same plants, although they are related. There are differences in the use of herbs, especially when used for medicinal purposes. The agricultural technology for cultivating perennial fennel is much more complex than anise and requires a significant amount of time.








