Content
Honeysuckle is famous for its healthy berries, which is why it is popular. The description of the Volkhov honeysuckle variety will allow you to decide on the choice of berry bush for your site.
This is a national culture created by Leningrad specialists. The parent variety is Pavlovskaya honeysuckle. Since 1999, the crop has been included in the State Register and recommended for cultivation in almost all regions of Russia.
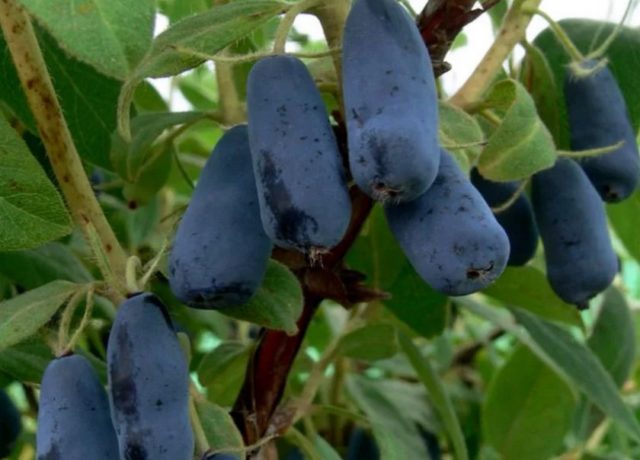

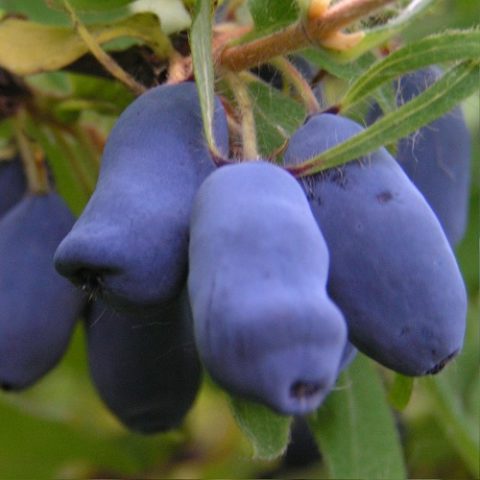
Blue berries covered with a bluish coating have beneficial and healing properties.
Description of the edible honeysuckle variety Volkhov
If you look at the external signs, the edible blue honeysuckle of the Volkhov variety is difficult to distinguish from other representatives of the culture. But this is an apparent dissimilarity, since the plant has qualities that are unique to it.
Bush
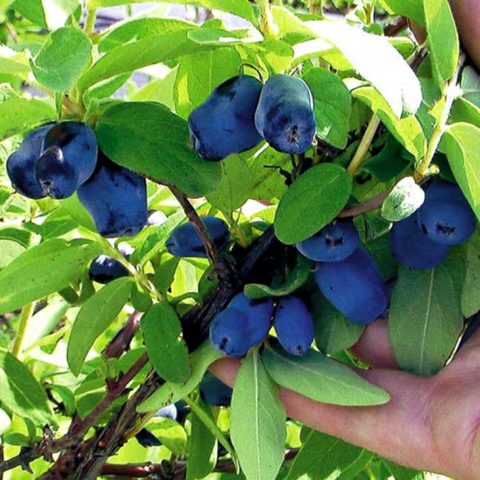
A bush with an oval dense crown and dark green flat leaf blades. It should be noted that the leaves are quite wide.
Numerous branches of the skeleton are thin but strong.Volkhov's honeysuckle grows up to 2 m.
Berries
The fruits of the Volkhova variety are bluish-gray, elongated in length (at least 2 cm). The top of the berry is pointed. The weight of one honeysuckle is approximately 1 g. The skin is thin but dense.
The berries are sweet, the acid is almost not noticeable. But the strawberry aroma will not leave anyone indifferent.
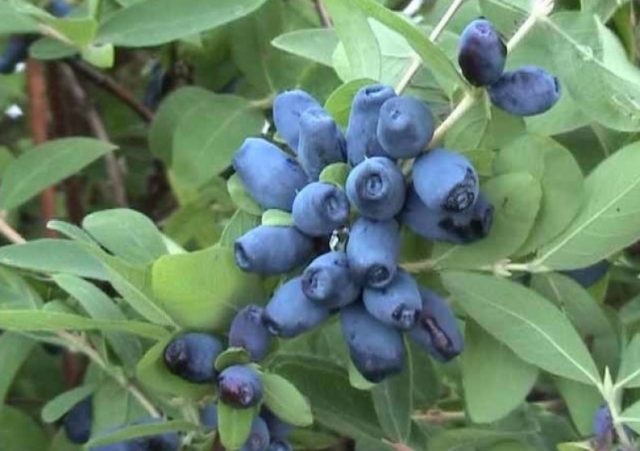

This is a dessert variety; tasters give it 4.7 points.
The chemical composition of the berries is also attractive. They contain:
- dry matter – 19%;
- sugar – 8.4%;
- fructose – 2%;
- vitamin C – 77 mg;
- vitamin P – 10.35 mg;
- provitamin A – 0.5 mg;
- vitamin B1 – 3 mg;
- vitamin B9 – 10 mg.
Specifications
Volkhov's honeysuckle is a mid-early ripening variety. Harvest can be done in early June in warm regions. In cooler zones - 7-12 days later. One bush produces an average of 2 to 3.5 kg of tasty fruit.
It is frost-resistant, so it is grown in regions where the thermometer drops to 40 degrees in winter. This allows you to reduce labor costs when preparing Volkhov honeysuckle for wintering.
Since harvesting can be done using machinery, the crop is planted on an industrial scale, for example, on farms.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Like any garden crop, the Volkhov honeysuckle variety has its pros and cons.
Positive sides:
- weak crumbling;
- winter hardiness of honeysuckle;
- unpretentiousness of cultivation and care;
- the ability to transport dense berries over long distances;
- long-term storage of the harvested crop;
- pleasant taste and beneficial properties of the fruit.
Cons of honeysuckle:
- small fruits;
- the need to place pollinating plants on the site;
- late dates for the start of fruiting after planting - after 3-4 years.
Planting and caring for Volkhov honeysuckle
As already noted in the description and characteristics of Volkhov’s edible honeysuckle, the culture is distinguished by its unpretentiousness in cultivation and care. You just need to take care in advance about choosing the right place, since she does not like transfers.
Landing dates
According to experienced gardeners, it is better to plan the planting of honeysuckle on the site at the beginning of autumn. Seedlings can be of different ages; even 3-4 year old bushes take root well. You just have to shorten the shoots to 50 cm.
Selection and preparation of a landing site
The variety should be planted in well-lit areas, since a lack of sun can sharply reduce the taste of the berries and slow down the development of honeysuckle. The bush itself can be constantly exposed to sunlight, but the lower branches should be in the shade. Plants feel great next to a fence or hedge, which will protect the plantings from winds and drafts.
The Volkhova variety prefers fertile, moist soil. Sandy soils are not suitable for the plant, as are wetlands where groundwater is located close to the surface. In this case, the root system will suffer, which will lead to a decrease in the plant’s immunity.
When planning to plant a crop, you need to prepare the site in advance:
- Water the soil well.
- Dig a hole 2-3 weeks before planting.
- Fill it with a nutrient mixture consisting of humus, potassium salt (70 g), superphosphate (15 g).
If seedlings are chosen for planting at the age of six years, then the additives need to be doubled
- Heavy soils should be diluted with peat, sawdust, and coarse sand.
- In the lowlands at the bottom of the pit it is necessary to make a thick layer of drainage.
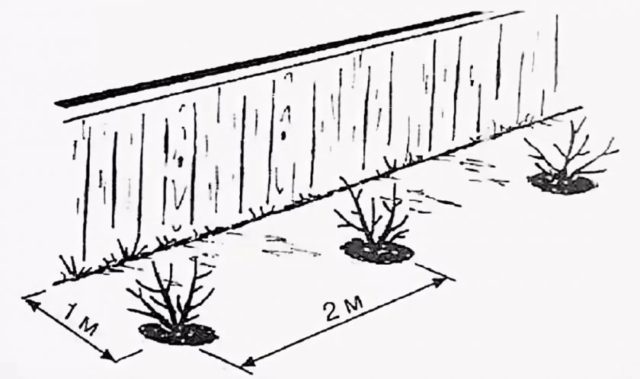
The optimal planting scheme for honeysuckle, allowing the bushes to develop well and bear fruit
Rules for planting the Volkhov honeysuckle variety
When planting honeysuckle on a site, you need to strictly follow the algorithm:
- Since the bushes of the Volkhova variety are tall, at least 2 m are left between them.
- The pit should be 60x70 in size.
A drainage layer of about 20-25 cm must be poured onto the bottom.
- For 10 kg of compost add wood ash (1 kg), superphosphate (200 g). Mix everything thoroughly and pour into the hole.
- Pour out two buckets of warm water.
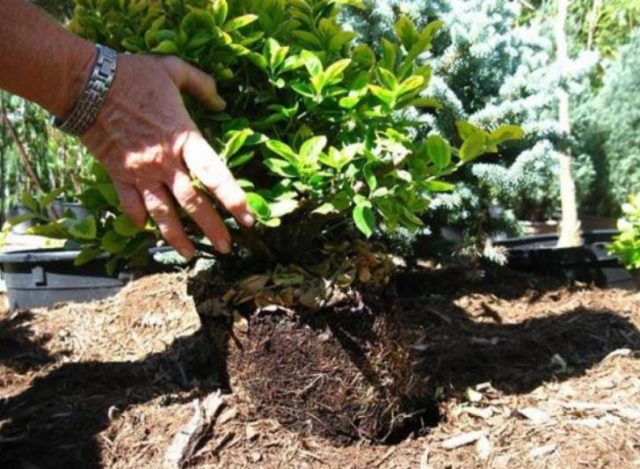
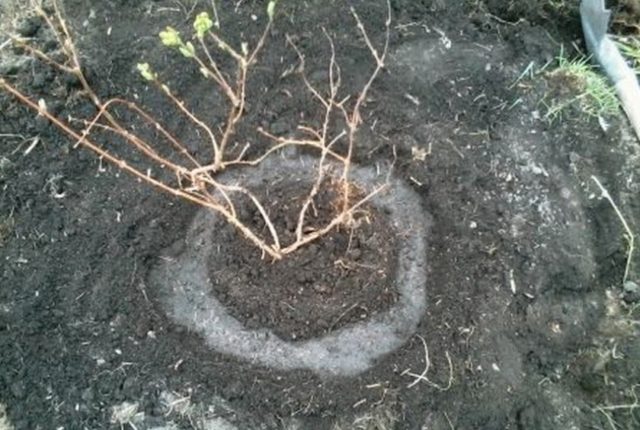
- After it is absorbed, planting begins. The roots of the bush are straightened and placed in the center of the hole.
Seedlings with a closed root system are easier to plant
- Cover the honeysuckle with soil, with the root collar remaining above the surface at a height of 3-4 cm.
The soil is compacted and well watered
- The root zone is covered with mulch.
Mulching will help retain moisture in the soil
Watering and fertilizing
The roots of Volkhov's honeysuckle are superficial, so the soil should not be allowed to dry out.

The plant cannot tolerate stagnation of water, otherwise the roots will begin to rot.
Watering should be done moderately. Only in hot weather should you increase the amount of water, especially at the time when the fruits begin to form and fill.
Feed the bushes several times:
- early in the spring, when the snow just begins to melt, the Volkhov honeysuckle variety needs nitrogen fertilizers;
- after the foliage appears, organic matter is used as fertilizing;
- During budding, flowering and filling of berries, the plants need to be watered with an ash solution;
- Before preparing for winter, so that honeysuckle can better withstand frost, fertilizers containing potassium and phosphorus are applied.
Trimming
Pruning is an important activity when growing Kamchatka honeysuckle Volkhov, but it must begin two years after planting.
Sanitary and shaping pruning is carried out to remove damaged branches, as well as those that have grown inside the bush, otherwise thickening cannot be avoided. Volkhov's honeysuckle grows slowly, so pruning is done after 2-3 years so as not to reduce the yield.
As for anti-aging haircuts, it is carried out on bushes older than 15 years. Moreover, no more than two branches need to be removed annually, otherwise the bush will dry out.
Wintering
As already noted in the description, the Volkhov variety is frost-resistant. And in the spring, when the temperature drops to 8 degrees, the shoots and buds do not suffer. In snowy regions, covering mature bushes is not required. Where there is no precipitation in winter, you need to insulate the root zone with mulch.
But it is recommended to additionally protect seedlings 2-3 years after planting with spruce branches. Work begins after the average daily temperature has been established within -3 degrees.

You can use humus, fallen leaves, cardboard as mulch.
Reproduction
Volkov's honeysuckle is propagated by cuttings or dividing the bush. Both methods are suitable for amateur gardeners. You just need to remember that planting material is cut from young green shoots.
Pollinators of Volkhov honeysuckle
Volkhov's honeysuckle needs pollinating plants, without them the yield will be minimal. The following species should be planted on the site:
- Amphora;
- Pavlovskaya;
- Azure.
Diseases and pests
Mature plants are resistant to many diseases. But young bushes are often attacked by pests: aphids or honeysuckle borers.
Problems that arise need to be dealt with using specialized insecticides or folk remedies. There is no need to wait for mass damage to honeysuckle to begin, but rather take preventive measures.
Conclusion
A description of the Volkhov honeysuckle variety will help gardeners decide on the choice of plants. As a result, bushes with tasty and healthy berries will appear on the site. They can be eaten fresh, made into jam and compotes.