Content
Gentian yellow (Gentiana yellow) is a perennial herbaceous plant from the Gentian family. The inhabitants of Ancient Egypt were well aware of the healing properties of the plant, who used it in the treatment of stomach diseases, inflammation, tuberculosis and many other ailments. In ancient Rome, remedies based on gentian yellow were used to treat scorpion and poisonous snake bites, and to treat diseases of the blood, kidneys, liver and upper respiratory tract.
Description of the plant
The yellow gentian flower is a herbaceous perennial, reaching a height of 120 cm. The plant is distinguished by a short forked rhizome that turns into a root. The stems of the crop are characterized by an erect cylindrical shape. The leaves of yellow gentian are opposite, entire, bluish-green in color. The basal leaf plates have an elliptical shape, the stem plates have an ovoid-elliptical shape.

Yellow gentian inflorescences are bunches collected from small-sized leaves
The fruits are multi-seeded capsules of lanceolate-oblong shape. Inside are many small flattened, oblong or round brown seeds.
Where does yellow gentian grow?
Yellow gentian is considered an endangered plant. The culture grows on the mountain ranges of Asia Minor, in the Alps, Pyrenees, Eastern Carpathians and on the Balkan Peninsula. Yellow gentian is cultivated in Ukraine, India, France, Great Britain, the Czech Republic, Germany and some regions of Russia. The crop blooms for several weeks from June to July.
Composition and value of yellow gentian
Yellow gentian has a rich composition, including the following substances and compounds:
- Alkaloids, the main one of which is gentianine. Found primarily in the roots of the plant. In medicine it is used as a bitter remedy to treat various digestive disorders. Does not dissolve in water.
- A number of disaccharides (gentiobiose, sucrose), monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), as well as gentian trisaccharides and polysaccharides (pectins).
- Secoroidoids: gentiopicrin, gentiomarin, sweroside, swertiamarin. The most bitter component of the plant is amarogentin. The bitter taste is also provided by amarosverin and amaropanan.
Yellow gentian also contains: inulin, essential and fatty oils, tannins, resins, flavonoids, mucus, aromatic compounds, ascorbic and phenolcarboxylic acids.
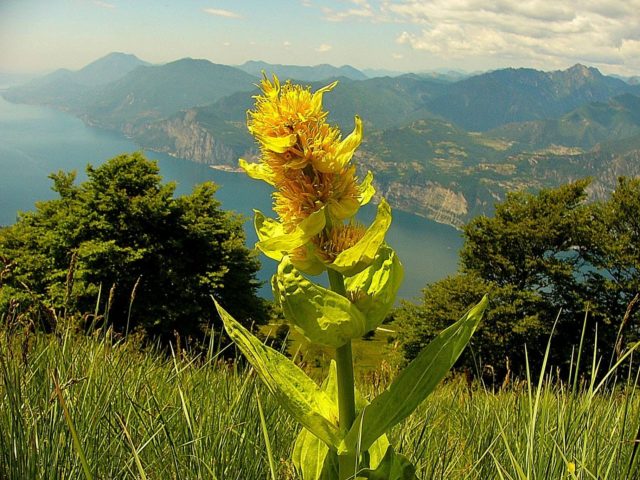

The yellow color of gentian is due to the high concentration of pigment, which belongs to the group of xanthones.
Medicinal properties of yellow gentian
The famous botanist and doctor of German origin, Hieronymus Bock, described yellow gentian as a miraculous remedy for fighting worms, tuberculosis and fever. During the Middle Ages, the flower was revered as having magical properties and was one of the twelve magical plants of the Rosicrucians. Residents of mountainous countries prepared a strong tincture from the roots of yellow gentian, which they used for diarrhea and intestinal colic. It was also used as an anthelmintic and general tonic.
The therapeutic effect of yellow gentian is ensured mainly by the high content of gentiopicrin and other bitter glycosides. They have a stimulating effect on the motor and secretory function of the gastrointestinal tract, increase food digestibility and stabilize the digestion process. The therapeutic effect is more pronounced in the case of normal secretion. Preparations from yellow gentian have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. They are prescribed for diseases of the gallbladder and liver, intestinal atony, spasms, colitis and diabetes.
Preparations based on Gentian yellow are widely used for achylia and dyspepsia, as well as for lack of appetite, diarrhea, heartburn, constipation, scrofula, anemia, arthritis and pancreatitis. The plant stabilizes metabolic processes in the body and helps increase the amount of milk in women. Due to their pronounced hepatoprotective properties, preparations made from Gentian yellows protect the liver from destruction. They are used for inflammation of the bladder and kidneys, and also as an antiallergic agent.

The special substances that make up Gentian yellow are considered analogues of anabolic steroids
The plant can be used to safely increase muscle mass.
Use of yellow gentian in folk medicine
For dyskinesia affecting the biliary tract, the use of a cold infusion of gentian yellow (pictured) is carried out according to the following recipe: 1 tbsp. l. dried and ground gentian is poured with half a liter of boiled water (the temperature should be between 22-25 ° C). The container is put away overnight in a dark place at room temperature. In the morning, filter the solution and take ½ glass twice a day.
There are other recipes based on yellow gentian:
- Tea drink. Increases appetite, prevents bloating, cramping pain in the stomach and stabilizes the digestive process. The drink is prepared in this way: vegetable raw materials (in the amount of 1 tsp) are poured into 250 ml of purified water and boiled for five minutes. The healing drink is filtered and consumed 100 ml shortly before meals.
- Tincture of yellow gentian. Used for colitis, constipation and intestinal atony. To prepare it, take 100 g of dried, ground parts of the plant and pour it with a liter of vodka or high-quality distillate. The tincture is placed in a place protected from sunlight. After a few days, it is filtered and consumed 15-25 drops, which are diluted in 50 ml of clean water. Take the drug 15 minutes before meals 3 times a day.
- Decoction for external use.
Gentian yellow remedy can be used externally
2-3 tablespoons of crushed parts of the plant are mixed with an identical amount of dry chamomile, poured with purified water (1 liter) and boiled for 10 minutes. The decoction is filtered, and the finished product is used to treat burns and wounds.Dry chamomile and gentian powder (the ingredients are taken in equal proportions) are sprinkled on ulcers on the skin to disinfect, disinfect and accelerate regeneration.
In medicine, it is customary to use mainly the root of yellow gentian, since the rest of the plant cannot boast such a high concentration of valuable substances and compounds. Excessive sweating of the feet is treated with a decoction of the leaves. Collection from the roots of yellow gentian in combination with centaury and yarrow helps against gastritis and various disorders of the digestive tract. Take 1 tablespoon of each ingredient, add four glasses of water and boil over low heat for 15 minutes. You need to take 50 ml of the decoction three times a day before meals.
Restrictions and contraindications
Like other medicines, yellow gentian has contraindications and restrictions for use. The use of plant-based preparations is strongly discouraged for the following diseases: stomach ulcers, hypertension, as well as during pregnancy and lactation.
Planting and care
Gardeners practice growing yellow gentian mainly from seeds. However, the crop propagates without any problems or difficulties by dividing the bush, as well as by layering and cuttings. It is preferable to plant gentian in partial shade. Plants need to be provided with drainage in the form of pebbles or gravel.
When and how to plant
Gentian yellow seeds are planted in open ground in mid-spring or in the last days of September. Seed material needs preliminary stratification for three months at a temperature not exceeding 8 °C. Good air ventilation must be ensured.The soil is dug up, weeds are removed, and five to six buckets of compost are added. The optimal soil for growing yellow gentian is with neutral acidity. When planting, it is necessary to maintain a distance between plants of 55 to 65 cm.

A good soil for the plant is a mixture of sand and peat in a ratio of 3:1
Since the crop does not tolerate transplants well, it must be propagated by the vegetative method with great care. Damage to the root system can be detrimental to the plant. The flower goes well with ferns, hostas, rhododendrons, primrose and edelweiss. The culture is used to create ridges, flower beds and rocky hills.
Watering and fertilizing schedule
Gentian is very picky about watering and does not tolerate dry soil and increased dry air. The ideal place for the plant is an area near a pool or fountain.
Watering the plant with hard water is strongly discouraged, as this step can cause slow development and delayed flowering.
Gentian prefers organic fertilizers, especially rotted manure. Immediately after planting, ash or bone meal is added under the roots. During the growing process, mineral complex fertilizers with prolonged action are used. Horn flour, as well as crushed limestone, which ensures high growth rates of green mass, are considered good feeding for semi-shrubs.
Weeding and loosening
The crop does not tolerate proximity to weeds, so it requires periodic weeding and loosening of the soil. It is necessary to loosen the soil only after watering and removing weeds.Mulching the soil in the tree trunk area with peat, sawdust and straw allows the semi-shrub to be provided with natural protection from adverse environmental factors.
Preparing for winter
It is necessary to promptly rid semi-shrubs of dried inflorescences by pruning using garden tools. If grown in a region characterized by the sudden onset of winter, yellow gentian must be provided with shelter from spruce branches.
Diseases and pests
Since the plant has a high concentration of alkaloids and bitter acids, various pests are in no hurry to settle on it. When grown in open ground conditions, the danger to the crop is posed by ants and thrips (small insects from the order Colonidae that cause plant diseases). They get rid of them with the help of special insecticides and systemic drugs.

If a plant is damaged by gray mold, spotting, rust, root collar rot or other fungal diseases, it must be treated with a fungicide
Collection and procurement of raw materials
The root part of yellow gentian is harvested in early spring or autumn. For medicinal preparations, only plants that have reached four or five years of age are used. The roots are dug up, cleared of soil, washed and cut into small pieces, and then quickly dried in a special cabinet or oven, keeping the temperature within 51-60 degrees. Dried roots have a distinct specific odor and persistent bitter taste.
Conclusion
Yellow gentian has been used for thousands of years as a raw material for the production of medicinal remedies for a wide variety of diseases.Preparations based on this herb are effective in the treatment of chronic forms of hepatitis, diathesis, anemia, upper respiratory tract diseases and many other ailments. The therapeutic properties of the plant are recognized by official medicine. Many pharmaceutical companies produce extracts and tinctures of yellow gentian.








