Content
Reviews of Jura potatoes from those gardeners who bought branded seeds and grew the Isle of Jura variety are the most positive. After heat treatment, table tubers have a pleasant taste and consistency. The plant is little susceptible to common diseases.
Description of the Jura potato variety
Isle of Jura - developed by breeders from Great Britain. It has been in the State Register of the country since 2007; in addition to the foreign company, the domestic originator of the variety, New Potato LLC from the Moscow region, has been named. Medium-sized Jura bushes of intermediate type, with strong, semi-erect stems. Large leaves are dark green with slightly wavy edges. In June, flower stalks grow on individual stems of the Jura variety. The corollas are white and large.
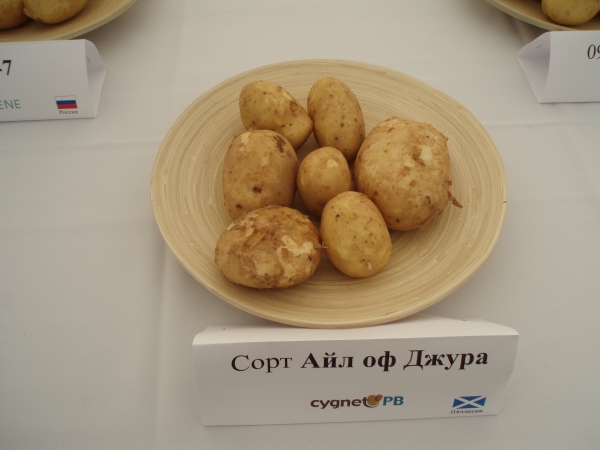
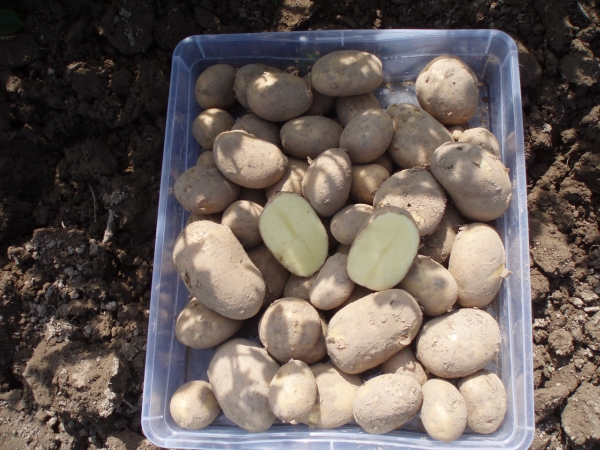
The oval tubers of the Jura potato variety, as seen in the photo, are elongated. The eyes are sparsely located, small, small. The smooth peel is yellow-beige, thin after digging, gradually becoming coarser during storage. Light sprouts are thick and whitish.The pulp is creamy-yellowish, which indicates the presence of a large amount of beta-carotene.
Tubers of the Jura variety for table use belong to the culinary type BC:
- universal;
- moderately mealy;
- the pulp is slightly boiled.
Depending on agricultural cultivation technology and weather conditions, the starch content in mid-early potatoes ranges from 12 to 16%. The figures correspond to the average indicators for the level of accumulation of the substance on which the boilability of the tuber depends. Tasters gave the variety a taste rating of 4 to 5 points.
Pros and cons of the Jura variety
Potatoes have proven to be high-yielding and hardy in cool summer conditions and frequent rainfall, typical for areas of the Central region, where the variety is recommended for cultivation. Tubers quickly form and gain weight. The variety begins to be dug 65-80 days after emergence. Over the years of cultivation, gardeners have compiled a list of advantages of Isle of Jura potatoes:
- early production;
- good yield in the group of mid-early varieties;
- high marketability of tubers;
- excellent keeping quality;
- versatility;
- pleasant taste of dishes;
- unpretentiousness to the weather conditions of central Russia;
- resistance to a number of diseases.
If the disadvantages include the specially selected by breeders undemandingness to rather harsh weather conditions, then the disadvantage of this variety is that it is not adapted to droughts. The Isle of Jura is the brainchild of Scottish agronomists, where areas are more likely to suffer from plenty of rain, but not from dry periods.
Planting and caring for Isle of Jura potatoes
The variety must be planted and grown using standard agricultural technology.Potatoes develop well after last year's planting of any grains, legumes and melons, as well as after cabbage, beets, and carrots.
Selection and preparation of a landing site
For the Isle of Jura potato variety, the plot is prepared in the fall, enriching every square meter with nutrients:
- before plowing, add 6-8 kg of humus or manure;
- 30 g of superphosphate;
- You can add humus before spring cultivation;
- Directly during planting, 130-180 g of wood ash is placed at the bottom of the hole.
Preparation of planting material
Jura potato tubers, according to the description of the variety, photos and reviews, form strong light sprouts after special preparation. A month before planting, seed potatoes are lifted from the cellars into the light for germination. The tubers are laid out in 2-3 layers in wooden or plastic boxes and placed in a bright, cool room. The temperature should not rise above + 14-15 °C so that the sprouts do not stretch. After proper vernalization, the shoots reach 0.5-1.2 cm.
Landing rules
In an effort to get a rich harvest of the Jura variety, they adhere to generally accepted rules:
- planting is carried out when the soil at the depth of potato placement warms up to 10-12 °C;
- on structured loams and sandy loams, the hole depth for the mid-early variety is 8-10 cm;
- on heavy clay soils, Jura potatoes are planted at a depth of 5-6 cm;
- optimal placement scheme for a small bush Isle of Jura - 50x60 cm;
- The location of the light sprouts when planting does not affect the potato yield.
Watering and fertilizing
Judging by the characteristics of the variety and reviews of Jura potatoes, the moisture-loving crop is regularly watered if there is insufficient rainfall:
- the beginning of watering - in the phase of 13-15 cm of stem height, 2.5-3.5 liters for each plant;
- when buds form, the bushes are watered with 6-7 liters;
- during the period of tuber formation they give 10-12 liters.
Organic fertilizers are not enough for good yield of the Jura variety. Potatoes are fed with complex mineral and organomineral fertilizers:
- "AVA";
- "Kemira";
- "Crystalon";
- "WMD";
- "Bulba" and others.
After the first watering or earlier, foliar feeding is carried out. To treat leaves, prepare a mixture in 10 liters of water:
- 90-110 g urea;
- 150 g of potassium monophosphate;
- 5 g boric acid.
After 2-3 weeks, feed again in the same way, but in a higher concentration - per 5 liters of water.
Loosening and weeding
Potato plantings are regularly looked after. After watering, loosen the soil with light tools without damaging the tubers. Weeds deleted.
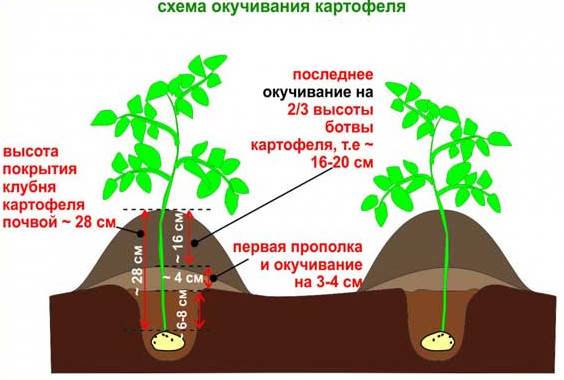
Hilling
The characteristics of the Jura potato emphasize that the variety is moisture-loving. Hilling will help create a convenient environment for the tubers to gain weight. Hill up in damp soil, forming ridges around the bush. Sometimes ridges are made at a stem height of 3-5 cm in case of threat of frost. Hilling is carried out 2-3 times until flowering.
Diseases and pests
Jura potatoes are resistant to cancer, common scab, black leg and late blight of tubers, and are not affected by the golden nematode. If late blight fungi begin to spread early, plants may suffer. Preventive spraying with fungicides “Oxyx” and “Ridomil” is recommended.
To protect tubers from wireworms and cutworms, remove weeds around the potato area. Insecticides are used against aphids and whiteflies. Colorado potato beetles are controlled with special preparations.
Potato yield
The mass of tubers of the Jura variety is from 90 to 190 g. From 6 to 10 potatoes are formed in the nest. At a summer cottage, you can get 1-2 kg from each bush, which depends on the fertility of the soil, the regularity of watering and fertilizing.
Harvesting and storage
Isle of Jura tubers are long-lived: 95% of the harvest is preserved. Dig new potatoes when they are the size of a chicken egg. Sometimes they dig up a bush, take larger tubers, and the rest continue to gain weight. Mid-early potatoes are completely removed if the skin becomes strong. The tubers are dried and stored.
Conclusion
Reviews of Jura potatoes confirm the description of a stable, productive variety of mid-early ripeness. Compliance with recommended agricultural practices will ensure a good harvest of tubers. According to their characteristics, potatoes are suitable for growing in the middle zone.