Content
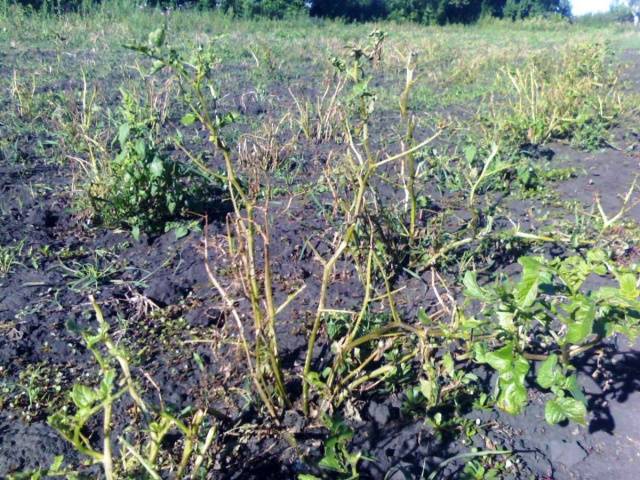
Withering of potato tops is a natural process that occurs during harvest. If the foliage turns yellow before this time, this indicates a disruption in the plant growing process.
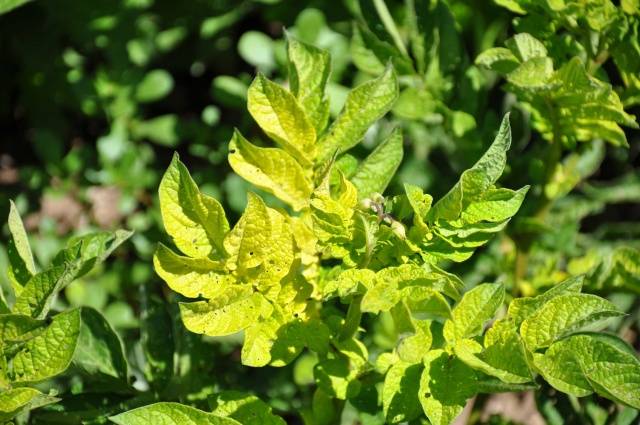
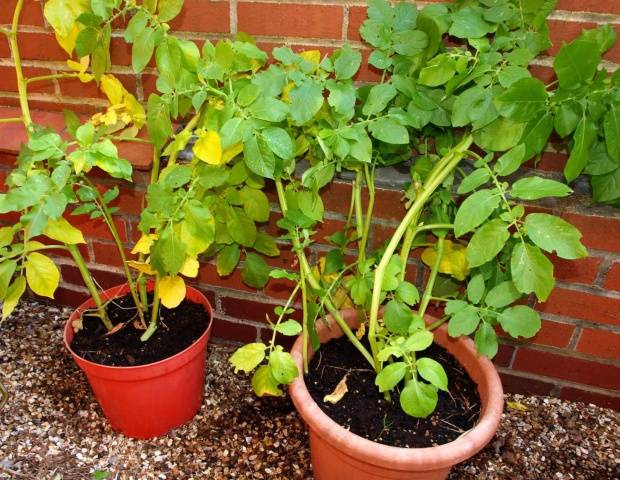
Reasons why it turns yellow potato tops, are very diverse. This includes increased air temperature, lack of nitrogen, phosphorus and other fertilizers. Yellow leaves often indicate the spread of disease or pests.
Reasons for yellowing of potato tops
Temperature and humidity
The main reason for potato tops to wither before harvest is a violation of the temperature regime. During drought, potato leaves begin to turn yellow from below, and gradually this negative phenomenon spreads to the entire bush.
Constant rain or heavy application of moisture will not correct the situation. Then a crust forms on the surface of the soil, which prevents the flow of air to the root system.
If the temperature reaches 30 degrees, then the plant’s metabolism is disrupted. As a result, potato yields decrease.
During the growing season, soil moisture levels should remain at 70%. In arid regions, plantings require irrigation. The need for additional moisture increases as potatoes bloom.
During the period of tuber formation, it is necessary to ensure the supply of oxygen to the soil. To do this, the soil is periodically loosened.
Fertilizer shortage
Potato tops turn yellow due to insufficient supply of nutrients. Most often, plants lack the following substances;
- Nitrogen. If there is not enough nitrogen in the soil, the potato leaves turn pale green, then turn yellow and fall off. When nitrogen is supplied, the plant increases its green mass and forms new tubers. For 10 kg of root vegetables, up to 50 g of nitrogen-containing substances are required. For feeding, mineral compounds are used, which are added to the soil before planting the tubers.
- Phosphorus. Phosphorus fertilizer helps the development of the root system, accelerates the formation of tubers and increases the starch content in them. With a lack of phosphorus, plants tolerate hot weather less well. As a result, the potatoes do not grow to the required height, and their leaves turn yellow. Up to 0.9 kg of superphosphate is required per hundred square meters. It is better to apply fertilizer in the fall so that easily digestible forms of phosphorus are formed in the spring.
- Potassium. Potassium increases plant immunity, improves the taste and shelf life of tubers. With a lack of potassium, the process of photosynthesis is disrupted, and plants tolerate drought worse. To fertilize potatoes, potassium sulfate is used, which is applied in the fall or spring before planting. The fertilizer rate is 1 kg per hundred square meters.
- Iron and manganese. With a lack of iron and manganese, potatoes wilt. Feeding the plantings with potassium sulfate will help correct the situation. A bucket of water requires 5 g of fertilizer, after which the bushes are watered at the roots. To spray potatoes, a solution of copper sulfate is prepared (50 g per bucket of water). The procedure is carried out every 5 days.
Development of the disease
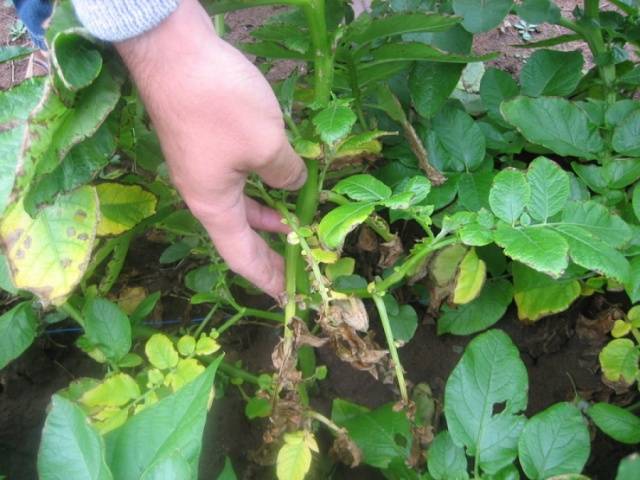
Early yellowing of tops is often associated with the development of diseases:
Verticillium wilt
If the leaves of a potato turn yellow and dry out, this is a sign of a viral infection. Verticillium wilt spreads at temperatures from 17 to 22 degrees. Dark spots form on the cut of the potato stem. If the disease develops, the bush must be removed from the site. To prevent wilting, plantings are treated with a solution of copper oxychloride.
Fusarium
If the yellowness spreads from the top of the potato, it is a sign of fusarium blight. The disease develops in high humidity in cool climates. In this case, it is impossible to save the plantings, so it is necessary to eliminate the affected plants.
To prevent fusarium, you need to follow the rules of crop rotation. Planting material is processed for disinfection.
Late blight
If the tops at the bottom of the bush turn yellow, this is the first symptom of late blight. At the same time, dark spots form along the edges of the leaf plate, gradually spreading to the entire bush.
What to do if late blight spreads? Potatoes must be treated with fungicides: copper oxychloride, Kuproxat, Ditamine.
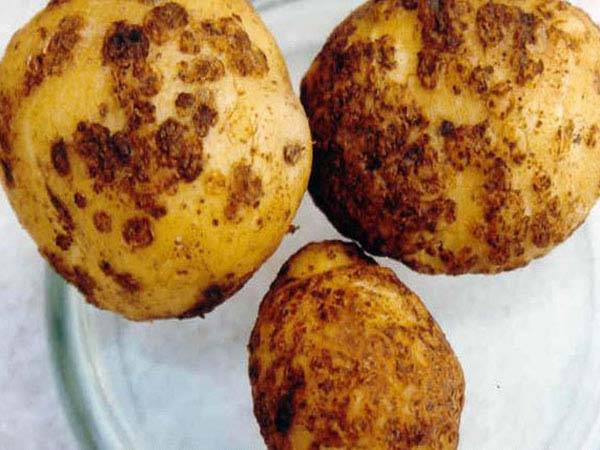
Dry spotting
The disease appears on potato leaves two weeks before flowering. First, rounded brown spots appear on the potato tops, which gradually grow. Dry spotting is determined by the presence of yellowed tops.
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus. To combat it, chemicals are used: “Quadris”, “Oxychom”, “Ridomil”.
Pest attack
Potatoes are susceptible to various pests, under the influence of which the tops become yellow:
Nematode
The potato nematode lives in the soil and feeds on the sap of the root system of plants. As a result, the stem and leaves of the potato turn yellow. The nematode leads to crop loss, which can be up to 80%.
To combat nematodes, fescue, lupine, marigolds, rye, oats or peas are planted next to potatoes. Before planting tubers, urea is added to the soil (1 kg per hundred square meters).
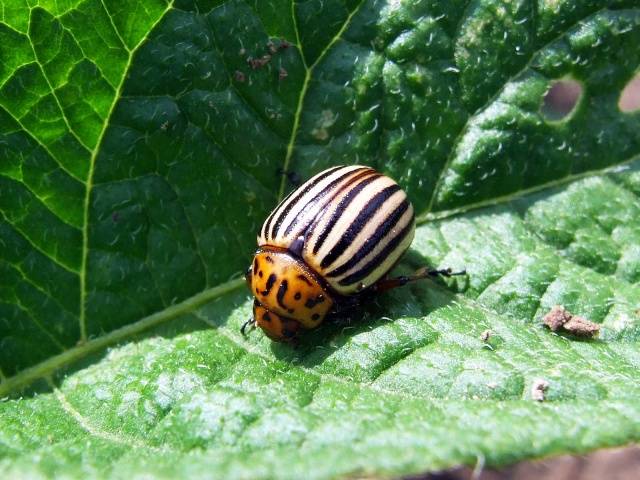
Colorado beetle
One of the most common pests in the garden is the Colorado potato beetle. This insect eats potato tops, causing them to wilt.
The use of special preparations allows you to cope with the Colorado potato beetle: “Iskra”, “Bankol”, “Commander” and others. For processing you need to make a solution. The procedure is carried out during the growing season of plants before harvesting.
Next to potatoes you can plant calendula, beans, marigolds, and tansy. These plants have a strong smell that repels pests.
To get rid of the Colorado potato beetle, traditional methods are used: an infusion is prepared based on dandelion, celandine or garlic.
Conclusion
When yellow leaves appear on potatoes, you need to analyze the conditions in which the plants grow. The irrigation and fertilization scheme must be adjusted.If diseases or pests are detected, the plantings are treated with chemicals. For prevention, tubers are treated before planting, and marigolds, calendula and other useful plants are planted next to the plantations.