Content
Powdery mildew is a very common disease that affects many garden crops. These include berry bushes, which include gooseberries. Next we will tell you when it is better to treat gooseberries for powdery mildew in the spring, what preparations are best to use for this and what results this can bring.
Signs of powdery mildew on gooseberries
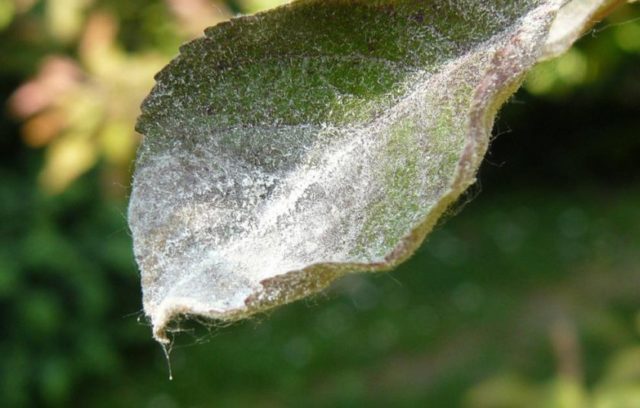
The causative agent of powdery mildew is a fungus that affects all above-ground parts of the plant: shoots, berries, leaves.It usually appears at the beginning of summer, the gooseberry is covered with a white coating, the affected areas look as if they were sprinkled with flour or light ash. Because of this, the disease is often called linen or ashtray. Over time, the plaque darkens, turns brown and acquires a dense structure. The affected shoots stop growing, become deformed and dry out, the leaves become brown, curl and dry out completely, the gooseberries crumble before they have time to ripen, crack or become covered with a white coating and then a dense brown crust.
The photo below shows a white coating of powdery mildew on gooseberry leaves and affected berries.
Over time, the disease progresses, and fungal spores are carried by wind and water to other areas of the bushes and neighboring plantings. If treatment is not taken, the bush will completely die within 2-3 years.
There are 2 types of powdery mildew:
- American (sforoteka). Forms a powdery coating on young leaves and shoots, which over time acquires a felt structure and brown color.
- European. It appears as a cobweb-like thin coating on the leaves. The fruiting bodies of the fungus are small and black. Currently it is very rare, since at the beginning of the last century it was almost universally replaced by American gooseberry powdery mildew.
Signs of gooseberry damage by this fungal disease can be seen by the characteristic white coating, which is easily erased.
Causes of infection and characteristics of spread
Most often, the causes of powdery mildew are unfavorable weather conditions coupled with improper care of shrubs or a complete lack thereof.The development of the disease is facilitated by excessive humidity and dense plantings, the presence of fallen leaves and debris in the root zone. In conditions of difficult air exchange, the fungus develops intensively, gradually spreading throughout the entire above-ground part of the plant.
Another factor that increases the risk of gooseberry disease with powdery mildew is an excess of nitrogen fertilizers or fresh organic matter, manure or chicken droppings, which are used to feed berry bushes. The reverse situation is no less dangerous. If a gooseberry bush grows on poor, unfertilized soil, then the risk of fungus appears increases. Often the disease is a consequence of improper pruning of the bush. If you do it too much, the gooseberry becomes very weak and may get sick.
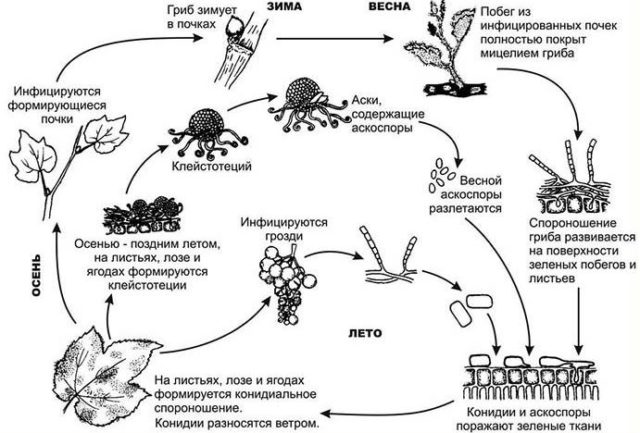
The figure clearly shows 2 stages of fungal development: conidial and marsupial. Conidial sporulation, or mycelium, is the same white powdery coating on the shoots and leaves of gooseberries. After infecting leaves and young shoots, the fungus enters the second phase - marsupial. The brown coating on various parts of the plant is nothing more than mycelium with the fruiting bodies of the fungus. In this form, the fungus goes to winter. In the spring, the sacspores mature and open in the spring along with the blossoming of the leaves. The discarded ascospores infect only young leaves and shoots, berry ovaries, again forming that same white coating.
How to deal with powdery mildew on gooseberries
The best way to combat the disease is prevention. If powdery mildew does appear on gooseberries, then measures must be taken immediately.
Agrotechnical measures to combat powdery mildew on gooseberries
Following correct agricultural practices can prevent gooseberry disease from powdery mildew or stop the disease at an early stage. First of all, this concerns the choice of variety at the planting stage. Among the gooseberry varieties resistant to powdery mildew are the following:
- Harlequin.
- Kolobok.
- Finnish.
- Houghton.
Every spring and autumn, it is necessary to inspect and sanitize the bushes, removing thickening, broken and dry branches, as well as shoots with signs of infection. Fallen leaves in spring and autumn should be completely removed from the root zone and burned or taken out and buried outside the boundary of the site.
How to save gooseberries from powdery mildew using folk remedies
Among the methods of combating this fungal disease there are many folk ones, proven by many generations of gardeners. The following formulations can be used for treatment.
- Infusion of wood ash. 1 kg of ash is soaked in 10 liters of heated water, stirred well and allowed to brew for several days. The resulting ash infusion is filtered, and then gooseberry bushes that have a white coating are treated with it three times, leaving intervals between applications of 2 days.
- Tincture of iodine and whey. To prepare a composition for treating gooseberries, add 1-2 drops of a regular medical iodine solution to 1 liter of whey.
- Soap solution with soda. For 10 liters of water you will need 50 g of laundry soap and 2 tbsp. l. baking soda. Before mixing, it is better to grate the soap into shavings, this will speed up its dissolution.
- Zelenka (alcohol solution of brilliant green). Add 1-2 drops of brilliant green to 10 liters of water.
- Aspirin. 2 tablets of acetylsalicylic acid should be diluted in 3 glasses of water.
- Garlic arrows.To prepare the infusion for spraying, add ½ bucket of fresh garlic arrows with water. Leave for at least 24 hours before use.
- Mustard. 2 tbsp. l. mustard powder is poured into a bucket of boiling water. After mixing and cooling, the composition can be used to spray gooseberries.
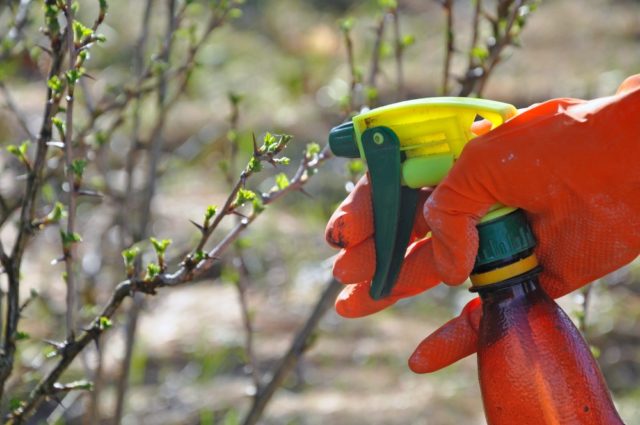
Usually gooseberries are processed in the evening, in dry, cool weather. When spraying, it is very important that the composition also gets on the back side of the leaves. It is advisable to treat the root zone along with the shrub.
How to deal with white plaque on gooseberries with chemicals
Treating gooseberries with chemicals is often the only possible way to save the bush, especially in advanced cases. Traditionally, to combat fungal diseases, gardeners used fungicides - chemical compounds that have a pronounced antifungal effect. Such substances include, for example, copper compounds.
Here are some drugs designed to combat powdery mildew on gooseberries.
- Copper sulfate. A widely used remedy for powdery mildew on gooseberries, it has long been successfully used by many gardeners to combat many fungal diseases. It is a bright blue powder. It dissolves well in water. To prepare a solution for treating gooseberries per 10 liters of water, you need to take 40 g of copper sulfate. To increase the stability of the solution and its wetting ability, 100 g of laundry soap shavings are added to it.
- Topaz. An effective fungicide based on penconazole.The mechanism of action of this drug is to inhibit fungal spores; under the influence of penconazole, they completely stop growing. The drug penetrates perfectly into plant tissue, its effectiveness does not depend on air temperature and humidity.
- Home. This is nothing more than an abbreviation for the words “copper oxychloride.” An effective fungicide, almost a complete analogue of the famous Bordeaux mixture - a solution of copper sulfate in lime milk. Sold dry. Before use, the mixture is diluted in water in the required proportion. It is easily washed off with water, so the treatment is not carried out in cloudy weather.
- Fundazol. A benomyl-based fungicide that inhibits not only fungi, but also some insect pests, such as spider mites. The drug is non-toxic and is well absorbed by all parts of the plant. Can be used to process gooseberries at different temperatures.
- Vectra. The basis of the drug is a mixture of dichlorophenyl and triazole. Effective against many fungal diseases, stops the growth of pathogens. Non-toxic, does not have a negative effect on plants and animals. Quickly absorbed by any tissue and spread to all parts of the bush
Gardeners often use a solution of colloidal sulfur against powdery mildew. For 10 liters of water you need 70-80 g of sulfur. It is necessary to use the solution for processing gooseberries only in freshly prepared form; it is not stored for a long time. It should also not be used in combination with other drugs.
How to cure gooseberries from powdery mildew with biological products
The action of biological products against powdery mildew is based on microorganisms that themselves or in the process of vital activity inhibit pathogenic fungi, suppress their growth, and prevent reproduction. Unlike chemicals, they are absolutely harmless to plants and animals; they can be used even while the berries are ripening. The disadvantage of biological products is that they have a rather short duration of action; after about 2 weeks their activity decreases sharply. Therefore, it is recommended to repeat the treatment monthly. Biological products include:
- Gaupsin.
- Trichodermin.
- Fitosporin.
Rules for combating powdery mildew on gooseberries
Before processing gooseberries, the bushes must be cleared of diseased and dried shoots, pick off rotten berries, remove fallen leaves, debris and weeds from the root zone. All drugs must be diluted strictly according to the instructions, strictly observing the prescribed dosages. If signs of the disease are detected early, it is necessary to use the most gentle, traditional methods. After this, it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of using a particular drug. If the disease continues to progress, it is necessary to move on to more radical methods based on the use of biological products or fungicides.
It is better to start treating gooseberries against powdery mildew in early spring. At this stage, before the buds open, it is necessary to spray the bushes with a solution of copper sulfate. Not only the shoots should be treated, but also the soil in the root zone.Repeated treatment is carried out after flowering. The third time the gooseberry bushes are sprayed after harvesting, without waiting for the leaves to fall off. Such treatments are preventive. If spraying is carried out for medicinal purposes, then use drugs that are most suitable for the degree of damage and the period of vegetative development of the gooseberry.
Educational video about methods of treating powdery mildew on gooseberries:
Prevention measures
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of powdery mildew appearing on gooseberry bushes. Such measures include the following:
- Avoiding dense plantings. It is imperative to maintain intervals between neighboring bushes (at least 1.5 m) and remove thickening shoots.
- Spring treatment of gooseberries against powdery mildew with boiling water. In early spring, before the start of the growing season, the bushes need to be scalded with very hot water in which a small amount of potassium permanganate or a few spoons of soda is diluted. The measure is effective both against pathogens of fungal diseases and against pests whose larvae overwinter in folds and cracks of the bark.
- Sanitary reading. Every year, in early spring and autumn, it is necessary to remove dry, broken and damaged branches, as well as remove fallen leaves from the root zone.
- Installation of bush fencing. The bushes should not be allowed to “fall apart” and their shoots to touch the ground.
- Spraying. Preventive treatment can be carried out not only with a solution of copper sulfate. You can use an infusion of mullein, ash or soda ash.
- Avoid using fresh organic fertilizers. Manure and chicken droppings contain a large amount of nitrogen, which provokes the development of powdery mildew on gooseberries.
The more carefully preventive measures are carried out, the less likely it is that powdery mildew will appear on gooseberry bushes. And even if powdery mildew does appear on the gooseberries, it is much easier to cure well-groomed bushes and you do not have to use serious pesticides.
Gooseberry varieties resistant to powdery mildew
When choosing a gooseberry variety, you should pay attention to varieties that are resistant to powdery mildew. Although there is no complete immunity from this disease, some representatives of these berry bushes are affected by the disease much less frequently. These include the following gooseberry varieties:
- Ural grapes.
- Beryl.
- Firework.
- Ural emerald.
- Kolobok.
- Commander.
Conclusion
Treating gooseberries against powdery mildew in the spring means protecting your future harvest. Even if the appearance of the disease was not registered in the past season, this procedure should not be neglected. This can significantly reduce the likelihood of the disease occurring, and if the entire range of preventive measures is carried out in a timely manner, it can be eliminated completely.