Content
Cherry is one of the most popular fruit crops. To obtain berries in warm and hot climates, two types are most often grown - ordinary and sweet cherries. Entire scientific teams are engaged in breeding new varieties, however, successful cultivars appear infrequently. Even more rarely, noteworthy dukes are created - hybrids of cherries and sweet cherries.
History of selection
The Garland cherry variety is a typical Duke cherry. It was created by A. Ya. Voronchikhina, an employee of the Rossoshansk Experimental Horticulture Station. The parent crops were Krasa Severa and Zhukovskaya. Both varieties are ancient dukes. Beauty of the North is the first Russian cherry-cherry hybrid, bred back in 1888 by Ivan Michurin. Zhukovskaya is a frost-resistant duke created in 1947.
Since 2000, the Garlyanda variety has been recommended for cultivation in the North Caucasus region.
Description of culture
Cherry Garland forms a low tree, not exceeding four meters in size. The rounded, not too dense crown consists of branches extending from the trunk almost at a right angle. Young shoots are smooth, reddish-brown, with long internodes. With age, the bark first becomes grayish-brown, then gray-black.
The leaves are large, smooth, concave. They have an almost round, often asymmetrical shape. The tip of the leaf blade is sharply pointed, the base is either wedge-shaped or rounded. The central vein and long petiole are anthocyanin colored; there are no stipules.
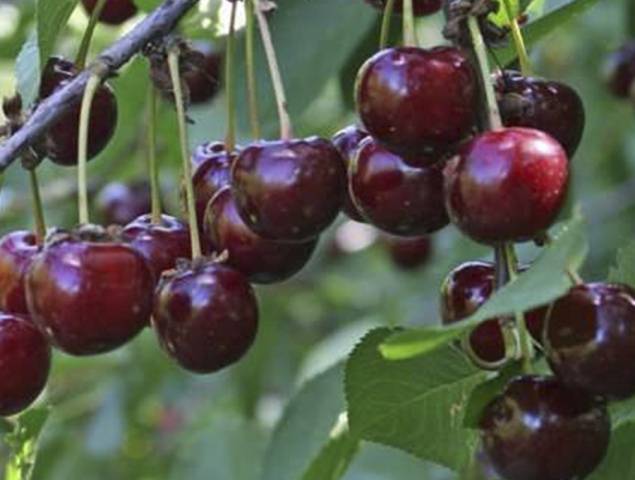
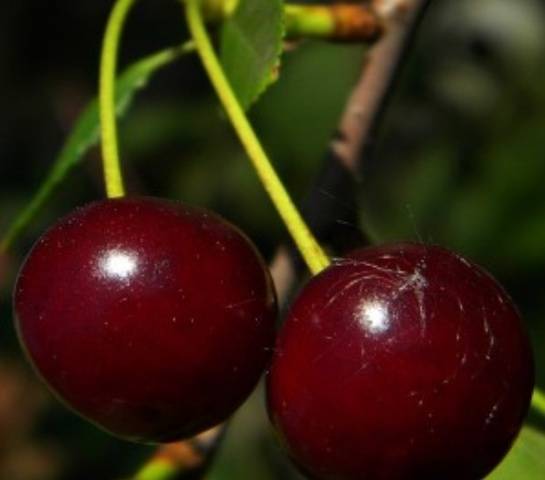
Large white flowers on long stalks are collected in groups of 3-5, less often - 1-2 pieces. They reach 3.5-4 cm in diameter. Garland fruits are large, weighing about 6 g, with a diameter of up to 2.5 cm. The shape of the berry can resemble a heart or a ball tapering towards the top with clear edges and a small funnel. The skin of the fruit is dark red, the pulp is bright, with light veins, the juice is pink.
The berry is tender, juicy, with a sweet and sour pleasant taste, rated 4.2 points. The stone is large, oval, and separates well from the pulp.
The Garland cherry variety is recommended to be grown in the North Caucasus region. At the moment, its distribution is small - the south of the Voronezh and the north of the Rostov region.
Characteristics
Cherry Garland has great potential. Perhaps over time it will become more popular and its growing area will increase.
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
The drought resistance of the Garlyanda variety is average, the frost resistance of the wood is high. In the south, it can withstand even harsh winters well. Flower buds withstand frosts well, which are common in the area recommended for growing the variety. Some of them will die if the temperature drops below -30⁰ C.
Pollination, flowering period and ripening time
The Garland cherry variety is self-fertile. Some sources even claim that it does not need pollinators at all. Perhaps they think so because in the southern regions cherries grow everywhere, and there are a lot of them. The crop is often planted even along roads as protection from dust. Berries are not collected from such trees, but they bloom and produce pollen.
Flowering and fruiting occur in mid-early periods. In the south, berries appear at the end of June.
Productivity, fruiting
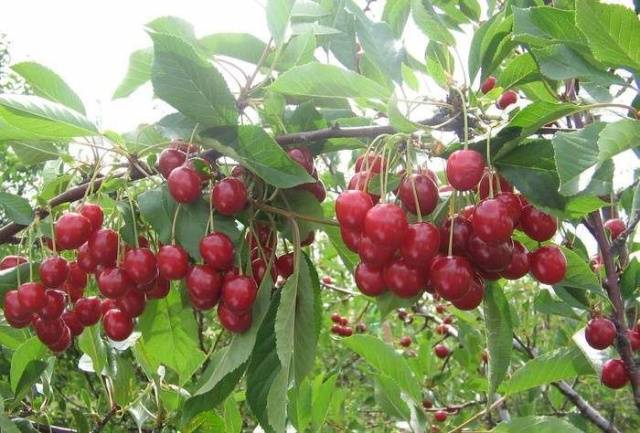
The Garland cherry, which was grafted on an antipka, begins to bear fruit after planting for 3-4 years. A young tree produces about 8 kg of berries, then this figure rises to 25 kg. In a particularly good year, up to 60 kg of fruit can be harvested from a mature Garland cherry. It is thanks to the many berries that decorate a small tree in mid-summer that the variety got its name. This is clearly visible in the photo of the cherry Garland.
When fully ripe, berries come off cleanly, while unripe ones come off with pieces of pulp. The transportability of the fruit is low due to the pulp being too tender.
Area of application of berries
Garland cherry berries have a universal purpose. They can be eaten fresh, canned, or made into jam. The fruits are suitable for making juices and wine - they contain enough acid and sugar.
Resistance to diseases and pests
Cherry Garland can be affected by typical crop pests.Its resistance to coccomycosis is average, but to monilial burn – high.
Advantages and disadvantages
The characteristics of the Garland cherry variety suggest that its numerous advantages outweigh its disadvantages. Benefits include:
- High yield.
- Large berries.
- High resistance of wood to freezing.
- The berry is firmly attached to the stalk.
- High resistance to moniliosis.
- The Garland cherry tree is compact, which makes harvesting easier.
- Fruits of universal use.
- High self-fertility of the variety.
Disadvantages include:
- Insufficient frost resistance of flower buds.
- Low transportability of berries.
- Moderate resistance to coccomycosis.
- A big bone.
Landing Features
The garland is planted in the same way as other varieties belonging to the Ordinary Cherry species.
Recommended timing
In the south of the North Caucasus region, Garland cherries are planted in the fall, after leaf fall, in the north - in the spring, before the buds open. The pit for the culture must be prepared in advance.
Choosing a suitable location
A well-lit place is suitable for Garland cherries. It should be flat or located on a gentle slope of a hill. If cold winds prevail in the planting area, the tree must be protected by a fence, buildings or other crops.
The soil you need is neutral, rich in organic matter, loose.
What crops can and cannot be planted next to cherries?
Next to the Garland variety, you can plant other cherries, cherries or any stone fruit crops. You should not place birch, maple, walnut, oak, or elm nearby. Sea buckthorn and raspberries should be planted further away - their root system will grow in width very quickly, produce abundant growth and suppress the cherries.
After the Garland is well rooted, ground cover plants can be planted under it.
Selection and preparation of planting material
Seedlings take root well at the age of 1-2 years. Their root should be well developed and not damaged. The color of the bark of young Garland cherry is reddish-brown. The stamp must be straight, without damage or cracks, with a height of:
- annual seedling – 80-90 cm;
- two years old - no more than 110 cm.
Pre-planting preparation of cherries involves soaking the root. If it was wrapped in film or coated with clay mash - for at least three hours. The unprotected root is dipped in water for at least a day.
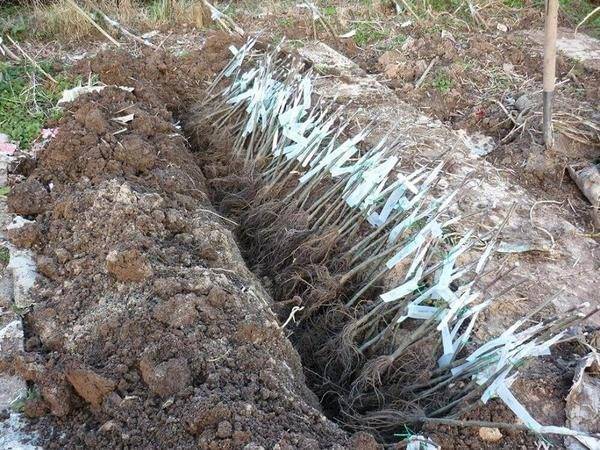
Landing algorithm
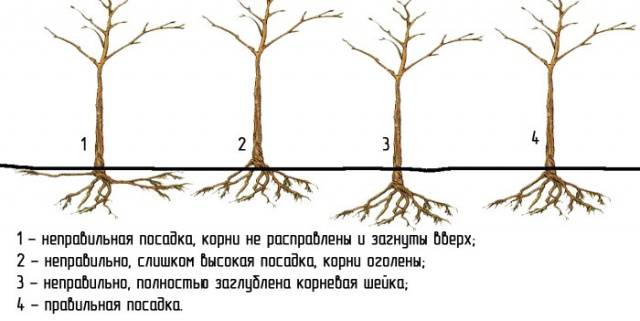
The hole dug in advance should have a diameter of about 80 cm and a depth of at least 40 cm. When planting in autumn, it must be filled with water before planting the cherries. A fertile mixture is prepared from the top layer of soil obtained by digging a hole, a bucket of humus, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, taken 50 g each. If the soil is acidic, add lime or dolomite flour. Add 0.5-1 bucket of sand to dense soil.
Planting is carried out in the following sequence:
- A support is driven in at a distance of 20 cm from the center of the pit.
- The cherry seedling is placed in the middle and covered with a fertile mixture. The root collar should rise 5-8 cm.
- The soil is compacted and watered with 2-3 buckets of water.
- A hill of soil is formed around the perimeter of the planting hole to retain moisture.
- The cherry is tied to a support.
- The soil is mulched with humus.
Subsequent care of the crop
After planting the cherry Garland, the seedling is watered abundantly and often. An adult plant needs this only in dry summers. In the fall, moisture recharging is carried out.
During the first years, the soil under the cherry tree is regularly loosened.When the Garland begins to bear fruit, ground covers can be planted under it.
The best feeding is the autumn application of a bucket of humus and a liter jar of ash into the tree trunk circle. It contains all the elements a cherry needs. Mineral fertilizers are applied as follows:
- nitrogen - in spring;
- potassium and phosphorus - in autumn.
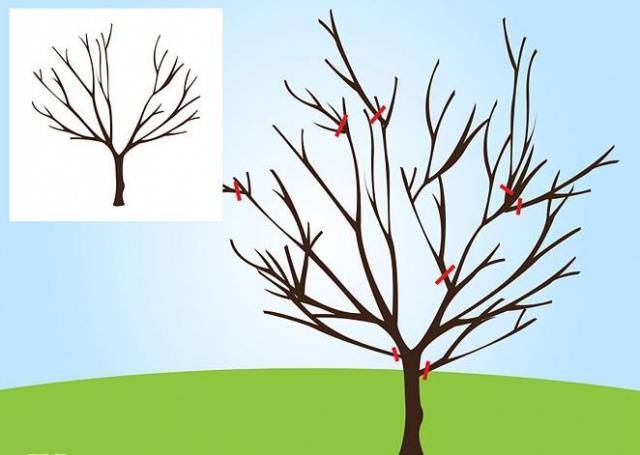
In the regions recommended for cultivation, the Garland variety does not need shelter for the winter. But it needs to be trimmed regularly - formed before the sap begins to flow, sanitation is carried out as necessary.
The trunk is protected from hares by burlap, straw or by installing a special metal mesh.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
Garland cherry variety is moderately susceptible to pest damage. To avoid trouble, you need to find out what insects are attacking crops in your area and carry out preventive spraying with the appropriate insecticides.
Garland almost never gets sick with moniliosis, it will be enough to carry out preventive treatments: in the spring, along the green cone - with copper-containing preparations, in the fall, after leaf fall:
- in the south - copper-containing preparations;
- in the northern regions - iron sulfate.
In places where autumn is long and warm, a third treatment is carried out before the onset of frost - with iron sulfate.
Conclusion
Cherry Garland is a variety that has not yet been appreciated. High self-fertility, excellent yield, compact size and universal purpose berries with a pleasant taste will make it more popular over time.