Content
Compact cherry of the Anthracite variety with dessert-type fruits - medium-late ripening. In spring, a fruit tree will decorate the garden, and in summer it will be convenient to collect fruits from it. Winter hardiness, transportability and average susceptibility to stone fruit diseases make this variety suitable for cultivation in private gardens.
History of selection
For a wide range of gardeners, the Anthracite cherry variety has become available since 2006, when it was included in the State Register and recommended for the central regions of Russia. Employees of the All-Russian Research Institute worked at the experimental station in Orel to develop a productive variety, selecting high-quality material from randomly pollinated seedlings of the Shirpotreb black cherry.
Description of culture
The new variety was bred for cultivation in the regions of the center of the country; its characteristics are suitable for almost all regions.
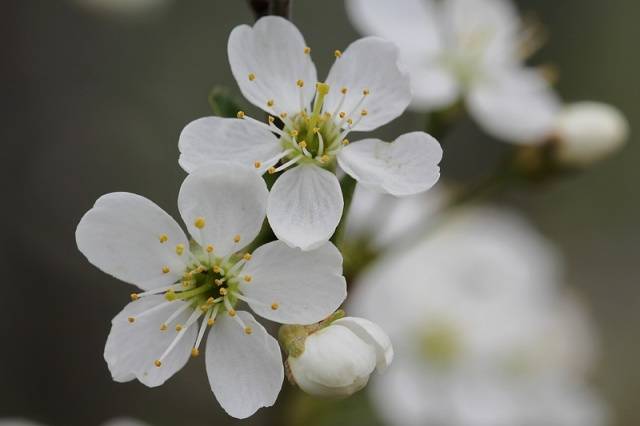
The tree of the common cherry variety Anthracite with a spreading, raised crown grows up to 2 m. The branches are not dense. The cone-shaped buds are small, up to 3 millimeters long, located close to the branch. Dark green, finely serrated leaves up to 6-7 cm long, in the shape of a wide ellipse, the apex is sharp, the base is rounded. The top of the leaf blade is glossy, curved, with veins protruding sharply from below. The petiole is long, up to 12 cm, with a bright anthocyanin hue. The umbrella inflorescence forms 3-5 flowers with white petals, up to 2.3 cm in diameter.
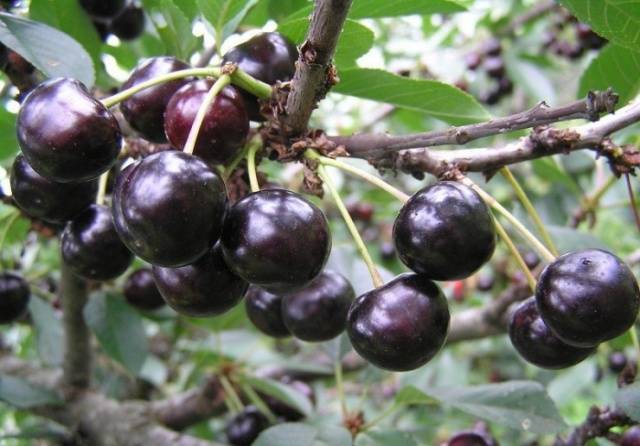
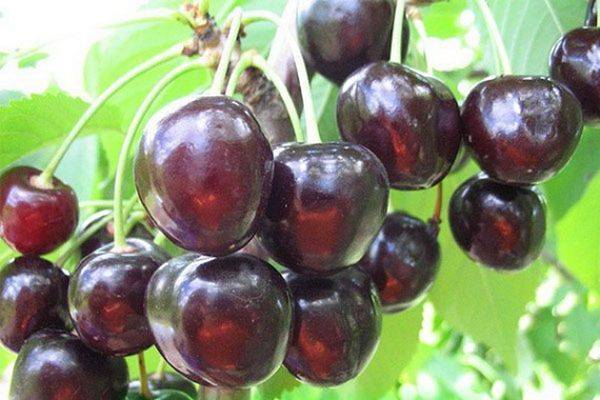
The fruits of the Anthracite cherry are heart-shaped, the fruit funnel is wide, the apex is rounded. The peduncle is short, on average 11 mm. The size of medium berries is 21x16 mm, the thickness of the pulp is 14 mm. The weight of the berries is from 4.1 to 5 g. The skin of the Anthracite cherry variety is dense, but thin, and by the time of ripening it acquires an intense dark red, almost black hue. The rich color of the berries gave the variety its name.
Juicy, sweet and sour cherry pulp Anthracite dark red in color, medium density. The berries contain 11.2% sugars, 1.63% acid and 16.4% dry matter. The yellow-cream seed, which occupies only 5.5% of the berry mass - 0.23 g, is easily separated from the pulp. Based on this characteristic, Anthracite cherries are compared with sweet cherries. The attractiveness of the fruits received a very high score - 4.9 points. The dessert taste of Anthracite cherries is rated 4.3 points.
Characteristics
A distinctive feature of the new variety of sweet cherries with dark fruits is many positive traits inherited from the mother plant.
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
The Anthracite cherry variety tree can withstand the winters typical of central Russia.The Anthracite cherry variety will take root well and bear fruit in the Moscow region. But the plant will not withstand very low, prolonged temperatures.
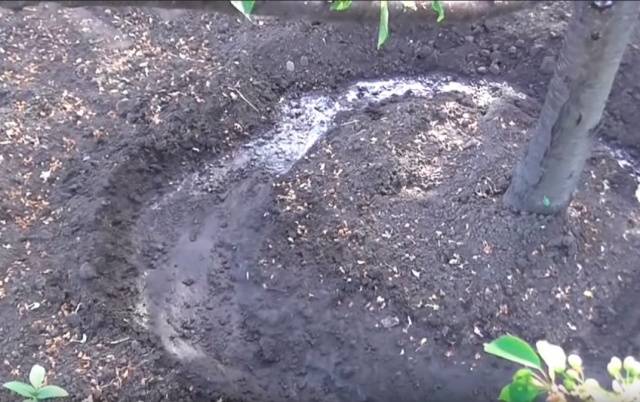
Anthracite is resistant to short-term droughts. To obtain a good harvest, the tree must be watered in a timely manner in grooves made around the circumference of the crown.
Pollination, flowering period and ripening time
A specific feature of the mid-late Anthracite variety is partial self-fertility. Even from a lonely tree you can get a small harvest. The berry picking will be much richer if you plant cherries of such varieties as Vladimirskaya, Nochka, Lyubskaya, Shubinka or Shokoladnitsa nearby. Experienced gardeners also advise placing cherries nearby.
Anthracite cherry blossoms from the middle or end of the second ten days of May. The fruits ripen after July 15-23, depending on climatic conditions.
Productivity, fruiting
Ovaries are formed on bouquet branches and shoots of last year's growth. The tree begins to bear fruit already 4 years after planting. The fragility of the plant should be taken into account: Anthracite cherry bears fruit on average for 15-18 years. Under conditions of good care, timely watering and proper feeding, up to 18 kg of berries ripen on a tree of this variety. During testing, the variety showed an average yield of 96.3 c/ha. The maximum harvest rose to 106.6 c/ha, which indicates the positive production characteristics of the Anthracite cherry variety.
Area of application of berries
Anthracite cherry berries are consumed fresh and processed into various compotes and jams. The fruits are also frozen and dried.
Resistance to diseases and pests
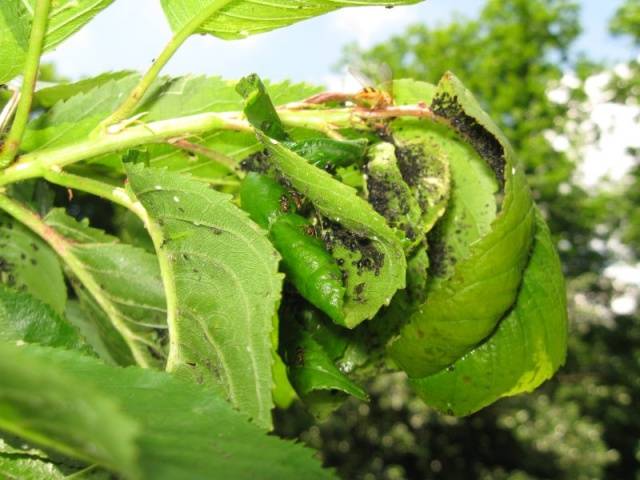
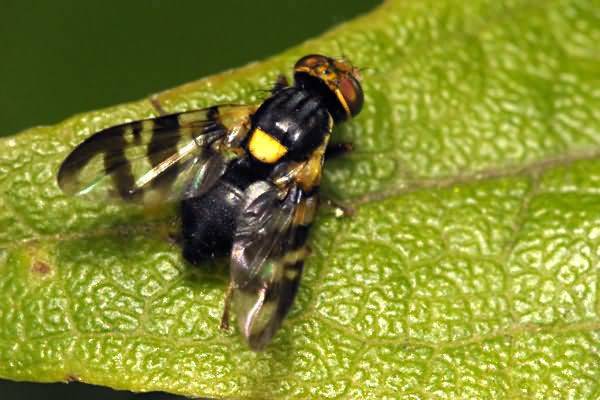
Cherry of the Anthracite variety is moderately affected by moniliosis and coccomycosis. The tree must be inspected during the growing season for early detection of pests: aphids, codling moths, cherry flies.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Anthracite cherry variety has already gained strong popularity in the Central region and is spreading in other areas due to a number of advantages.
- Excellent consumer qualities: beautiful appearance of the berries, thick pulp and pleasant taste;
- Transportability;
- High yield;
- Relative self-fertility;
- Winter hardiness and ability to tolerate short-term droughts.
The disadvantages of the variety are:
- Average immunity to fungal diseases: coccomycosis and monilial burn;
- Susceptibility to pests.
Landing Features
To enjoy the harvest of sweet berries, you need to choose the right place and time for planting Anthracite cherries.
Recommended timing
A seedling with an open root system will take root well only in the spring. Trees in containers are planted until September.
Choosing a suitable location
Placing an Anthracite variety seedling on the south side of buildings is the best option. Avoid places blown by winds.
- Cherries should not be planted in areas with stagnant water or in lowlands. Or placed on a mound;
- Trees develop well on loamy and sandy loam soils with a neutral reaction;
- Heavy soils are improved with sand, peat, humus;
- Acidic soils are diluted with lime.
What crops can and cannot be planted next to cherries?
Cherries or sweet cherries are planted near the Anthracite variety. Good neighbors are hawthorn, rowan, honeysuckle, elderberry, and currants that grow in partial shade.You cannot plant tall apple trees, apricots, linden, birch, and maples nearby. The proximity of raspberries, gooseberries and nightshade crops is undesirable.
Selection and preparation of planting material
High-quality Anthracite cherry seedlings are purchased from specialized farms.
- The best seedlings are two-year-old;
- The standard is not lower than 60 cm;
- Stem thickness 2-2.5 cm;
- Branch length up to 60 cm;
- The roots are elastic, without damage.
Anthracite seedlings are transported from the place of purchase to the site by wrapping the roots in a damp cloth. Then they are immersed in a clay mash for 2-3 hours. You can add a growth stimulator according to the instructions.
Landing algorithm
A peg is driven into the finished hole with the substrate to secure the Anthracite cherry seedling.
- The seedling is placed on a mound, straightening the roots;
- The root collar of the cherry is placed 5-7 cm above the soil surface;
- After watering, add a layer of mulch up to 5-7 cm;
- The branches are cut to 15-20 cm.
Subsequent care of the crop
When growing Anthracite cherries, the soil is loosened to a depth of 7 cm and removed weeds. The cherry tree is watered once a week, 10 liters in the morning and evening. Watering Anthracite cherries after flowering and during fruit set is important.
Feed the tree for 4-5 years of growth:
- In early spring, urea or saltpeter;
- Organic matter is introduced into the flowering phase;
- After collecting the berries, they are fertilized with urea using a foliar method.
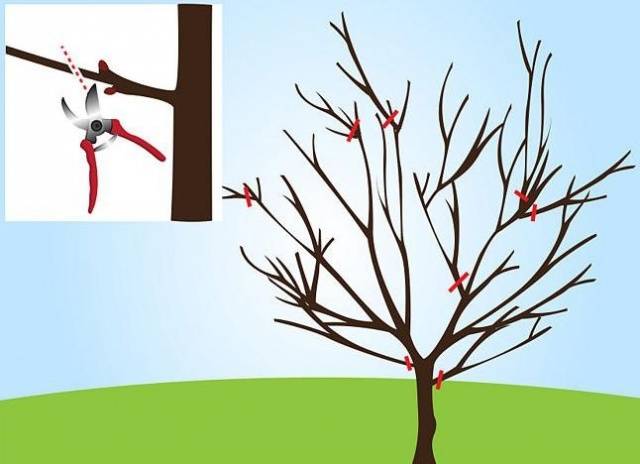
Weak branches that thicken the crown are pruned in early spring.
Before winter, the tree trunk circle is mulched. The trunk of a young tree is protected with several layers of agrotextiles and a rodent net.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
Diseases/pests | Signs | Fighting methods | Prevention |
Moniliosis or monilial burn | Shoots, ovaries and leaves look like burnt | Spraying with copper-containing products in early spring, after flowering, in autumn | Infected branches are removed, fallen leaves and diseased branches are burned |
Coccomycosis | There are red dots on the leaves. Below are grayish clusters of mycelium. The leaves are withering. Infection of branches and fruits | Spraying with fungicides at the end of flowering and after picking berries | Treatment in early spring with Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate |
Aphid | Colonies from the bottom of curled leaves | Treatment in early spring, after flowering, in summer: Inta-Vir, Actellik, Fitoverm | Spraying in spring: Fufanon |
cherry fly | Larvae spoil fruits |
| Treatment after flowering: Fufanon |
Conclusion
Planting this variety is a good choice if you take care of the pollinator tree. A sunny place, watering and fertilizing are important for the quality of the berries. Early treatment will protect the tree from diseases and pests.