Content
- 1 Applying fertilizers to the soil in autumn
- 2 Application of mineral fertilizers
- 3 Soil deoxidation
- 4 Application of organic fertilizers
- 5 Fertilizers for germinating seeds and growing seedlings
- 6 Fertilizing seedlings
- 7 Fertilizing the soil in spring
- 8 Fertilizers when planting tomato seedlings in a greenhouse
- 9 Fertilizing tomatoes in a hole when planting in open ground
- 10 Applying fertilizer to unfertilized soil
- 11 Foliar feeding of tomatoes
- 12 Approximate feeding scheme
- 13 First aid for nutritional deficiencies
Tomatoes are on the table all year round, in fresh and canned form. Tomatoes are sold at the market and in supermarkets, but the most delicious and aromatic are those grown with your own hands in your own garden. To get a rich harvest, choose proven regional tomato varieties, follow agricultural practices, and use suitable fertilizers when planting tomatoes.
The tomato bush is a powerful plant, its root mass correlates with the ground part 1:15, timely and adequate fertilization of tomatoes will increase productivity, improve the presentation of the fruit, and grow it perfectly balanced in the content of nutrients. Learn what fertilizer to apply when planting a tomato throughout the entire growing season.
Applying fertilizers to the soil in autumn
You need to prepare the soil for growing tomatoes and add fertilizers to the soil in the fall, immediately after harvesting the predecessor crop.It is preferable to plant tomatoes after cucumbers, legumes, onions and early cabbage. You can’t plant tomatoes after peppers, eggplants, and potatoes, because they all have common pests and diseases.
Application of mineral fertilizers
Spread the fertilizer and dig up the soil using the bayonet of the shovel. Digging will saturate the soil with oxygen and help destroy some tomato pests. In autumn, organic matter, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers should be applied. These rules are due to the fact that many potash fertilizers contain chlorine, which is harmful to tomatoes, which is quite mobile, and by the time the tomato is planted in the ground it will sink into the lower layers of the soil. Phosphorus is poorly absorbed by the root system, however, by spring, it will turn into a form accessible to plants. Nitrogen mineral fertilizers of the soil before winter are practically useless, because nitrogen will be washed out of the fertile layer by autumn precipitation and spring floods.
Soil deoxidation
If the soil on the site is acidic, then it is necessary to deoxidize it. The safest and most convenient substance to use is dolomite flour. It is not necessary to carry out liming and fertilization in the same year. Maintain the pH balance of the soil, plan liming every five years.
Application of organic fertilizers
Which organic fertilizer is best for tomatoes? Cow dung can be used. The optimal combination of price, availability of purchase and content of almost all the nutrients necessary for tomatoes. Manure not only enriches the planting area with nutrients, but also promotes soil aeration, brings the pH reading to neutral, and promotes the development of beneficial microflora. Fertilizer application rate 5-8 kg per 1 m2. If you can find horse manure, then take 3-4 kg of it per 1 m2 beds, becausethe content of phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen in it is higher. By spring, the manure will rot, mix with the soil and enrich it.
Fertilizers for germinating seeds and growing seedlings
Do you buy ready-made tomato seedlings or want to grow them yourself? In the second case, prepare the soil by taking one part of peat, forest or garden soil, one and a half parts of humus and half of river sand and add a glass of crushed shells. Steam or spill the soil mixture with a pink solution potassium permanganate. Mineral fertilizers are not used. Tomato seeds in branded packages can be germinated immediately, but collected ones require pre-sowing treatment. Pour the seeds with 1% salt solution, take those that sink to the bottom of the container. Rinse and disinfect by soaking for half an hour in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate. Rinse and dry again. Soak according to the instructions for the preparations in Epin or Potassium Humate. After keeping the seeds in a warm solution for a day, germinate them on damp gauze.
Fertilizing seedlings
Novice gardeners are often interested in what fertilizers should be used when growing tomato seedlings. Feed the planted tomatoes with yeast solution. Infuse 5 grams of bread for 24 hours yeast for 5 liters of water. Water twice during the entire period of growing seedlings at home. The plant needs more serious fertilizers in the following phases of the growing season.
Fertilizing the soil in spring
If for some reason the soil was not enriched in the fall, then fertilizers for tomatoes can be applied in the spring. Modern complexes contain both basic elements and additional ones: sulfur, magnesium, iron, zinc.You can scatter fertilizer granules on top of the snow, or after it melts, rake the fertilizer into the soil. Well suited for feeding tomatoes:
- Kemira universal 2. Balanced complex of minerals for spring use;
- Kemira Lux. Water-soluble drug, very convenient for application;
- A universal product containing, in addition to macro and micro elements, humic substances. The product is environmentally friendly and completely digestible.
The dosage of universal fertilizers is given on their packaging.
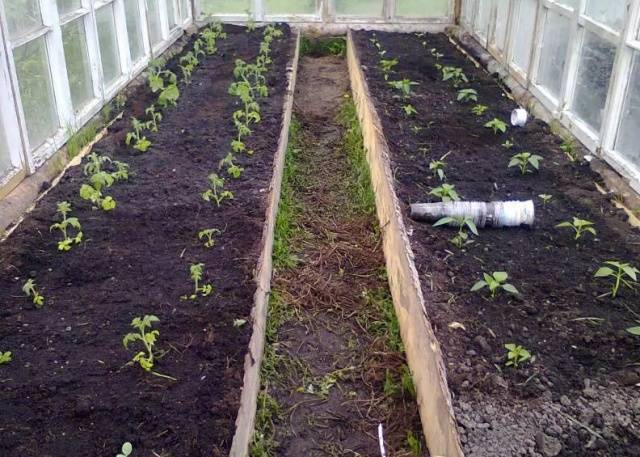
Fertilizers when planting tomato seedlings in a greenhouse
If the climate does not allow growing tomatoes in open ground, then they can be planted in a greenhouse. Let's consider which fertilizers are optimal when planting tomatoes in a greenhouse. Fertilizing is done during planting of seedlings. Make holes in advance, put humus, compost in them and add ash. By applying fertilizer when planting tomatoes, you will provide them with minerals, macro- and microelements.
Feeding with herbal tea
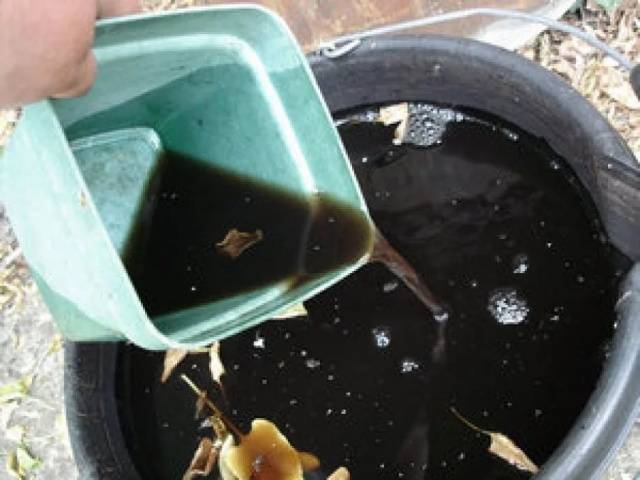
When planting greenhouse tomatoes, you can add a natural fertilizer: “herbal tea” to the hole. You can prepare it by chopping 4-5 kg of plantain, nettle and others weed. A glass of ash is diluted in 50 liters of water, a bucket of mullein is added and left to infuse for several days. The fermented infusion is added to a volume of 100 liters, and two liters of solution is poured under each tomato bush.
Fertilizing tomatoes in a hole when planting in open ground
A bed prepared in the fall is saturated with a complex of useful substances and does not require mineral fertilizing. A day before transplanting the seedlings into the hole, when planting a tomato in the ground, spill it with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate. Add 200 ml of pre-infused yeast mixture into the planting hole at the rate of 10 grams per 10 liters of water. Place crushed shells and wood ash under the roots of the tomato. After planting the seedlings, compact the soil and sprinkle with a pinch of black soil or compost. Excess fertilizer when planting tomatoes in open ground can destroy the root system. If the seedlings are grown in peat pots, fertilizing the tomatoes when planting is unnecessary.
Applying fertilizer to unfertilized soil
Sometimes it happens that fertilizers for tomatoes were not applied during the main cultivation of the beds. The situation can be corrected by mixing one part at a time: humus, peat and fresh compost. Superphosphate is added at the rate of a tablespoon per bucket of mixture. Leave the prepared mixture to mature for a month and a half. When planting tomatoes, add two liters of fertilizer under each bush. Water the planted tomatoes generously, and before the flowering period the fertilizing work can be considered completed.
Feeding with ready-made complexes
When planting tomatoes in a hole, you can use commercial fertilizers. They are balanced and formulated specifically for nightshade plants.
- "Hello" for tomatoes. Contains a complex of elements necessary for tomatoes.
- "Multiflor" for tomatoes. The complex can be dissolved in water, or it can be mixed dry with soil and applied under the root when planting.
- Agricolla for tomatoes. The balanced complex is used in the form of an aqueous solution. Watering is carried out under each bush, 4-5 times during the growing season.Nutrients are in a form accessible for absorption.
Foliar feeding of tomatoes
Tomatoes are responsive to foliar feeding. Spraying the stems and leaves improves the appearance of the plant within a day, and the result of root fertilizer is noticeable after a week, or even two. The leaves will absorb only the right amount of missing nutrients. During budding, you can spray the green mass of the plant with an extract of wood ash, for which two glasses of dry matter are poured with 3 liters of hot water, infused for a couple of days and filtered.
Approximate feeding scheme
If you follow all the rules for growing tomatoes, the approximate feeding scheme is as follows:
- 2-3 weeks after planting the seedlings. Dissolve 40 in 10 liters of water G phosphorus, 25 g nitrogen and 15 g of potash fertilizers. Watering 1 liter of solution under each bush.
- Fertilizing during mass flowering: use 1 tbsp per 10 liters of water. l. potassium sulfate and 0.5 liters of liquid mullein and bird droppings. Water one and a half liters of fertilizer under each plant. Another option: add 1 tbsp to a bucket of water. l. nitrophoska, pour 1 liter under each bush. To prevent blossom end rot, spray the bushes with a solution of calcium nitrate, 1 tbsp. l per 10 liters of water.
- You can help the formation of the ovary by feeding the tomatoes with a mixture of boric acid and wood ash. For one bucket of hot water, take 10 g of boric acid and 2 liters of ash. Leave for a day, water a liter under each bush.
- Final root fertilizer for tomatoes is aimed at improving the taste and ripening of the fruit. When mass fruiting begins, feed the tomatoes by dissolving 2 tbsp in 10 liters of water. spoons superphosphate and 1 tbsp. spoon of sodium humate.
First aid for nutritional deficiencies
Tomato bushes themselves signal a fertilizer deficiency. A lack of phosphorus is manifested by a purple coloration of the lower part of the leaf and veins; spraying with a weak solution of superphosphate is necessary. Lack of calcium leads to leaf curling and blossom end rot. Spray the plant with the solution calcium nitrate. With a lack of nitrogen, the plant becomes light green or yellowish in color and looks rickety. Spray with a weak urea solution or herbal infusion.
Watch your tomato plantation, monitor their well-being, and remember that it is better to under-fertilize than overdose.