Content
Eggplant is a heat-loving and rather “picky” plant. Its “capriciousness” concerns both cultivation conditions and agricultural technology. You can count on abundant harvests only if you choose the right place for the garden bed and carry out pre-planting treatment of the soil and seeds. It is equally important to know how to plant eggplants in open ground - with seeds and seedlings, and how to care for them throughout the season.
When to plant eggplants in open ground
Eggplant is originally a southern heat-loving crop. Therefore, they are planted in open ground only when the substrate at a depth of 12-15 cm warms up to 16-18 °C. By this time, consistently warm weather has established itself, and the likelihood of return frosts is minimized.
When exactly to plant seedlings in open ground is determined taking into account local climatic nuances. In central Russia, you can plan the procedure for the last ten days of May or the first days of June.In regions with a harsher climate, you will have to wait until the middle of this month. In the south, eggplants can be planted in open ground already at the “junction” of April-May.
Cultivation of crops by seeds in Russia is practiced exclusively in the southern regions. The seedlings do not differ in their rapid germination and development rate: they have time to mature in open ground if they are planted in the first ten days of April. However, even in the south by this time the substrate has not yet had time to warm up. Therefore, the bed on which eggplants are planted must be covered with plastic film, turning it into a temporary “greenhouse”.

It is very difficult to reap a bountiful harvest if you miss the timing of planting eggplants.
How to plant eggplants in open ground
Eggplant seeds are rarely planted in open ground in Russia. The growing season of the crop is long (100-160 days), the fruits may simply not have time to ripen. There is also a high risk of reducing the percentage of seed germination due to planting them in insufficiently warmed soil.
Site selection and soil preparation
Eggplants are very heat- and light-loving. Therefore, they are planted only in open areas, providing protection from cold drafts and strong winds.
Other criteria that need to be taken into account when choosing a place for a garden bed:
- Soil that combines looseness with fertility. The soil must provide normal air exchange. It is impossible for moisture to stagnate in it.
- Neutral or slightly acidic pH. This indicator must be determined in advance and, if necessary, adjusted during the preparation of the bed.
- Groundwater lying at least a meter below the soil level.

Bushes can easily tolerate heat and direct sunlight if they are provided with sufficient watering.
The bed where it is planned to plant eggplants in open ground has been prepared since the fall.The substrate is dug to a depth of approximately a spade's length, while simultaneously enriching the soil with humus (3-5 l/m²) and adding complex fertilizer (20-25 g/m²). It is advisable to plant eggplants in open ground after feeding them with specialized fertilizers for Solanaceae. From folk remedies, sifted wood ash (0.5 l/m²) is used.

During the digging process, weeds and other debris are removed from the garden bed.
In the spring, before planting eggplants in open ground, the area must be well loosened with a pitchfork or rake and leveled. This is done when the snow has already melted from the soil and it has dried out well.
Seed selection and preparation
If a gardener plants an eggplant variety, the seeds can be obtained from independently grown fruits. But such planting material also gradually degenerates. Every 3-4 years you need to buy new seeds. Hybrids are in principle unsuitable for generative propagation; specimens grown from seeds do not inherit the varietal characteristics of their “ancestors”.
In stores, seeds for planting in open ground are selected based on:
- fruit ripening period;
- type of cultivation;
- appearance of bushes and fruits, other varietal characteristics (yield, immunity, cold resistance);
- possibility of cultivation in a certain region.
Before planting eggplants in open ground, the seeds are checked for germination. They are soaked in saline solution (2 tbsp/l). After 7-10 minutes, specimens that do not contain embryos float to the surface.
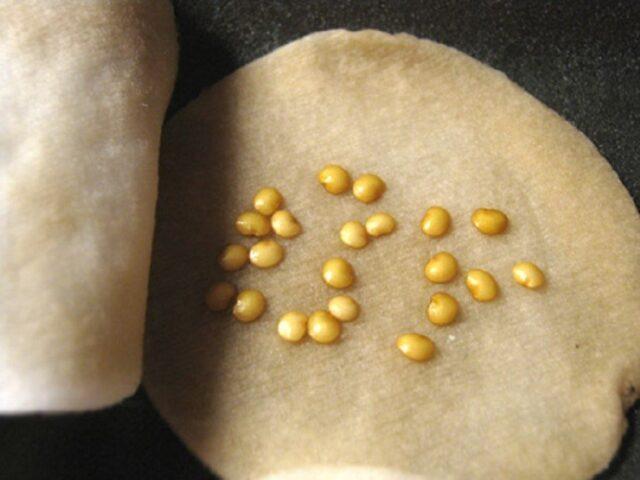

Seeds that have passed the rejection are dried and heated for 12-15 days, wrapped in cloth and placed on a radiator.
To improve germination, seeds are treated with any biostimulant. They are susceptible to many diseases, so before planting them in open ground, it is recommended to treat them with a solution of a suitable fungicide.
Gardeners have differing opinions regarding whether it is necessary to germinate seeds. Most limit themselves to soaking them in clean warm water for a day immediately before planting.
Sowing rules
Seeds are sown in open ground in pre-marked furrows in the garden bed, well watered. Their depth is a maximum of 1.5 cm, the row spacing is 30-50 cm. The seeds are laid out in 2-3 pieces at intervals of 30-40 cm, sprinkled with a mixture of humus and coarse sand, the substrate is slightly compacted, and the bed is watered again.
A thick polyethylene film is stretched over the arches. It is removed after about a month, when the seedlings in the open ground have formed two true leaves.
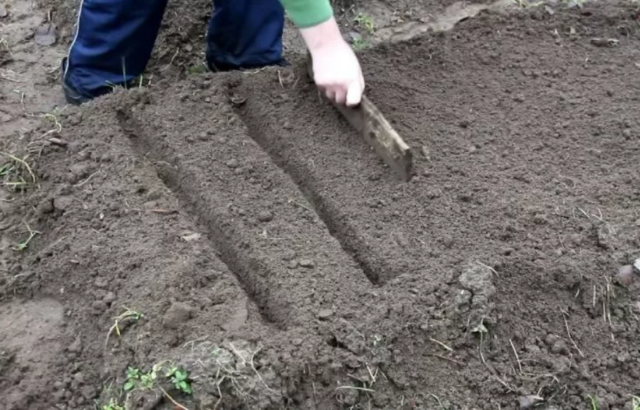

If more than one eggplant grows in a hole, obviously weak specimens are discarded
Planting eggplant seedlings in open ground
Seeds for seedlings are planted from the end of February to the 20th of March.The procedure for its cultivation does not have any specific features; the process follows a standard algorithm for all garden crops.
How to choose seedlings
Seedlings selected taking into account the following criteria are planted in open ground:
- minimum age 70-75 days;
- the presence of 4-5 pairs of true leaves;
- height about 20 cm;
- main stem at least 5 mm thick,
- the presence of “rudiments” of lateral shoots.
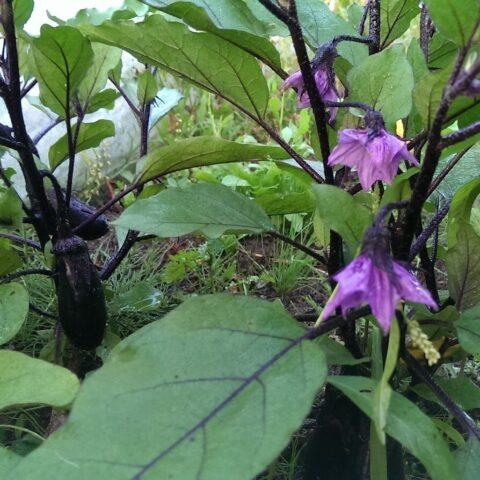

Buds and flowers on seedlings are not an obstacle to planting them in open ground; on the contrary, their presence is even welcome
Transplanting seedlings into the ground
The bed in which it is planned to plant seedlings is prepared in the same way as for sowing seeds. A few hours before the procedure, holes are dug 12-15 cm deep. The approximate scheme for planting eggplants in open ground or in a greenhouse is 30-40x50-60 cm, but here it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of adult plants indicated in the varietal characteristics.
Eggplants are planted in well-watered holes, almost in “mud.” If the seeds were sown in peat cups, they are placed in the bed directly with the container, otherwise, they are removed from it, trying to prevent the earthen lump from falling apart. Then the hole is filled with soil, lightly compacted and the seedlings are watered again. After the water is absorbed, it is advisable to mulch the bed on which the eggplants are planted.
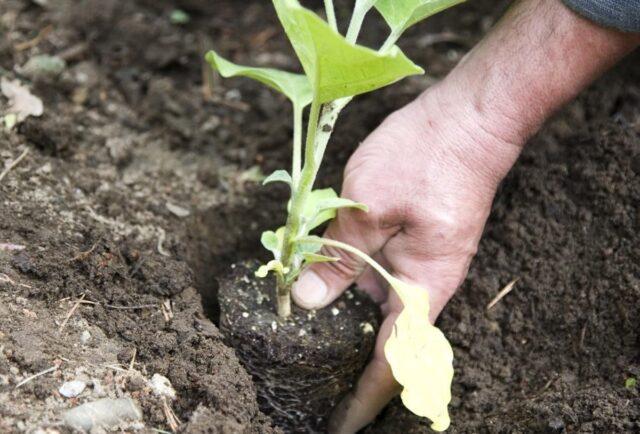

The less the roots are damaged during replanting, the faster and more actively the bushes will begin to grow.
Caring for eggplants in open ground
Of all the Solanaceae, eggplant is the most demanding to care for. Without studying the general rules and important nuances of agricultural technology in advance, it is impossible to reap a good harvest.This video will help beginning gardeners learn about growing eggplants in open ground:
Watering
Agricultural technology for growing eggplants in open ground provides for constant moderate humidity of the substrate. The seedlings are watered for the first time immediately after they are planted. Then the soil is moistened after waiting 5-6 days.
Water is always used only after settling (or softened in some other way) and heated to 28-30 °C. Any watering method is suitable that prevents drops of water from falling on the plant. The soil needs to be wetted 20-25 cm deep - the root system of the bushes, when they are planted in open ground or in a greenhouse, begins to actively grow, eventually becoming quite powerful.
The approximate interval between watering eggplants after the seedlings are planted in open ground is 5-7 days. In extreme heat and in the absence of precipitation, as well as from the moment fruiting begins, it is reduced to 2-3 days. If the substrate dries out, eggplants that are planted in open ground quickly react to this by dropping flowers, buds and fruit ovaries.
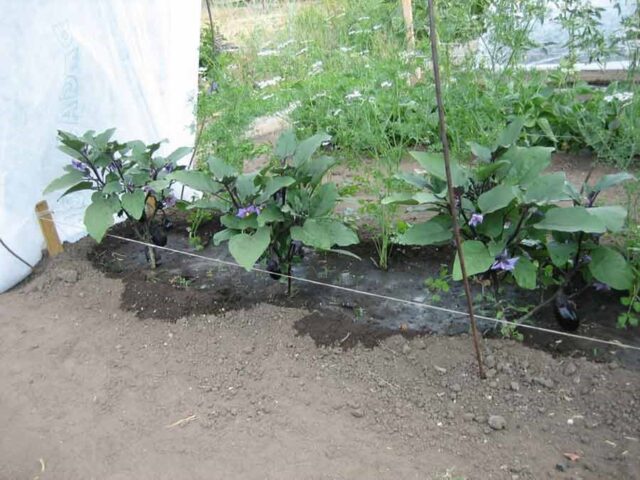

The best option for eggplants is drip irrigation
Feeding
The crop has a fairly high yield, especially in comparison with the size of the bushes. Therefore, it is impossible to grow eggplants in open ground without fertilizers. They need feeding every 2-3 weeks. The first is carried out 10-12 days after the bushes are planted in open ground.
Eggplants respond well to both store-bought fertilizers and folk remedies.But it is still recommended to give preference to the former, choosing special preparations for Solanaceae - they are distinguished by a balanced composition, taking into account the needs of the crop for macro- and microelements. You can also alternate different types of fertilizing.

Eggplants will benefit from the same fertilizers as other Solanaceae.
Weeding and loosening
Ideally, the soil in the beds where eggplants are planted should be loosened after each watering. If that doesn’t work, at least 2-3 times a month. Otherwise, the soil surface “sinters” into a crust, which prevents oxygen from reaching the roots. The approximate depth of loosening is 5-7 cm, otherwise mechanical damage is possible.
At the same time, weeding is carried out. The crop reacts very negatively to the “neighborhood” of weeds; they also become “intermediate hosts” for pathogenic microflora and pests.
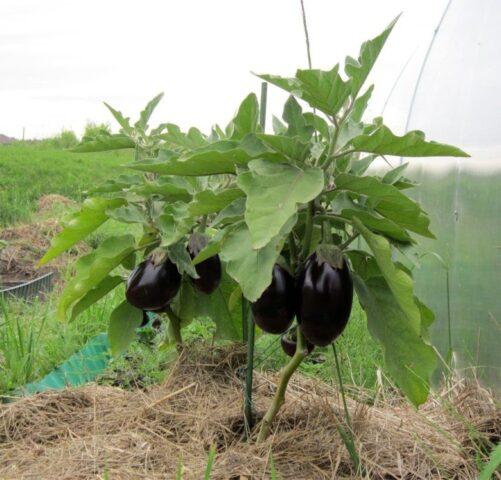

Mulching for eggplants is not mandatory, but a very useful agrotechnical measure.
Formation of bushes
Many gardeners plant low-growing varieties and hybrids that do not need their “help” to form bushes. The technology for growing medium-sized and tall eggplants in open ground involves structuring them. It begins from the moment they grow to 25-30 cm, and takes into account the following principles:
- Be sure to pinch the top once for more intense branching.
- Cut off all the “stepchildren” at the bottom of the stem.
- On plants that form many buds, pick off one of 3-5 buds, choosing the least well located ones. Otherwise, the fruits become very small.
- Mid-season and late varieties of eggplants, as a rule, form tall, intensively branching bushes. It is recommended to “lead” them into 2-3 stems - the stepsons located immediately above the first flower turn into additional shoots. A maximum of 1-2 ovaries are left on them, other flowers are torn off.
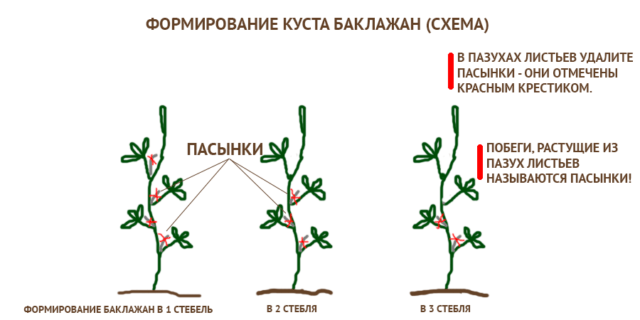
The “stepchildren” on eggplants do not grow very actively; it is enough to pick them twice a month
Garter
Only tall varieties and hybrids of eggplant need gartering. Plants need it both in open ground and in greenhouses. The latter turn out to be more “tall”.
It is most convenient to tie them to trellises made of several horizontal rows of twine, the beginning and end of which are fixed by vertical supports. This method prevents mutual shading, all plants receive enough heat and sunlight.
Eggplant bushes are quite fragile, so each branch must be fixed on the trellis. Otherwise, they will simply break under the weight of the fruit.
Disease and pest control
Eggplants, no matter whether they are planted in open ground or in a greenhouse, are susceptible to diseases and are often attacked by pests. To reduce the risk of infection of plantings, seeds are treated in a fungicide solution. The same preparations are recommended for soil treatment before planting.Deep digging of the bed and clearing it of plant debris will help get rid of insect eggs and larvae.
During the season, eggplants are inspected every 5-7 days for characteristic signs that help identify the problem. It is much easier to cope with diseases and pest attacks at an early stage of development; sometimes you can even manage with folk remedies. In more severe cases, suitable fungicides, insecticides or acaricides are used.

The dosage of drugs, frequency and method of treatment are determined according to the instructions
Secrets of growing eggplants in open ground
It’s not enough to know how to properly grow eggplants in open ground. To increase harvest volumes and improve fruit quality, knowledge of some secrets and important nuances of agricultural technology is required:
- It is recommended to plant herbs and other plants with a strong, specific odor along the perimeter of the beds and between the rows. They repel many dangerous pests from eggplants.
- If you equip warm beds, eggplants can be planted in open ground 15-20 days earlier than usual. The “service life” of such beds is three seasons.
- It is not advisable to use pine needles, sawdust from coniferous trees, or peat as mulch. This provokes acidification of the soil; from such soil, eggplants are not able to “pull” nutrients in the required volume.
- When planting together, eggplants are planted on the south side of taller plants so that they receive enough sunlight and warmth.
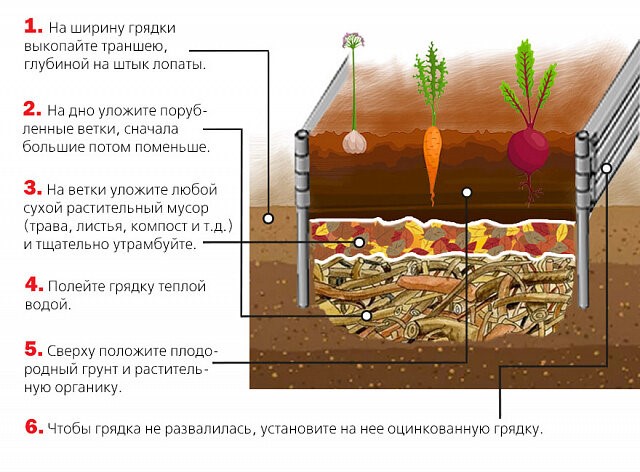
In spring, the soil in a warm garden bed warms up faster due to the conversion of organic matter into compost.
Conclusion
Before planting eggplants in open ground (no matter with seeds or seedlings), it is necessary to study in advance all the important nuances of agricultural technology. This is a rather demanding garden crop; its yield directly depends on many factors. The most important of them are the choice of location for the garden bed, pre-planting preparation of soil and seeds, general rules and individual nuances of agricultural technology, prevention of diseases and pest attacks.








