Content
Actinidia arguta is a beautiful and quite unpretentious plant. Before planting a crop on a site, you need to carefully study its characteristics.
Description of Actinidia arguta
Acute actinidia, or arguta (Actinidia arguta) is a perennial vine of the Actinidia family. Reaches 30 m in height, the trunk diameter is on average about 15 cm. The vines are covered with light brown bark, the tops of the shoots are herbaceous with reddish hairs. The leaves are round or oval, with a whole or finely toothed edge, shiny and glabrous, located on dark curved petioles.
In June, Actinidia arguta bears greenish-white flowers that emit a pleasant aroma. The buds remain on the shoots for 7-10 days. The fruits of the plant are spherical or cylindrical berries covered with thin dark green skin. The pulp is juicy and tender, with a sour or sugary-sweet taste, reminiscent of figs. The weight of a ripe fruit averages 1.5-10 g.
Under natural conditions, actinidia arguta is found in Japan, Manchuria, Korea, as well as on Sakhalin, Primorye and the Kuril Islands. Grows mainly in dry forests.

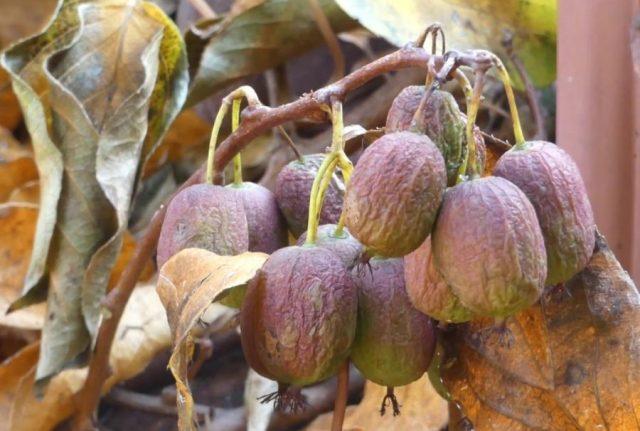
The fruits of Actinidia arguta ripen from late September to late October
Frost resistance of actinidia arguta
Actinidia arguta is a fairly hardy perennial vine. With minimal shelter, the plant can withstand temperatures as low as -30 °C. At the same time, spring frosts pose a great danger to the crop - they can damage flowering and the subsequent harvest.
Advantages and disadvantages
The early-fruiting actinidia arguta has its own advantages and disadvantages when planted on a site. Among the strengths of culture are:
- long life expectancy - about 80-100 years;
- high frost resistance;
- good yield - up to 20 kg of fruits per bush;
- high content of ascorbic acid and other vitamins in berries;
- versatility - the harvest can be consumed fresh or processed into jams, preserves and compotes;
- resistance to diseases and pests.
Actinidia arguta has valuable decorative qualities. During the flowering and fruiting periods, the vine looks attractive on the site.
As for the disadvantages of actinidia arguta, these include:
- small weight and small size of fruits;
- uneven ripening - it is impossible to harvest at one time.
Actinidia arguta begins to bear fruit after an average of 3-4 years of life. Despite good frost resistance, the crop requires insulation for the winter.
The best varieties of actinidia argut with photos and descriptions
Male varieties of Actinidia arguta and female varieties are presented in a wide variety. Before planting a crop on a site, you should study the existing choice.
Pineapple
The domestic variety bears oval fruits with thin green skin. The berries ripen in October and when ripe have a pleasant sour-sweet taste. When cut they release a bright and strong fruity aroma. The variety is frost-resistant and unpretentious.
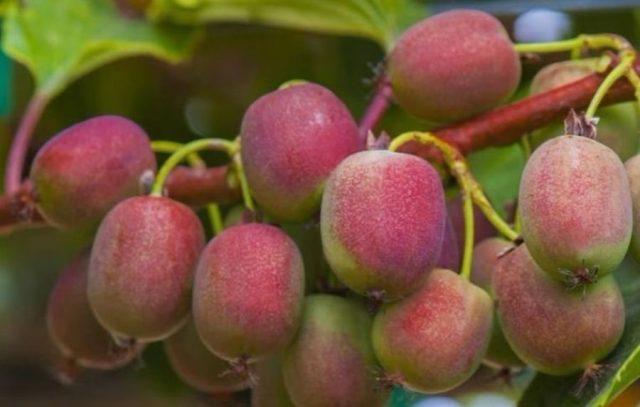

Pineapple actinidia arguta needs regular watering for abundant fruiting.
Viti kiwi
A variety for private and industrial cultivation produces oval green berries with juicy pulp and thin edible skin. A special feature of Actinidia arguta is the small number of seeds inside the fruit. The variety grows quickly, produces stable high yields, and requires annual pruning.

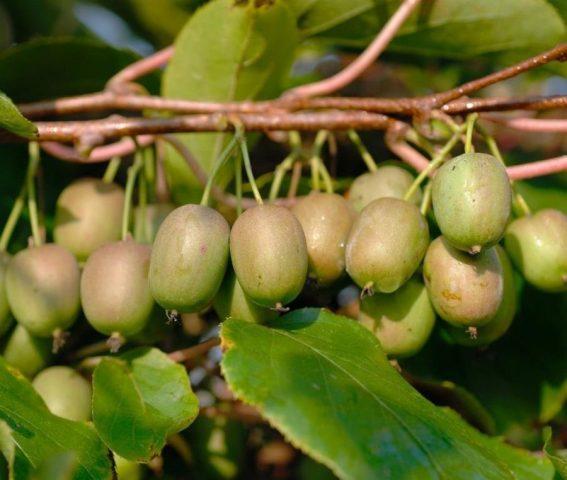
Viti kiwi is a self-fertile variety that does not require pollinators
Weiki
Female actinidia arguta of German selection is characterized by high productivity. It bears green fruits with a bright reddish blush on the sides facing the sun. It requires very simple care and can serve as a pollinator for self-sterile varieties. Performs decorative functions due to beautiful berries and leaves with reddish or purple petioles.
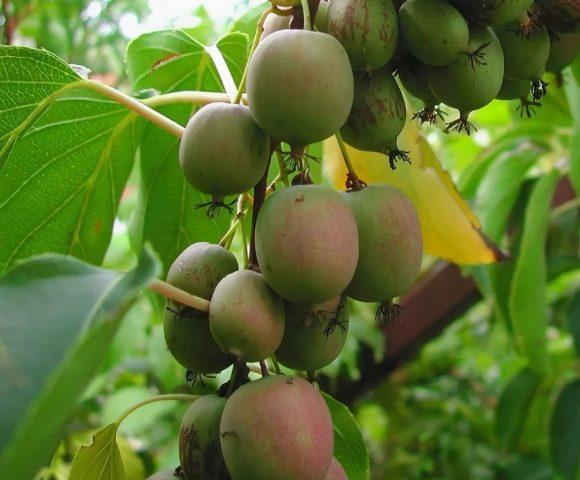

Actinidia arguta Veiki quietly winters at -30 °C
Jumbo
The Italian variety begins to bear fruit for the first time 3-4 years after planting. It produces elongated green or yellowish berries with sweet flesh, and the crop is fully ripe by mid-September. The fruits of the variety are quite large, reaching 6 cm in length. They are well preserved when fresh.
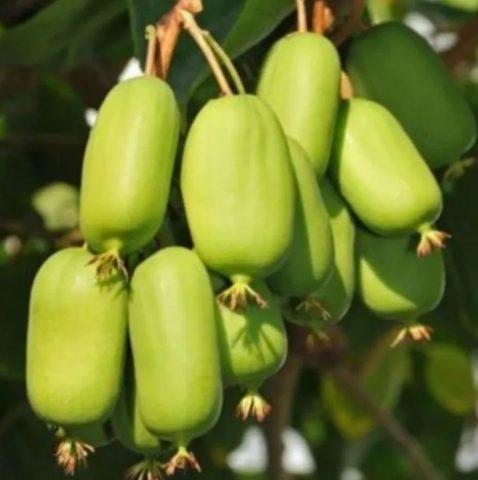

The fruits of Actinidia arguta Jumbo reach an average weight of 30 g
Issei
Actinidia arguta, bred in Japan, bears fruit at the end of September. The fruits are small but tasty, with a sweetish pulp. A special feature of the variety is that the berries begin to ripen a year after planting. The plant is compact, reaching only 3 m in height, ideal for private summer cottages. The variety is capable of self-pollination.
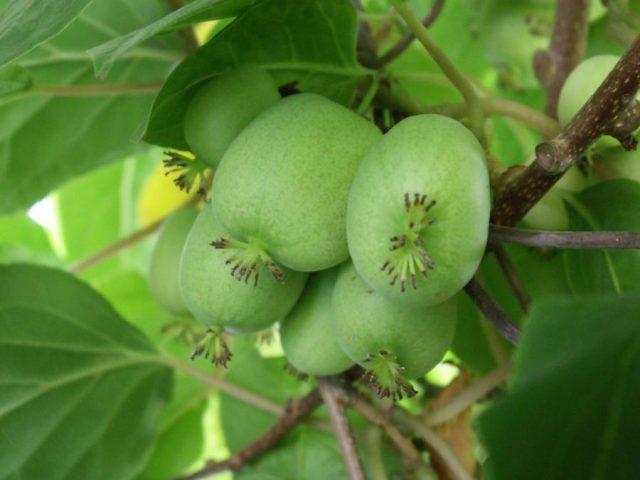

The Issei variety tolerates winter frosts down to -25 °C
Geneva
The popular variety of actinidia arguta ripens in the first half of September. The berries of the crop are round in shape and small in size. The skin of the fruit is initially brown-green, then gradually becomes reddish. Ripe pulp has a bright aroma and honey taste.
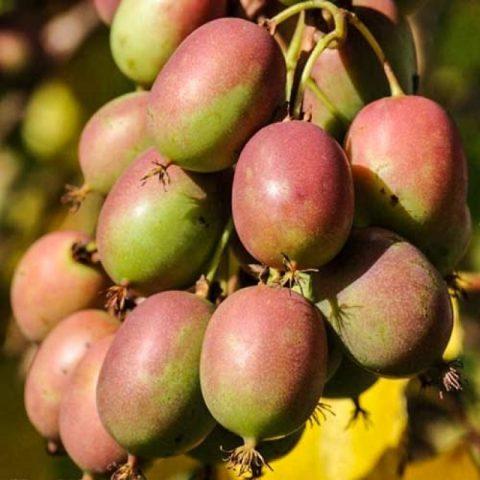

The weight of Actinidia arguta fruits reaches 5-8 g
Kokuwa
The self-pollinating Japanese variety bears small fruits in mid-September. From an adult plant you can harvest up to 10-20 kg of harvest. It is also valued by gardeners for its decorative flowering - the buds of the crop are densely double, creamy-apricot in color, with a dark center. They reach about 8 cm in diameter.
Actinidia arguta grows up to 3-4 m in height. The frost resistance of the variety is not the highest - up to -28 ° C.
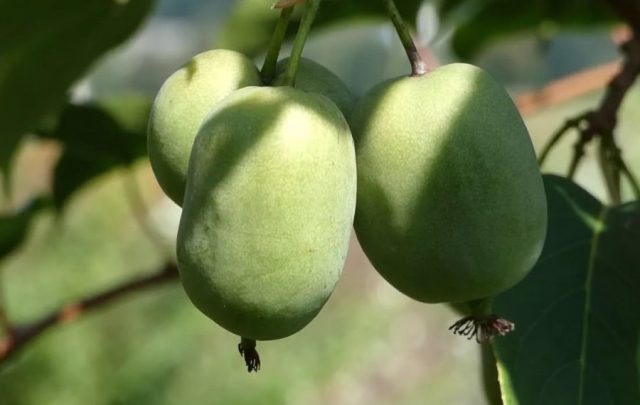

Kokuwa berries have a pleasant lemon aroma
Kens Red
The Actinidia arguta variety was developed in New Zealand. Bears dense, round berries about 4 cm long. The fruits have a good taste, easily withstand transportation and do not wrinkle during storage. The skin of the berries is greenish-red.
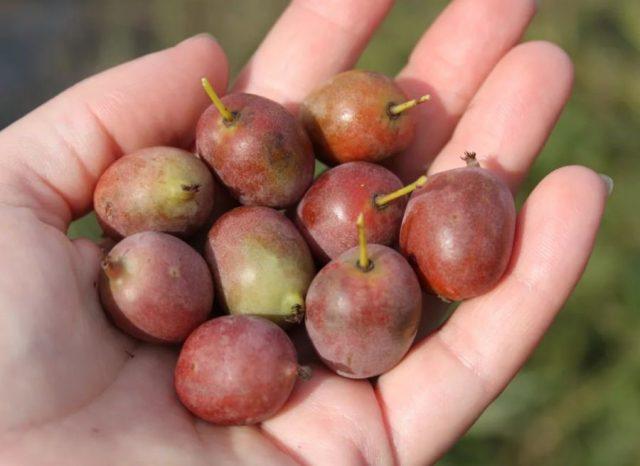

The Kens Red variety is able to winter at -25 ° C without shelter
Purple garden
The Actinidia arguta variety of Ukrainian origin is popular in the CIS countries and Europe. It has an unusual purple coloring of fruits and pulp. The berries taste sweet and sour, very juicy. The fruits are small in size, but with good care the variety produces abundant harvests. Berries need to be picked in early October.
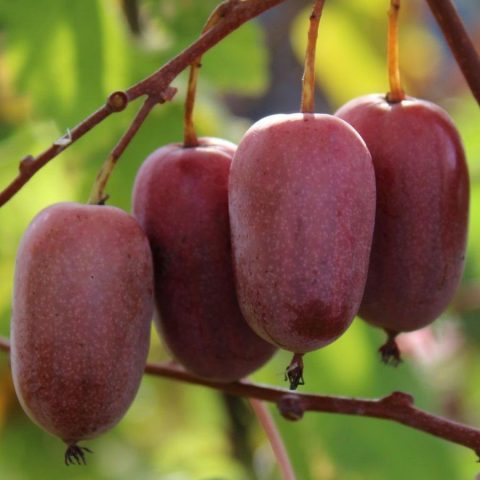

Actinidia Purple Garden produces its first crop in the third year of life
Planting actinidia arguta
During initial cultivation, actinidia arguta is usually sown with seeds. The process is quite labor-intensive and requires increased attention from the gardener. Planting material must first be prepared. They do this as follows:
- At the beginning of December, the seeds are soaked in lukewarm water for several days.
- The grains are removed and placed in damp sand.
- For 3-4 weeks, keep at a temperature of about 20 ° C and, if necessary, re-moisturize.
At the end of December, the container with the seeds is placed in the refrigerator and stratified for 2.5 months. After the expiration of the period, the material is again transferred to heat and wait for the thin roots to hatch.
The container for planting actinidia argut is chosen to be wide but shallow. The nutrient substrate is prepared from turf soil and sand, taken in equal proportions; humus can also be added. The soil and containers are disinfected with boiling water or a solution of potassium permanganate, and then the seeds are sown on the surface of the soil, moistened and covered with film.
After planting the vine, the container is placed in a moderately lit place. At first, the seeds are only ventilated for 20 minutes a day. When the green sprouts hatch, you will need to remove the film and move the container to the sunniest windowsill.
Caring for actinidia argut seedlings mainly involves regular watering.When the seedlings have 3-4 true leaves, they will need to be planted in separate containers.
The crop is moved to open ground in the middle or at the end of May. It is necessary to wait for the end of the return frosts, since actinidia is afraid of spring cold snaps. On a site for perennial vines, choose a slightly shaded place, dig up the soil and make holes in it up to 50 cm deep.
The algorithm for planting actinidia argut in the soil is as follows:
- The holes are filled up to half with a substrate with the addition of humus, sand and wood ash.
- Sprinkle the soil generously with lukewarm water.
- Carefully transfer the seedlings into the ground, trying not to damage the roots.
- Sprinkle with soil and water again.
It is recommended to plant actinidia arguta first in a temporary area. In the fall, grown and strengthened bushes are transferred to a permanent place according to a similar scheme. Leave 2 m of free space between individual plants. The root collar is buried approximately 5 cm.
Caring for actinidia arguta
Actinidia on the site requires attention, but caring for it is generally not difficult and consists of several activities:
- Watering. The crop reacts negatively to both waterlogging and drying out of the soil. The vine should be watered as needed. Typically, water is added to the root of the plant weekly in extreme heat. During the rainy season, watering can be completely abandoned.
- Loosening. In order for actinidia arguta to develop safely and receive enough oxygen, the soil at its roots is regularly weeded and turned to a shallow depth.
- Feeding.Fertilizers for perennial vines are applied to the soil three times a year. In the spring, the plant is fed with ammonium nitrate or urea, and at the time of fruit set and after harvesting - with potassium and phosphorus.
- Garter. To prevent the perennial vine from falling to the ground, trellises are installed next to it and wire or rope is pulled at a height of 50 and 200 cm from the ground. Growing shoots are promptly tied to supports.
In the middle zone and in regions with a harsh climate, attention must also be paid to preparing the crop for winter. With the onset of autumn, the tree trunk circle is cleared of plant debris and the soil is mulched with a thick layer of humus or dry leaves. The shoots are removed from the trellises and placed on a formed “cushion”, and the top is insulated with agrofibre and spruce branches.
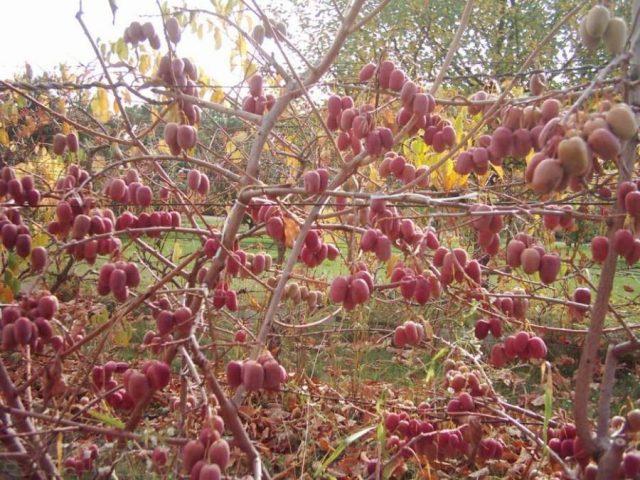

Even frost-resistant varieties of actinidia arguta need to be insulated for the winter up to 4-5 years
Even frost-resistant varieties of actinidia arguta need to be insulated for the winter up to 4-5 years
Pruning actinidia arguta
Actinidia arguta is characterized by very fast growth, so pruning is carried out annually. The procedure is performed only in early spring or late autumn; during the active growing season, the vine cannot be touched.
The first pruning is carried out in the third year after planting. In the process, all broken, dry and barren shoots are removed, and the remaining ones are cut by 1/3 and fixed on a trellis, pointing vertically upward. The following year, the procedure is repeated, the new regrown stems are placed horizontally on supports.
Correctly performed pruning allows you to maintain the decorative appearance of a perennial vine. In addition, the plant does not waste resources on maintaining excess green mass and bears fruit more actively.
Diseases and pests
With proper care, actinidia arguta rarely suffers from illnesses and parasites. But the following may pose a danger to her:
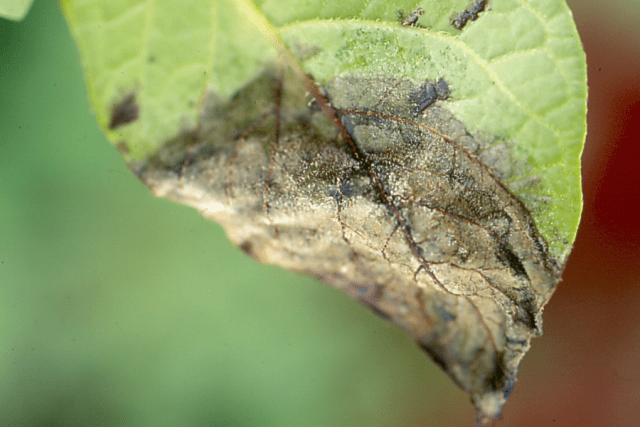
- late blight - the disease affects the roots and neck, the leaves fall off, and the shoot at the base becomes stained and cracks;
Actinidia late blight develops against the background of soil acidification
- gray rot - a whitish “fluffy” coating appears on the surface of young stems and on the plates, the vine begins to soften and rot;
Gray mold is caused by waterlogged soil
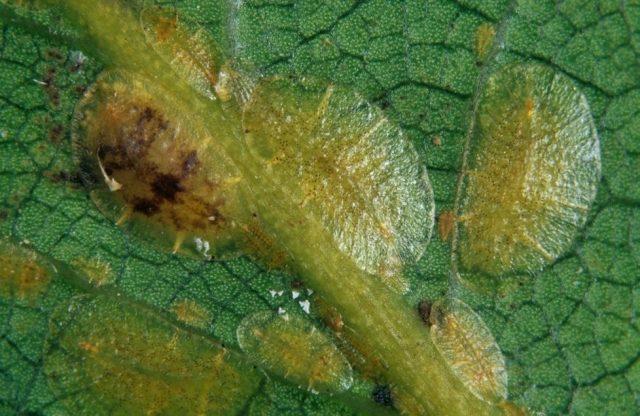
- scale insect - an insect attacks the leaves and shoots of a plant, feeds on juices and interferes with the development of the crop.
Scale insects impair the flowering of actinidia and reduce the volume of fruiting
If there are symptoms of fungal diseases, the plant must be pruned and treated with Bordeaux mixture, XOM or copper sulfate. The drugs Karbofos, Confidor and Mospilan help well against pests. Spraying against parasites is carried out several times a season at intervals of 1-2 weeks.
Reproduction of actinidia arguta
To propagate actinidia, two main methods are used:
- Seminal. It is recommended to grow new varieties through seedlings; planting material is purchased from a trusted supplier. In the spring, after long-term stratification, the grains are sown in a nutrient substrate and the seedlings are cared for in warmth until the beginning of summer. Then the seedlings are transferred to open ground and provided with standard care.
- Cuttings. From an adult healthy bush, several semi-lignified shoots with three buds are cut and the bottom part is placed in water. Then the cuttings are planted in the soil at an angle, moistened and covered with film until rooting. The shoots should be kept at a temperature of about 25 °C.When planting, cuttings should be deepened to one bud. When the shoots begin to grow, they can be moved to a permanent place.
Most often, the vegetative method is used to propagate adult bushes. It is not recommended to grow actinidia arguta from your own seeds, as this will result in the loss of varietal characteristics.
Conclusion
Actinidia arguta is a plant with beautiful flowering and delicious aromatic fruits. Caring for crops on the site is quite easy if you follow the basic rules.
Reviews of actinidia arguta