Content
- 1 History of selection
- 2 Description of the tomato variety Pepper-shaped robust
- 3 Characteristics of the pepper-shaped robust tomato
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages
- 5 Landing dates and rules
- 6 How to properly care
- 7 Disease and pest control
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 Reviews from gardeners about the pepper-shaped robust tomato
The robust pepper tomato stands out among others due to the unusual shape of its fruit, which is why it got its name. Tomatoes are easy to grow in open garden beds. They adapt to different weather conditions and are resistant to major diseases.

The new variety has already become popular among gardeners not only because of its appearance, but also for the taste of its fruits.
History of selection
As a result of breeding work, the Pepper-shaped robust tomato variety was born. Its authors were breeding scientists O. V. Postnikova and V. N. Dederko. The new variety was patented on March 12, 2005.
Description of the tomato variety Pepper-shaped robust
General description of the pepper-shaped tomato:
- The bush is low-growing, standard, no more than 40 cm high. The stem is straight, short and stable.
- The crown is compact and squat.The foliage is good. The leaves are gray-green with slightly dissected edges. The leaf blades are not very pubescent.
- Simple flower brushes. They contain yellow, star-shaped flowers. Full-fledged fruits are formed from the flower ovary.

Tomato leaves of the Pepper-shaped robust variety emit a pronounced tomato aroma
Characteristics of the pepper-shaped robust tomato
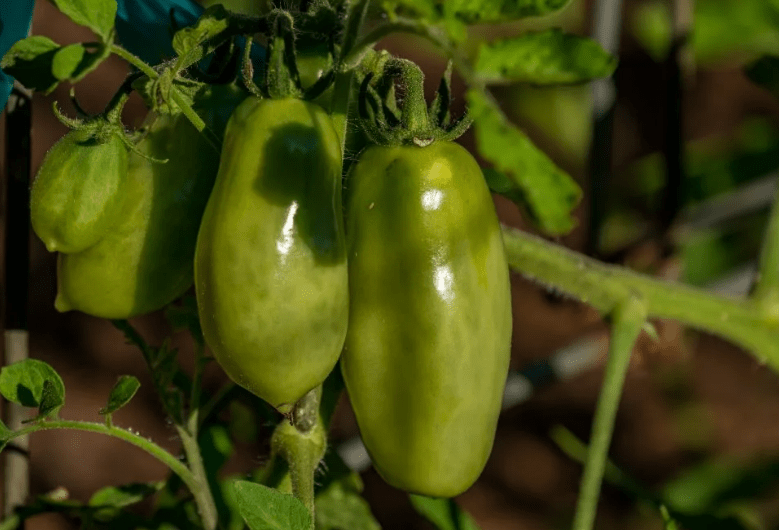
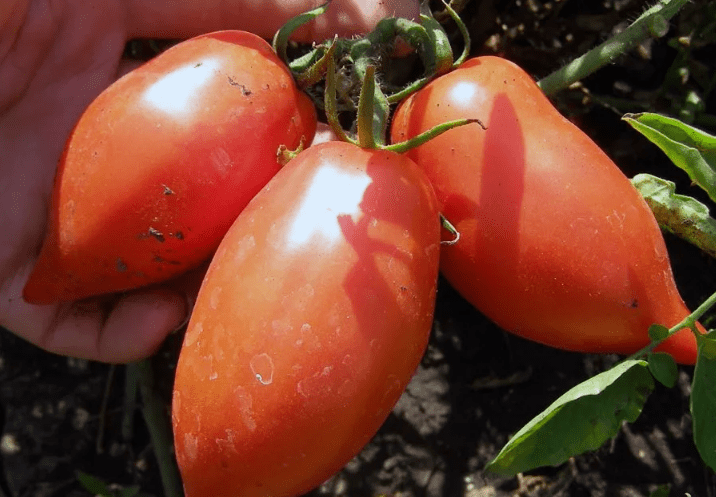
Pepper-shaped tomatoes are collected in tight, heavy clusters. They change color as they mature. At first the fruits are green, then light pink and at the moment of biological ripeness they become crimson. The average weight of one tomato is 140 g. Due to their small size, it is convenient to roll them whole into jars.
Ripening time
Tomato ripening period Pepper-shaped robustness is typical for mid-early varieties. From the beginning of the growing season to harvest, approximately 105-110 days pass. The first ripe fruits are picked from the bush in mid-July.
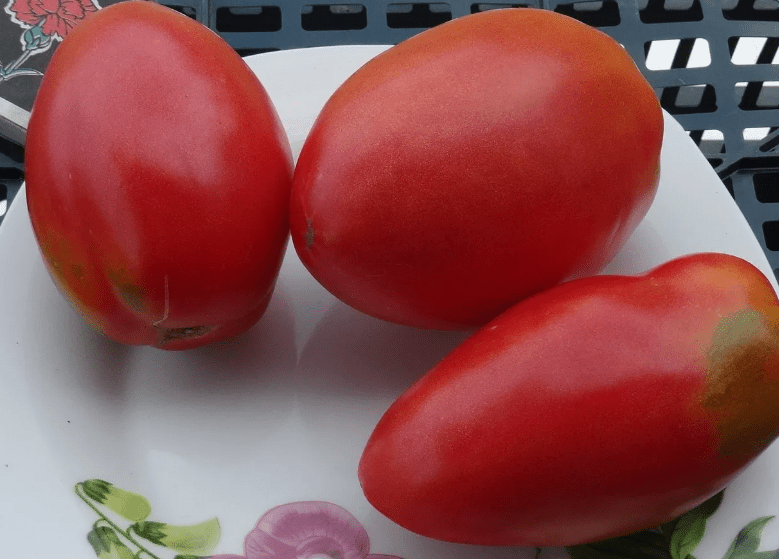

Tomato fruiting is stable
Tomato yield
The Pepper-shaped robust variety brings from 1 sq. m about 6-8 kg of commercial fruits. Yields are average, but they may vary depending on the quality of care. Compliance with the basic rules of agricultural technology will increase the productivity of the variety.
Resistance to adverse factors
Pepper tomatoes are resistant to external adverse factors. They tolerate short-term drought well and do not like it when moisture accumulates in the root area.The variety is tolerant of frost and low temperatures, so it grows well in open ground.
Pepper-shaped robust tomatoes are weakly resistant to late blight and are often damaged by harmful insects. To enhance the protective properties of the crop, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures in a timely manner.
Where is it grown?
The variety is grown almost everywhere. Pepper tomatoes are common in gardening in the middle zone, including the Moscow region. Bushes are grown in the Far East and the Urals, as well as in Eastern and Western Siberia.
Methods of application
Tomatoes of this variety are created for universal use. They are used to prepare fresh salads, vegetable slices, soups and stews. They are suitable for any type of processing: preservation, drying, freezing. They are used to prepare very tasty and simple snacks that are an integral part of a family lunch or dinner.
Advantages and disadvantages
Fruits can be stored for a long time and transported over long distances. They do not deform because they have a dense texture and are covered with elastic skin.
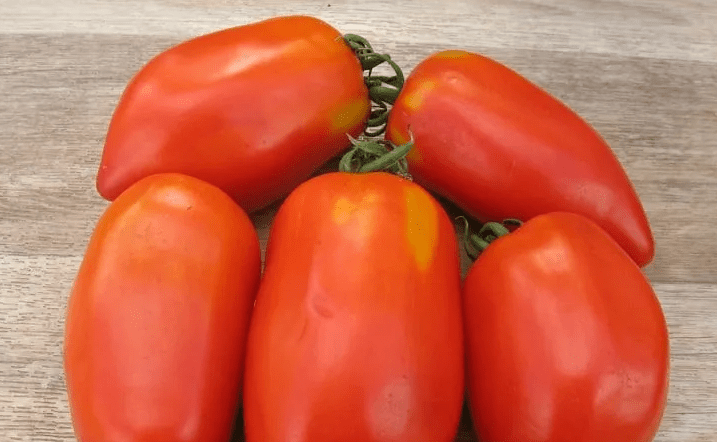

Even in autumn, fresh tomatoes delight with their taste and aroma
Pros:
- possibility of growing in cold regions;
- versatility of application;
- high shelf life in cool conditions;
- stable and long-term fruiting;
- commercial appearance.
Minuses:
- weak resistance to diseases;
- the need for pinching and gartering.
- average yield.
Landing dates and rules
The seedlings are transferred to the greenhouse in early May, and transplanted into open ground in the middle of the month. Usually by this time the height of the seedlings reaches 30 cm. They also have 1-2 inflorescences and several true leaves.
When planting tomatoes, maintain a distance of 30 cm from each other between bushes, and 40 cm between rows. To make harvesting more convenient, seedlings are planted in 2-3 rows. After planting, tomatoes are provided with standard care.
How to properly care
Caring for low-growing tomatoes is not too difficult and can be done by a novice gardener. They can easily withstand bad weather and bring quite a good harvest.
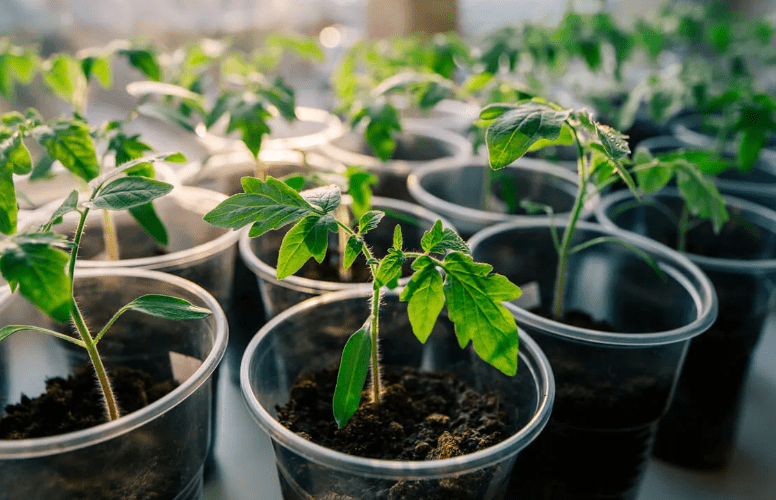

Standard bushes have a compact appearance and look beautiful in the garden
Low-growing tomatoes, unlike tall ones, grow horizontally, and they also require pinching. To do this, remove the side shoots on the bushes and the lower leaves under the first fruit cluster. As a result, by the time the fruits ripen, the bushes remain practically bare. But that's how it should be. This allows the tomatoes to concentrate their energy on ripening the fruit.
Low-growing tomatoes need abundant but infrequent watering - 1-2 times a week. Use warm water for irrigation, otherwise the skin of the fruit will begin to crack.
The first feeding is carried out after 20 days, as soon as the seedlings take root in the new place. Next time the bushes are fed when the ovary appears. When the fruits begin to fill, mineral fertilizers are applied, but in moderation.

As a top dressing for tomatoes, you can use an infusion of nettle or chicken manure.
Disease and pest control
Tomatoes of this variety are not endowed with strong immunity and will get sick without preventive treatments. Fungicidal preparations, for example, Fitosporin-M, Ordan, Profit, are suitable for this. During the period of pest invasion, which usually happens in early spring, insecticides Match, Iskra, Fitoverm are used.
It is not recommended to grow tomatoes where other crops from the Solanaceae family, such as eggplants, peppers and potatoes, grew before them.
Conclusion
The robust pepper tomato produces sweet, cone-shaped tomatoes. The bushes can be affected by blossom end rot, but they do not cause much trouble when growing. The variety can be cultivated in all regions of Russia.
Reviews from gardeners about the pepper-shaped robust tomato








