Content
Catatelasma inflated is a fungus of Far Eastern origin. A fairly large representative of its kingdom, noticeable from afar in the forest when collected. It has good taste and versatility in preparation. Virtually odorless. It has several counterparts with a common habitat.
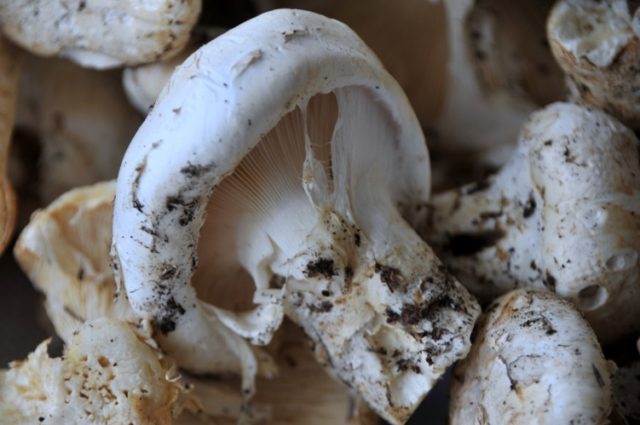

The fruiting bodies of catatelasma inflated are similar to ordinary store-bought champignons.
Where does catatelasma inflata grow?
The main habitat of this species is in the coniferous and mixed forests of the Far East. It has been noticed that mycorrhiza catatelasma inflated forms more often with coniferous trees. There is evidence of the discovery of the species in North America (the mycelium was found once) and Europe.In the latter case, facts of its discovery were repeatedly recorded in Germany and France.
What does Sakhalin champignon look like?
At the beginning of life, the fruiting body is hidden under a common blanket that has a brownish tint. During the growth process, it breaks at the point of contact with the cap. But even after rupture, the veil protects the hymenophore for a long time.
The cap has a diameter from 8 to 30 cm. At the beginning of the life cycle it is round, then convex. Old mushrooms have a flat cap. The hymenophore is lamellar, extremely thick.

Young mushrooms with an unbroken veil are similar to ordinary champignons
The leg dimensions can reach up to 17 cm in length and 5 cm in diameter. At the base it is traditionally narrowed, but in the middle it has a pronounced convexity. Most of the stem is located underground, so when collecting the fruiting body you have to dig up a little. The ring remains for quite a long period. Sometimes it does not fall off throughout the existence of the fruiting body.
The swollen flesh of catatelasma resembles ordinary champignons in consistency and taste.
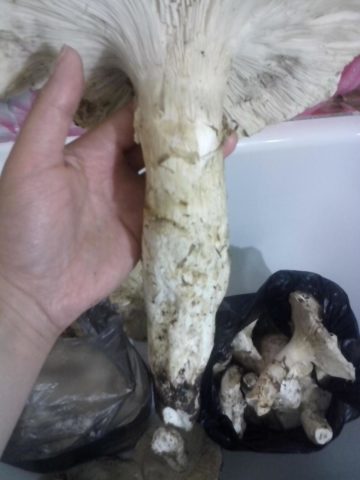
The size of catatelasma inflated can be quite impressive.
Is it possible to eat catatelasma bloated?
This species is a high quality edible mushroom. Due to its fairly high unpretentiousness, it is grown industrially in a number of countries.
False doubles
All counterparts of the Sakhalin champignon are edible. In addition, they have divergent habitats. Therefore, although confusion in determining species identity will arise, it will not lead to critical consequences. The doubles of catatelasma inflata are discussed below.
Imperial champignon
Has slight differences in the smell and color of the cap.In Sakhalin it has a white tint, which shrinks and cracks with age. The imperial cap is yellow, later turning brown. No cracking is observed.
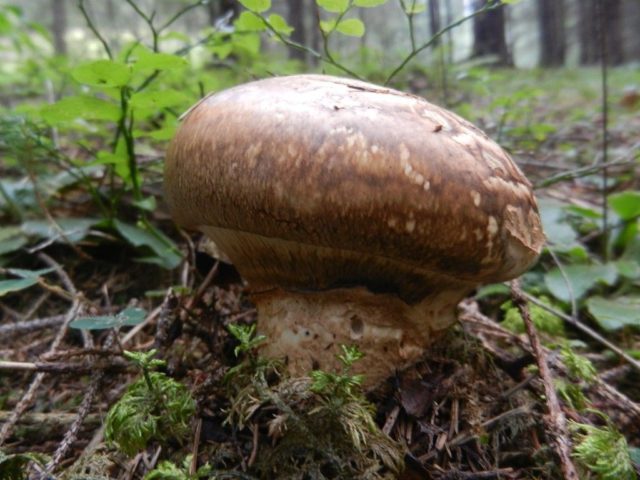

The brown cap of the imperial champignon has no signs of aging
The difference in smell is actually negligible. The Sakhalin champignon has a faint mushroom smell, and the aroma of the imperial champignon contains slight floury notes. It is not easy to distinguish these species using the sense of smell, but with enough experience it can be done almost immediately.
Matsutake
Another double of catatelasma bloated. Its name translates from Japanese as “pine mushroom.” This is true, since this type of mycorrhiza occurs exclusively on coniferous trees.
Main differences from Sakhalin champignon:
- the cap is brown throughout the life of the fruiting body;
- the pulp is white, with a strong spicy odor;
- long dark brown leg of equal thickness.
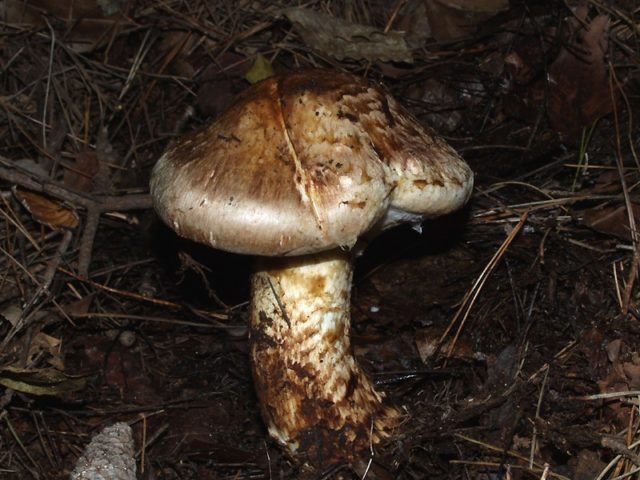

Often the matsutake cap cracks at the edges and its flesh becomes visible.
This twin grows at the foot of trees; it needs thick roots for symbiosis. The fruiting bodies are small, hidden under a thick layer of foliage. It is much more widespread than catatelasma bloat. It can be found in Japan, China, Korea, and North America. Among all conifers, matsutake prefers pine trees, but in their absence, the mycelium can also enter into symbiosis with fir and spruce.
It is of increased value for oriental cuisine. In the countries of the Western Pacific region it is in great demand among gourmets.
Rules for collection and use
Collection is carried out from early summer to mid-autumn. It is recommended to collect young fruiting bodies, since old ones become too elastic and are even difficult to cut with a knife.
Universal use: swollen catatelasma is boiled, stewed, fried, pickled. Drying and freezing are allowed.
Conclusion
Growing in the forests of the Far East, catatelasma inflated is a tasty mushroom from the Tricholomov family. The distinctive features of this type are good taste and the absence of an unpleasant odor, which explains its popularity among consumers. The mushroom grows throughout the summer and most of the fall.








