Content
- 1 Methods for seed disinfection
- 2 Eggplant seeds do not germinate
- 3 Non-contagious diseases of eggplant
- 4 Infectious diseases of eggplant seedlings
- 5 Invasive diseases of eggplant
Eggplants are more delicate plants than their relatives peppers or tomatoes, and growing eggplant seedlings is much more difficult than any other garden crop. Eggplant seedlings can get burned even from a lamp that is used to illuminate them in order to extend daylight hours for the plants.
The gardener’s “torment” begins almost from the moment he buys soil in a store or makes his own soil mixture. To begin with, before sowing eggplant seeds, it is necessary to disinfect the soil. Even when buying a ready-made mixture in a store, there is no guarantee that you will buy soil that is free from pathogenic organisms.If you prepare the mixture yourself, it will likely contain either a pest or an infection.
To disinfect the soil from pathogenic microorganisms, the soil can be generously shed with a solution of potassium permanganate. An even better option would be to calcine the soil mixture in the oven. This will destroy not only bacteria, but also multicellular organisms that can subsequently damage eggplant seedlings. During disinfection, beneficial bacteria will also die, but nothing can be done about it.
After preparing the soil, it’s the turn of the eggplant seeds. They also need to be disinfected, unless the packaging indicates that the seeds have already undergone this procedure. Coated seeds also do not require disinfection.
Methods for seed disinfection
At home, you can use one of two methods: disinfection with hot water and disinfection with a two percent solution of potassium permanganate.
Potassium permanganate solution
Eggplant seeds are disinfected for 20 minutes in a 2% solution of potassium permanganate. A solution with such a concentration of potassium permanganate is black, since to prepare it you will have to take 2 g of potassium permanganate crystals per 100 ml of water.
In addition, a weaker solution will not give the desired effect. Eggplant seeds will also turn black after bathing in the solution. After disinfection, the seeds are washed, dried and sowed.
Hot water
When disinfecting with a solution of potassium permanganate, only those pathogenic organisms that are on the seed coat die. If the seed is damaged inside, potassium permanganate will not work.Therefore, a more reliable method of disinfection is heat treatment of eggplant seeds.
In domestic conditions, such heat treatment can only be carried out using hot water. With severe temperature treatment, the germination of seeds is reduced and it is indicated only for seeds in which the loss of germination occurs more slowly than the destruction of the infection. These seeds include eggplants.
It should be taken into account that when disinfecting with hot water, weak, infected eggplant seeds will most likely die. But why are they needed, one wonders. Healthy and viable seeds will survive the procedure.
Eggplant seeds are placed in a bag and placed in a thermos with water, the temperature of which is 50-52°C. For eggplant seeds, the holding time in a thermos is 25 minutes. Immediately after the time is up, the seeds are removed and placed in cold water.
Failure to comply with the conditions in one direction or another will lead to the death of eggplant seeds either from temperature or from surviving infection. But if the conditions are met, this method gives a 100% guarantee that you only have healthy and infection-free eggplant seeds.
After the preparation has been completed, you can begin sowing the seeds and waiting for the eggplant sprouts.
Eggplant seeds do not germinate
Eggplant seeds usually germinate 5-10 days after sowing. There is no point in waiting for them earlier.
If all the deadlines have passed, but the eggplant sprouts have not appeared, there may be several reasons for this:
- soil temperature is too low. Typically, eggplant seeds are germinated at t = 25°C. The minimum temperature is 21°. At lower temperatures, the seeds will not germinate;
- "swampy" soil.If the soil is too wet, eggplant seeds do not receive oxygen and “suffocate”;
- sowing too deep. This can even happen by accident if the soil is watered after sowing the seed, and not before;
- eggplant seeds processed by the manufacturer are sown. Encrusted and pelleted seeds germinate later than usual.
The eggplant seeds have sprouted, and the gardener has other worries ahead of him. The seedlings may get sick. Diseases of eggplant seedlings can be divided into infectious, which can infect neighboring plants, and non-infectious, caused by external, relatively easily removable factors.
Non-contagious diseases of eggplant
Usually caused by too much or too little moisture, light or minerals.
Eggplant seedlings stopped growing
There may be two reasons:
- plants stopped growing after picking. Eggplants do not tolerate transplantation very well, so they can stop growing after transplanting them into personal pots. It is best to immediately sow eggplant seeds in separate containers. If you had to pick, you need to water the transplanted eggplant seedlings with a root system growth stimulator;
- lack of space. Growth cessation can also occur in eggplant seedlings in separate pots. Most likely, there is not enough space for the sprout. You can verify this by removing one plant from the container and carefully examining the roots. If the roots are brown, then the reason is in the cramped pot. It is necessary to transplant the eggplant seedlings into larger containers (+2-3 cm) by transshipment, adding soil.
Both problems, although unpleasant, are not dangerous to the plant.
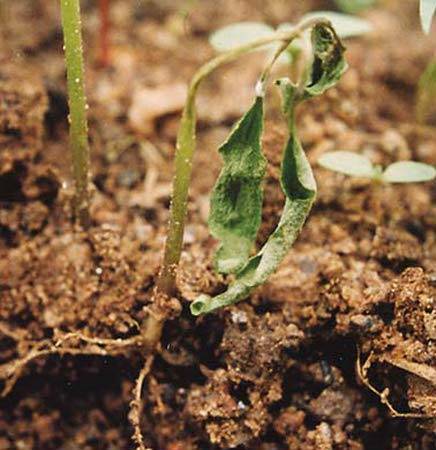
Eggplant seedlings wither
There is no need to worry, if eggplant seedlings drop their leaves while standing in the sun during the day (no, not to the state in the photo), and are completely restored overnight, then this is a normal reaction of plants to the heat. Problems begin when eggplant seedlings do not recover overnight with water and normal weather. There may be several reasons why eggplant seedlings wither.
Waterlogging and soil acidification
Occurs when watering too much, the soil acquires a musty smell. Eggplant seedlings need to be transferred to larger containers, adding soil, and watered more often, but little by little.
"Cold Feet"
There is too much difference in temperature between the above-ground part of eggplant seedlings and its root system. This happens when the seedlings are on the windowsill, and cold air from the street blows from the window slits, cooling the pots. The ground part, under the hot rays of the sun entering through the glass, actively evaporates moisture. The cooled root system cannot keep up with them. As a result, an imbalance occurs and the eggplants wilt.
The issue can be resolved either by raising the pots above the window sill by 20 centimeters and thus equalizing the temperatures, or by properly sealing the window cracks.
The roots of the seedlings were suffocated
Eggplant seedlings may wilt if they are planted in soil that is too dense, the drainage holes are clogged or missing, there is too much water, or if the eggplants are planted too close together. The latter concerns the general container for seedlings.
To eliminate it, it is enough to loosen the top layer of soil, punch, clean or widen the drainage holes and reduce the volume of water for irrigation.
Hypothermia of eggplant seedlings
From the cold, the seedlings wither to the state of a “rag”. This can happen when eggplant seedlings are taken out into the fresh air before planting in a permanent place. The consequences are eliminated by watering the plants with warm water at a temperature of 30°.
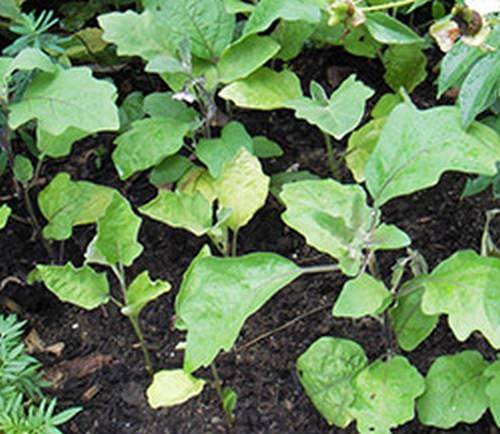
The lower leaves of the eggplants began to turn yellow
In animals this situation would be called vitamin deficiency. Eggplant seedlings do not have enough nutrients in the soil and for further development they begin to suck them out of the lower leaves. Typically, a similar situation occurs when growing eggplant seedlings in peat. Eliminating the situation is quite simple: the eggplants need to be fed with complex fertilizer.
The lower leaves also turn yellow due to a lack of nitrogen. This is also eliminated with fertilizers. Seedling leaves may turn yellow due to some infectious diseases or pest attacks. Pests are relatively easy to notice, but before you start treating eggplant seedlings for an infectious disease, it is better to first add fertilizer and see if the situation improves.
Light spots on the leaves of eggplant seedlings
When such spots appear, you must first make sure that there are no pests. If none is detected, then these are burns from the sun or the lamp under which the eggplant seedlings are placed.
Eliminating the cause is quite simple: move the lamp further away, and shade the eggplant seedlings from the sun with newspaper or tulle.
The edges of eggplant leaves turn yellow and dry out
This situation occurs when there is a lack of potassium in the soil.The issue can be resolved by adding potassium fertilizer to the soil. True, if the seedlings have recently been fed, then a similar phenomenon is possible due to an excess of fertilizer.
Infectious diseases of eggplant seedlings
Root collar rot
In first place among seedling diseases is the so-called “black leg,” another name for which is “root collar rot.”
This is a bacterial disease, the main cause of which is the increased humidity of the earthen coma. With a black leg, a constriction appears on the stem, separating the roots from the upper part. By this time, the roots and underground part of the plant have already rotted.
If seedlings become infected with root collar rot, the diseased plants are destroyed. If the seedlings grew in a common container, the entire crop will have to be destroyed.
The most reliable method of preventing blackleg is calcination of the soil before sowing seeds.
Black bacterial spot of eggplant
Affects eggplants at any stage of the growing season. The pathogen persists in plant debris and seeds. For this reason, for subsequent sowings, seeds should be taken only from healthy plants and do not forget to treat the seed before planting.
On seedlings, the disease will appear as the appearance of many small black dots with a yellow border on the leaves. As with any other similar infection, control measures consist of disease prevention. It is no longer possible to cure the plant. It is necessary to destroy diseased sprouts and change the soil if the seedlings are growing in a common container.
Mosaic of eggplant seedlings
Leaf mosaic can be caused by three different viruses: tobacco mosaic virus, cucumber mosaic virus, and mottled mosaic virus.
In all three cases, yellow spots appear on the leaves, which gives the viruses the name “mosaic.” The leaves look variegated, as if made from pieces of a mosaic. The virus is transmitted through the soil, where it is preserved due to the presence of plant debris and insect pests: aphids, mites, sciarid larvae.
There is no treatment. Prevention measures include the destruction of plant debris and pest control.
Invasive diseases of eggplant
Simply put, pests. Seedlings growing indoors are unlikely to be threatened by pests such as the Colorado potato beetle or locusts, but there are those who are able to penetrate even a city apartment. And sometimes they are brought in with undisinfected soil.
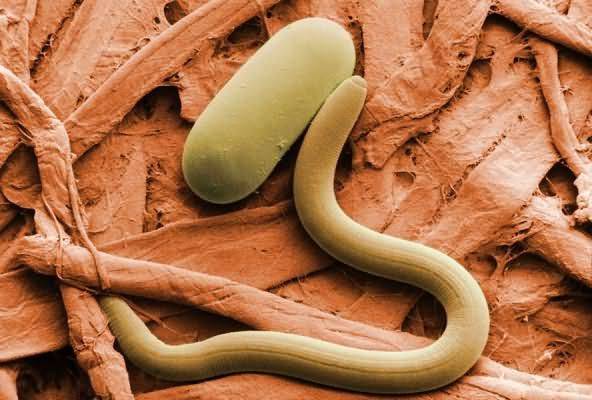
Nematodes
Nematodes are very small roundworms that are practically invisible to the naked eye. They are only 1 mm long. There may be three types of nematodes on seedlings. All of them penetrate the plant through contaminated soil, which explains the requirement to calcine the soil before planting seeds in it. Nematodes do not tolerate elevated temperatures very well. At a temperature of 40 degrees they die. But the range of 18-24°C is comfortable for their life.
Nematode eggs can be stored in seeds. During thermal disinfection they die.
Leaf nematode, in addition to the harm it causes itself, it also carries viruses, including those that infect plants of the nightshade family. Signs of its presence: leaves with randomly scattered dry spots.
Stem nematode It affects not only the stems, but also the buds, leaves, and flowers. The toxins it releases clog the channels, causing tissue thickening. The plant stops growing and eventually dies. Stem nematode enters the plant through the roots.
Root-knot nematode parasitizes plant roots. Swellings form in the affected areas, initially yellow and then brown. Due to thickening, the roots cannot function normally and the plant stops receiving nutrients.
Of all the above, the root-knot nematode is the most dangerous, since it can spread not only through the soil, but also through pots, equipment, and even through drops of water flowing from a diseased plant.
Unfortunately, the only truly effective means of combating nematodes is the complete destruction of diseased plants. Contact poisons do not have much effect. And if a nematode gets into the soil in the garden, it will be impossible to remove it from there.
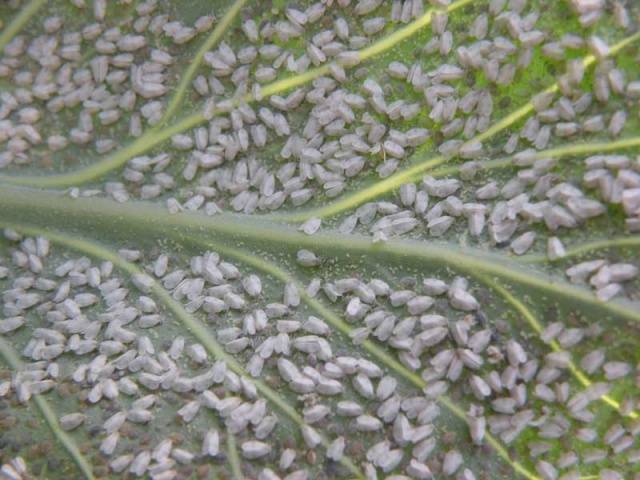
Whitefly
This is an insect that in adulthood looks like a very small white butterfly up to 1.5 mm in size. The whitefly is able to reproduce very quickly, while being active all year round. Eggs are laid on the underside of leaves, protected from the sun. It feeds on plant juices; because of this insect, the leaves begin to discolor and lose their shape. Eventually the leaves fall off along with the buds.
Signs of the appearance of whiteflies on seedlings are a black coating on the lower leaves, which occurs due to the fact that a sooty fungus settles on the sugary excrement of the whitefly. In addition, if you touch a seedling leaf with your hand, a flock of these insects will rise from under it. The whitefly is very mobile. If there are plants in the next room, she can move there too.
Folk remedies against whiteflies are effective with a small number of plants in the house. In the case of growing seedlings, it is easier to use insecticides, which will also have to be used more than once.
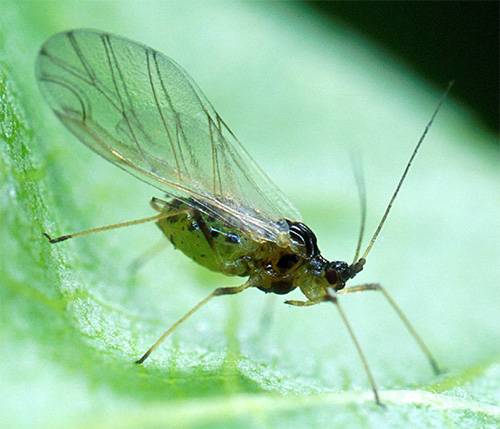
Aphid
Aphid queens have wings, so they can easily fly even into an apartment and lay eggs on seedlings. Aphids feed on plant sap. Just as in the case of whiteflies, a sooty fungus settles on aphid feces. The tops of plants and leaves curl and later turn yellow, signaling the appearance of aphids. Aphids are capable of transmitting viral diseases.
The most effective means of controlling aphids is an insecticide.
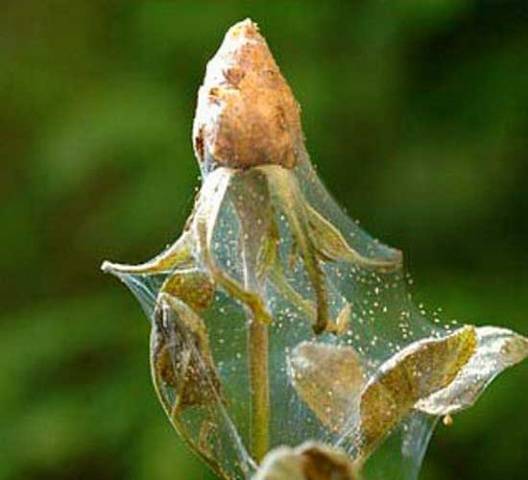
Spider mite
It also feeds on plant juices. If a cobweb appears on the seedlings, it means that the seedlings are affected by mites. Dry air is a favorable condition for tick development. It is enough to monitor the air humidity, if necessary, spraying water from a spray bottle over the seedlings so that the mite never appears.
If the mite does appear, you will have to use insecticides, carefully treating all the plants. Treatment will need to be carried out several times at intervals of one week until it becomes absolutely clear that the mite has been destroyed.
Sciarides
Another name is “fungus gnats”. Black-gray midges that breed in organic-rich environments. The flies themselves are not dangerous, but their larvae are dangerous, as they can damage the roots of the seedlings. Any insecticide is suitable against sciarids, including Dichlorvos.
Features of growing eggplants, seedlings, diseases and pests
If you managed to safely grow eggplant seedlings until they were planted in the ground, then new unforgettable adventures await you. Regardless of whether you plant eggplants in a greenhouse or in beds under the open sky.