Content
Oyster mushrooms are quite resistant to diseases and pests. It is for their unpretentiousness that mushroom growers value them. However, even with them problems arise during artificial cultivation. It happens that oyster mushrooms turn yellow, and also dry out and crack. Most often, the reasons are errors in care, the appearance of disease or attack by pests.
Why do oyster mushrooms turn yellow?
This can happen to oyster mushrooms at any time, regardless of the stage of cultivation. They may turn yellow for the following reasons:
- increased humidity in the room;
- too dry air;
- poor ventilation;
- drafts;
- pests;
- illness;
- sudden changes in air humidity.
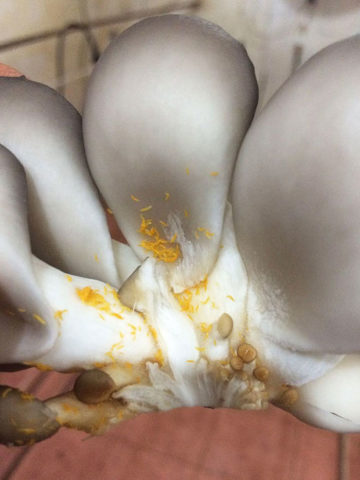
The color of the caps may become uneven. The appearance of yellow spots is due to the following factors:
- poor substrate;
- fungal or bacterial disease;
- the inability to evaporate drops of water falling on oyster mushrooms during watering or at high air humidity.
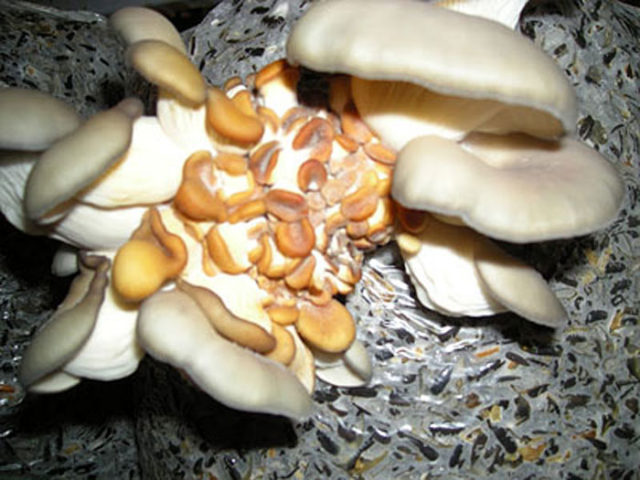

Yellowing of fruit bodies
What to do if oyster mushrooms turn yellow
First of all, you need to find out the reasons for this phenomenon. It is impossible to control the microclimate in the mycelium by eye, so you need to purchase a special device that will help maintain optimal humidity.
If oyster mushrooms are covered with a yellowish coating, then most likely the humidity is too high.
If the caps not only turn yellow, but dry out and crack, and the legs darken, then this indicates too dry air.
If the humidity is normal, but there are yellowish spots on the oyster mushrooms, this means that there is no ventilation or it is not working well.
Cracks can appear due to drafts, so it is important that the ventilation system does not create them. Air flows should not go at the level of growth of oyster mushrooms; their path should be directed higher and lower.
To rule out infections, you need to pick the fruiting body and do an analysis to identify the pathogen. Microorganisms may be present in the substrate, so it needs to be checked. If a pest is detected, it must be treated together with oyster mushrooms with special preparations.
Other oyster mushroom diseases and their elimination
There are other diseases of oyster mushrooms that can cause them to turn yellow. The mushroom picker must understand them well.
Bacteriosis
Oyster mushrooms may turn yellow due to bacteriosis. They are not exposed to this disease very often. This usually happens in the warm season, when the air temperature is quite high and the humidity is high. A symptom of this disease is the appearance of spots on the surface of the fruiting body, the color of which varies from beige to rusty brown. Gradually their surface becomes covered with mucus.
The cause of the disease is a bacterial infection caused by Pseudomonas tolaasii. The pathogen can enter the fruiting body from the soil.You need to pay attention to the following signs:
- yellow dots and spots are slippery when touched with your hands;
- the spots do not have clear edges;
- when pressed, the pulp is cottony and falls through;
- A very unpleasant odor emanates from the fruiting bodies.
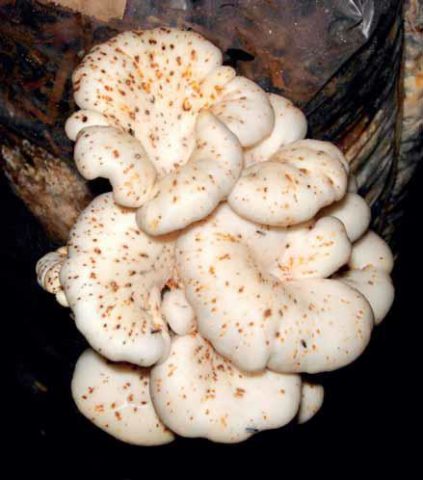

Bacteriosis of oyster mushrooms makes them unsuitable for use
It is impossible to accurately determine the presence of the disease and its causative agent by eye; it is necessary to conduct a laboratory analysis that will help identify it. If the infectious agent is not detected, then it is not bacteriosis.
If the red spots have clearly defined boundaries, then this is not a bacterial infection. Dots and small specks (less than 1 mm) of a rusty, brownish-red color are damage caused by flying insects or larvae located in the substrate.
If the spots are single and larger in size (from 2 to 3 mm), then these may be traces of drops of condensation or water that fell on the fruiting bodies during watering.
If the problem is in the soil, it is useless to treat oyster mushrooms. A mushroom infected with a bacterial infection emits an unpleasant odor and becomes overgrown with spots. Diseased bunches need to be picked and destroyed.
If oyster mushrooms are frequently affected by bacteriosis, it is recommended to add calcium chloride to the substrate.
Parasites
If the fruiting bodies turn yellow, this may be caused by fungus gnats, midges and other pests. The mushroom specialist usually does not notice the parasites themselves: he does not pay attention to the solitary flying midges, and the larvae are located inside the mushrooms.
Fungus gnats are especially dangerous, as they significantly reduce the quality of mushrooms and the yield. Oyster mushrooms most often harbor sciarids. Their females lay eggs in the substrate under the film next to the perforation. The larvae that emerge from them feed on the mycelium.The development cycle of mosquitoes is shortened at high temperatures and lengthened at lower temperatures. Mature individuals do not fly far from blocks with substrate and, after mating, lay eggs again under the film.
Fungus midge larvae
In case of mass infection, they are capable of completely destroying the rudiments of fungi. In addition, sciarids can be carriers of diseases and other pests.
If the mushroom has shriveled and begun to turn yellow, you need to remove it from the substrate and examine the root under a magnifying glass. You can detect the passages made by pests and the larvae of midges or fungus gnats themselves. Outwardly, they look like orange, white or pink worms.
Rusty spots scattered over the surface of the fruiting body may also indicate the presence of larvae.
It is necessary to combat mosquitoes and midges by treating the room where mushrooms are grown with products such as Fastak, Arrivo, Decis Lux, which belong to the pyrethroid group, as well as preparations based on organophosphorus compounds, for example, Nurel. To destroy the larvae, insecticides are added to the substrate while feeding the mycelium.
Prevention of oyster mushroom diseases
First of all, it is necessary to create optimal climatic conditions.
The growing room must be well insulated so that condensation does not form on the walls and other microorganisms cannot grow on the ceiling.
It is necessary to carry out sanitary and hygienic measures, that is, maintain cleanliness and control the development of diseases and the appearance of pests.The floor and walls in the room, as well as equipment and tools should be washed and disinfected.
For prevention, treatment is carried out with such preparations as bleach solution, “Whiteness”, chloramine, hydrogen peroxide and others. It is recommended to strictly adhere to the instructions when using them and periodically change the products to avoid harmful microorganisms becoming accustomed to them. It is advisable that the floor and walls be smooth: this makes them easier to clean before proceeding with disinfection.

One of the most effective broad-spectrum drugs, directed against bacteria, viruses, fungi
When working with chemicals, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment: an apron or gown, boots, gloves, goggles, a hat, a respirator.
Often the source of fungal infection is the covering soil, which must be treated with steam and formaldehyde. Materials for its preparation must be stored correctly - in uncontaminated places.
To prevent fungus gnats, insecticides are used to spray growing rooms.
To prevent larvae from hatching from the eggs of harmful insects laid in the substrate, drugs that block the synthesis of chitin (Dimilin, Fetoverm) are added to it.
Conclusion
If the oyster mushroom turns yellow, it is necessary to find out the reasons for the phenomenon. To prevent this from happening, it is important to initially create the right conditions for the mushrooms and carry out preventive measures to treat the room and growing environment.








