Content
Chugunka potatoes are a variety that has been “tested” by more than one generation of gardeners. Its advantages and disadvantages are well known. The former clearly “outweigh”, because it successfully withstands “competition” from new selections that appear on sale every year. Chugunka potatoes are valued for their excellent taste, original appearance, and are relatively easy to grow.
History of selection
Chugunka potatoes are an achievement of “folk selection”; its author and “ancestors” cannot be established for certain. However, modern experts claim with a fair degree of confidence that it was bred with the participation of other popular “folk” varieties - Sineglazka and Vasilek. Chugunka potatoes have been known for more than a hundred years; they are not listed in the Russian State Register of Breeding Achievements.
Description of potatoes of the Chugunka variety
Chugunka potatoes owe their name to the original appearance of the tubers. His bushes are not so “recognizable”; they look completely ordinary, especially to a non-specialist.
Bush
The height of Chugunka potato bushes varies from 0.5 to 1 m - mainly their “dimensions” depend on the quality and fertility of the substrate. The root system is very powerful, the stems are erect and strong. Also, Chugunka potatoes are characterized by dense “foliage” and a lush “crown”: leaf plates have a typical shape for the crop, medium size, a dense green hue, with strongly pronounced veins and a corrugated “border” along the edge. The flowers are large, bright lilac, but the corollas are compact. Very few “berries” are formed after flowering.
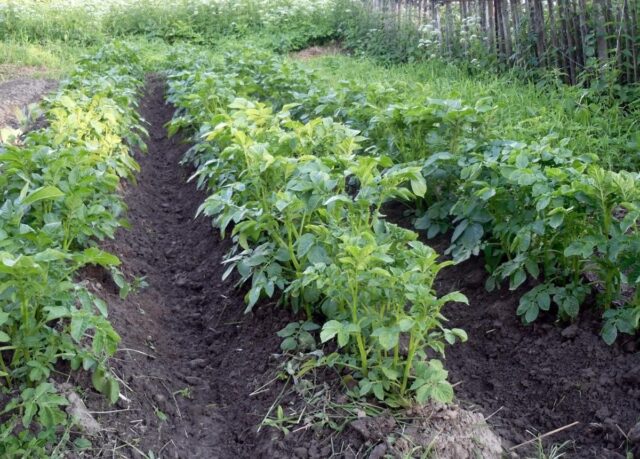

Bushes extremely rarely “fall apart”; the stems do not lie on the ground
Tubers
The tubers of the Chugunka potato are quite large and one-dimensional, weighing 100-130 g. There is practically no “trifle” in the “nests”. The shape varies from round-oval to distinctly elongated. The peel is dense, but not thick, it provides the tubers with good transportability and keeping quality. Painted in a very dark blue-violet color with a glossy sheen.
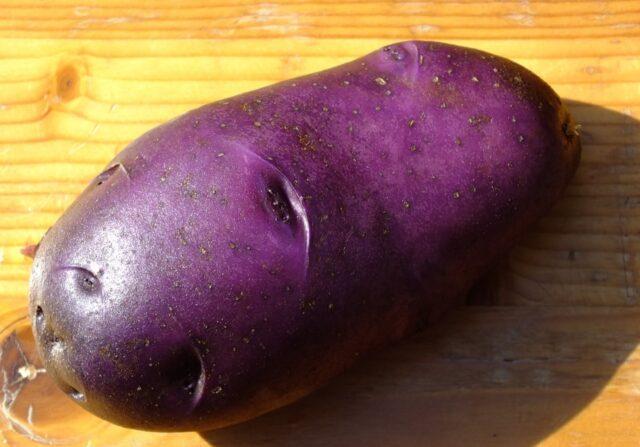

From a distance, the peel appears almost black and is very similar in color to eggplant skin
The “eyes” are few, superficial, and stand out with a brighter blue hue. The pulp is snow-white or light cream, and does not darken when cooked. It contrasts very effectively with the cut skin.
Characteristics of Chugunka potatoes with photos
Despite the official “non-recognition” and the lack of variety testing, the important characteristics of the Chugunka potato, its advantages and disadvantages, can be judged quite objectively.This is facilitated by the rich experience of amateur gardeners.
Taste qualities
Amateur gardeners evaluate the taste qualities of Chugunka potatoes extremely positively. The puree made from it receives especially rave reviews, as it turns out very tender and airy. It is the brightness and richness of taste that determines the stable demand for the variety, even despite the average yield.

The pulp of Chugunka potatoes after heat treatment retains its color and does not “fall apart” when slicing
In culinary terms, Chugunka potatoes are universal. It can not only be boiled, but also fried, stewed, baked, stuffed, and added to any soups, salads, and side dishes.
Ripening time
Chugunka is an early ripening potato variety. In central Russia, harvesting begins 70-75 days after the appearance of mass shoots. Moreover, the experience of gardeners shows that the weather during spring and summer has practically no effect on the ripening time of tubers.
Productivity
Chugunka potatoes have not undergone official variety testing, so their yield can only be estimated approximately. The experience of amateur gardeners shows that 6-11 tubers are formed in one “nest”. Accordingly, you can count on 0.8-1.2 kg per bush.
The yield of Chugunka potatoes is average or even below average. If it were grown on an “industrial scale”, it is approximately estimated at 100-200 centners per hectare.

Even ideal cultivation conditions and competent agricultural technology will not help to radically increase the yield of Chugunka potatoes.
Growing regions
Chugunka potatoes are cultivated mainly in the European part of Russia, in regions with a temperate climate. Apparently, its “homeland” is here; it is best adapted to local weather nuances.
Experiments by gardeners indicate that the variety takes root well and consistently produces yields in warmer southern regions, subject to regular and sufficient watering. But the northern territories are not very suitable for it. And so the low yield is further reduced, the taste of the tubers also suffers, and the concentration of nutrients in them decreases.
Disease resistance
Chugunka potatoes are valued by gardeners for their “stress resistance” and endurance, including high resistance to fungal and other diseases typical of the crop. Pests, including the Colorado potato beetle and wireworm, are also not particularly interested in this variety. Although it does not have the protection against pathogens and insects provided by breeders.
The most dangerous disease for Chugunka potatoes is late blight. In this variety, both the above-ground part of the plant and the tubers are susceptible to it.
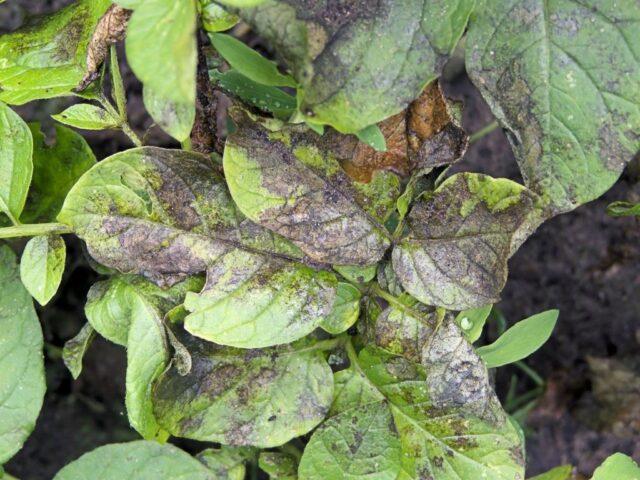

Late blight can develop both when growing potatoes in the garden and during storage
Advantages and disadvantages
The starch content in the pulp of Chugunka potatoes is quite high - 13-17%. Despite this, it cooks well, while maintaining its shape, and does not have the slightest “mealy” taste.

Official “non-recognition” does not prevent breeders from actively using Chugunka potatoes to create new varieties and hybrids
Pros:
- the ability to successfully resist “external” negative influences;
- good drought resistance;
- early dates and “massiveness” of crop ripening;
- ease of care;
- large size, presentable and original appearance of the tubers;
- outstanding taste;
- nutritional value of the pulp and high concentration of nutrients in it;
- versatility of tubers;
- extremely rare cases of infection by fungal and other diseases;
- lack of particularly expressed interest on the part of pests;
- excellent keeping quality and transportability.
Minuses:
- relatively low yield;
- “large size” of bushes;
- demands on soil fertility and regular fertilizing;
- tendency to be affected by late blight;
- unsuitability for mechanized harvesting;
- the need to update planting material every 2-3 seasons.
Landing Features
Chugunka potatoes in central Russia are planted in the last days of April or in the first ten days of May. You need to wait until the substrate at a depth of 10-12 cm warms up to at least 6-8 °C.
Since Chugunka is a potato variety that is extremely sensitive to the nutritional value of the soil, in the fall, during the digging process, humus or rotted compost (about 5 l/m²) must be added to the soil. It is also necessary to saturate the soil with potassium and phosphorus. Both complex store-bought fertilizers and folk remedies (wood ash) are suitable for this, but the former are preferable due to their balanced composition.
Pre-planting preparation of Chugunka potatoes includes germination of tubers. Treatment with any suitable fungicide to protect against late blight and a biostimulant to increase yield is also required.
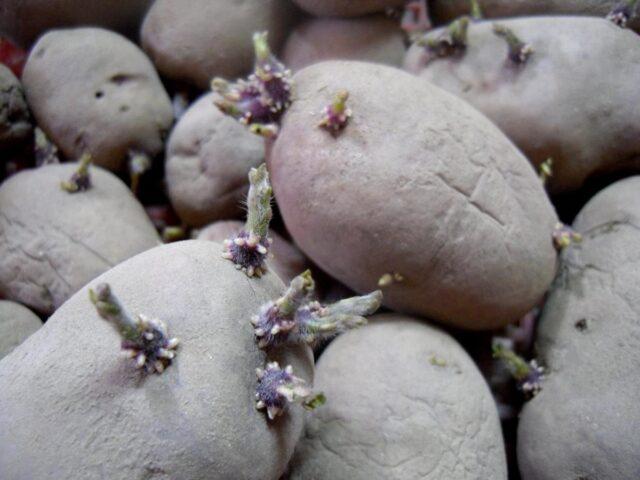

Germination proceeds quite quickly, usually 2-3 weeks are enough.
Chugunka potatoes are planted according to the “classic” scheme 30-35x65-70 cm.The depth of the holes ranges from 5-6 to 12-15 cm, it depends on the “lightness” of the substrate. To provide the tubers with nutrients, a handful of humus mixed with complex fertilizer is placed at the bottom.
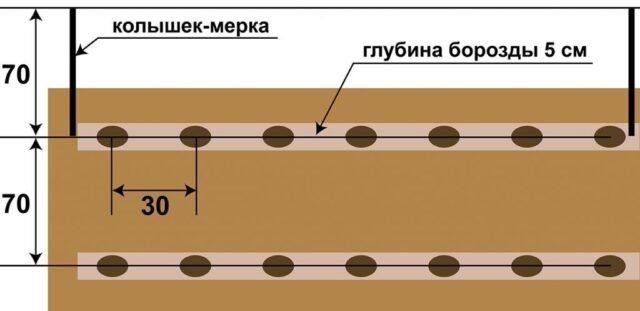
Chugunka potato bushes are not spreading, so you don’t need to leave a lot of space between them
Care instructions
Due to the ease of care, Chugunka potatoes are suitable even for inexperienced gardeners. Agricultural technology includes:
- Watering. The substrate is moistened only in the absence of natural precipitation. In central Russia - once every 2-2.5 weeks, in the south - every 10-12 days. Bushes especially need water at the stage of active growth of green mass, during the formation of buds and 7-10 days after flowering.
- Feeding. Fertilizers are applied three times per season - 12-15 days after the first shoots (nitrogen), at the beginning and “at the peak” of flowering (complex).
- Hilling. It is enough to hill up Chugunka potatoes twice a season - when the stems reach a height of 12-15 cm and after another 20-25 days. Further, there is no need for it - the bushes “fall apart” infrequently, the tubers “appear” from the ground rarely.
- Mulching. An optional, but very useful agrotechnical measure for Chugunka potatoes. Mulch on the garden bed helps to significantly save time on weeding and loosening it, and water the plants less often.

Chugunka potatoes respond positively to natural organic matter, folk remedies, and store-bought fertilizers
Harvest and storage
The approximate harvest date for Chugunka potatoes is the end of the second ten days of August.By this time, the stems should be at least half dry, the leaves should turn yellow almost completely. Tubers are dug up only by hand - with a pitchfork or shovel.

Tubers even with minor mechanical damage are unsuitable for storage
The harvested Chugunka potato crop is immediately sorted. Tubers suitable for long-term storage are dried for 7-10 days. In autumn and winter they are kept in any place where suitable conditions can be created:
- constant temperature 2-4 °C;
- air humidity 70-80%;
- lack of light;
- access to fresh air;
- protection from cold drafts.
Conclusion
Chugunka potatoes are a variety of “folk selection”. It is not in demand by professional farmers due to its relatively low yield, but amateur gardeners value it very much for the unusual appearance and rich taste of the tubers. The variety is suitable even for inexperienced summer residents: it does not suffer from the vagaries of the weather, rarely gets sick, and requires only standard care.
Reviews from gardeners about Chugunka potatoes








