Content
Treating grain allows you to protect the future harvest from diseases and pests. Fungicides are considered the best in terms of fighting fungi. Modern drugs are low-toxic and do not pose a particular danger to humans and the environment. One effective remedy is Triactive fungicide, consisting of three active components.
Compound
Triactive is the newest means of combating fungal diseases of grain crops. The drug consists of three active components:
- azoxystrobin – 100g/l;
- cyproconazole – 40 g/l;
- tebuconazole – 120 g/l.
Each constituent substance is an active fungicide.
Action
When considering the instructions for use of Triactive fungicide, it is worth paying attention to the action of each active substance:
- Azoxystrobin is a means of contact as well as translaminar action. The active component protects and treats grain crops from fungus. The fungicide inhibits the growth of mycelium and the awakening of spores. The active component has a systemic effect. After spraying the crops, the fungicide is able to be redirected to neighboring plants in contact with the foliage.
- Tebuconazole and cyproconazole similarly have systemic effects.Immediately after spraying, the substances are absorbed and distributed throughout the plant. The components destroy fungal cells and prevent them from developing, which leads to the complete destruction of the fungal organism.
Thanks to the successful combination of three components, Triactive cures a whole range of diseases of grain crops, and also provides protective preventive effects.
Positive qualities of the fungicide
The usefulness of Triactive is confirmed by five advantages:
- A successful combination of three active components with different actions.
- Triactive effectively protects and cures foliage, stems, and ears from fungal diseases.
- The fungicide has a long period of action. Active protection prevents re-infection of grain crops and preserves the integrity of foliage.
- Thanks to azoxystrobin, grain crops develop resistance to stressful conditions.
- Triactive ensures grain harvest even in bad weather conditions.
The disadvantages of the fungicide have not yet been identified.
The Importance of Chemical Grain Dressing
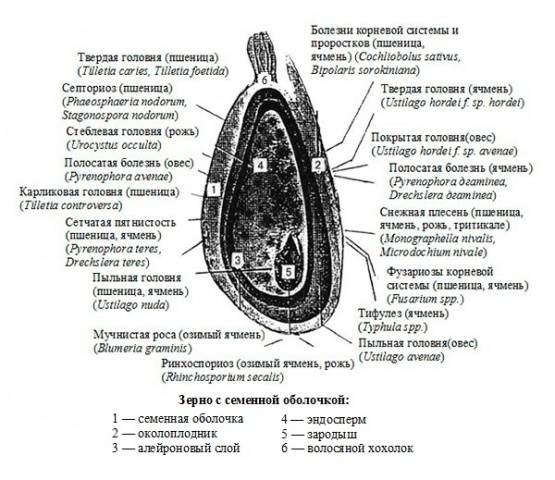
Treating grain with chemicals allows you to create integrated protection. Not only seed material is affected. Protection extends to sprouts, root system, leaves, stems and mature ears. Harmful microorganisms are destroyed by fungicide at different phases of development.
The causative agents of fungal diseases are found not only on grains or growing crops. Microorganisms take root well in the soil, overwinter, and in the spring they awaken and begin to spread over fresh crops.Winter and spring flies and aphids, which carry the pathogens of barley yellow dwarf disease, pose a great danger.
A systemic fungicide used for grain dressing protects crops at an early stage from fungus, the spores of which are carried by the wind. Farmers no longer need to spray their crops early against powdery mildew.
Methods for chemical treatment of grain
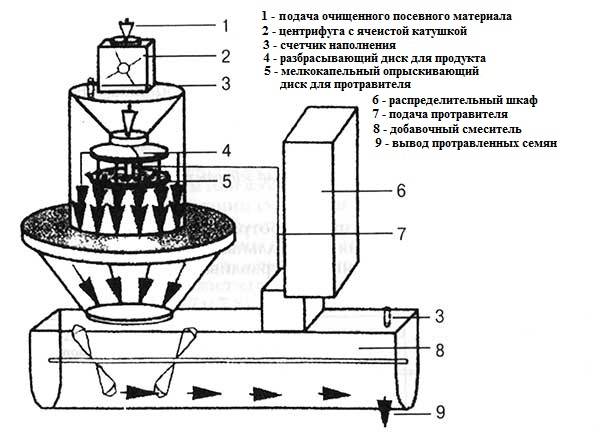
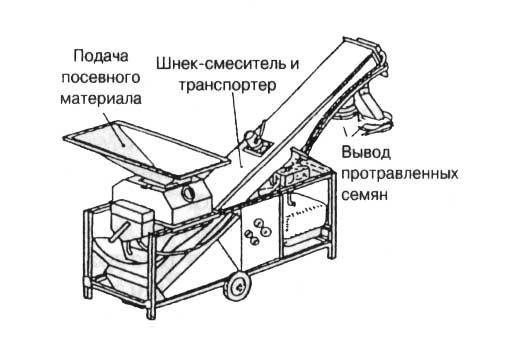
Chemical grain dressing is performed using machines or special devices. Each processing method uses its own form of the drug. There are four main ways to treat grain:
- The simplest way to treat grain is dry processing. The process takes place in a specialized machine. The disadvantage of this method is the uneven coating of all grains with a chemical preparation. The active substance is poorly retained on the dry seed coat. During pickling, heavy dust is generated.
- The semi-dry pickling method provides for light moistening of the grain. Spray no more than 10 liters of water per 1 ton of dry seeds. With this amount of liquid, the moisture content of the grain remains unchanged, which eliminates the need for additional drying. The processing process takes place in a specialized machine. The chemical is dissolved in water, which is used to spray the grains.
- The wet pickling method is based on strong moistening of the grain. The seed material is sprayed, watered or completely soaked in water with a dissolved chemical.Upon completion of pickling, the grains are subjected to additional drying until the optimum moisture content is reached.
- Treating the grain with a fungicide and a polymer substance before sowing gives good results. The process is called hydrophobization. After processing, a thin but very durable film is formed on the surface of the grain. The fungicide is securely held on the seed coat under the polymer. The method allows for good fungicide activity, increasing the germination process and yield. After hydrophobization, grains can more easily withstand low soil temperatures.
Of all the treatment methods, hydrophobization allows you to more effectively protect grain from diseases and negative natural factors.
The process of treating grain with fungicide
All grain crops, especially winter ones, require dressing before planting. Farmers who want to save money try to limit themselves to only autumn fungicide treatment. Unjustified savings lead to large crop losses. Expenses increase because the money invested does not generate profit.
Conventionally, the entire etching process can be divided into five steps:
- The grain material is sent for phyto-examination. In the laboratory, pathogens are determined. Based on the data obtained, a chemical preparation is selected.
- Before dressing, the grain material goes through a preparation stage. The seed of the middle fraction is selected. Dust impurities, weed grains, and damaged seeds are screened out. Etching without a selection process is irrational.About 20% of the fungicide is used for other purposes, as the drug is spent on unnecessary impurities.
- According to the results of the examination, a disinfectant belonging to the desired chemical group is selected. Additionally, not only the name of the drug is taken into account. It is important to choose the right fungicide according to its mechanism of action. Contact-action drugs form a protective shell around the grain, but do not penetrate into the tissues themselves. Systemic fungicides act from the inside, penetrating the seed, and also disinfect the soil around the grain. Complex preparations perform the functions of contact and systemic fungicides. As an example, we can take the disease of loose smut, where only systemic drugs can cope. And a simple contact fungicide will save you from smut. Products containing triazole are effective against root rot and mold on seed material. Considering that a grain crop can become infected with any disease, Triactive is considered effective for treatment.
- The fourth step can be called the most responsible. At this stage, the preparative form of the fungicide is selected. The quality of dressing depends on the intensity of adhesion of the product to the seed coat. Powdered fungicides, even when wetted, do not adhere well to the seed. It is better to use concentrated suspensions. And in this regard, Triactive wins.
- The last steps involve setting up the machine. The mechanisms are adjusted so that the seed material is supplied evenly and treated with the working solution. Achieve uniform mixing of grain during pickling. The supply of the working solution is adjusted so that the error in deviation from the norm does not exceed 5%.In this case, the completeness of seed treatment should be more than 80%.
Violation of seed treatment technology threatens yield loss in the range of 20–80%. The approximate consumption of Triaktiv fungicide per 1 ton of winter wheat is 0.2–0.3 liters.
When treating crops, the drug has proven to be an effective fungicide that helps protect grain crops from powdery mildew, fusarium and head blight, rust, as well as other types of diseases. The consumption of concentrated Triactive for spraying an area of 1 hectare ranges from 0.6 to 1 liter.
The video talks about protecting grain crops with fungicides:
The broad-acting drug Triactiv provides comprehensive protection of grain crops from diseases. For a farmer, this is a triple success in work, saving money and obtaining a stable harvest.