Content
An apple tree cannot be called a tree that is very susceptible to fungal and other diseases, but it is not completely immune from them. One of the most dangerous is cytosporosis of apple trees. If nothing is done, the tree will certainly die. It is difficult to cope with the disease, even using “heavy artillery” in the form of modern agrochemicals. Therefore, it is highly recommended to regularly devote some time and effort to its prevention.
Description and photo of cytosporosis
Cytosporosis is a disease from the category of necrosis-cancer, which develops as a result of the penetration of fungi from the genus Cytospora into the tissue of a tree (this is where the name comes from). Apple trees, along with pears, peaches and apricots, suffer from it most often. Although other fruit trees, both stone fruits and pome trees, are not immune from infection with cytosporosis.
In a special risk group are “weakened” trees with “suppressed” immunity. Most often, cytosporosis affects apple trees that have suffered from drought, severe winter frosts, or sunburn. Also, the cause may be illiterate or untimely pruning or other mechanical damage.
During its life, the fungus that causes cytosporosis releases toxins that “poison” the tree. The bark is the first to suffer: it dries out and the texture becomes unnaturally spongy or foamy. Then it darkens to a black-brown hue and dies. After this, cytosporosis “spreads” to the wood.
The disease develops quite quickly. The first characteristic symptoms appear already at the flowering stage or a little later (in the first half of June). However, it is difficult to notice them - so far only small “tubercles” on the bark indicate infection with cytosporosis.
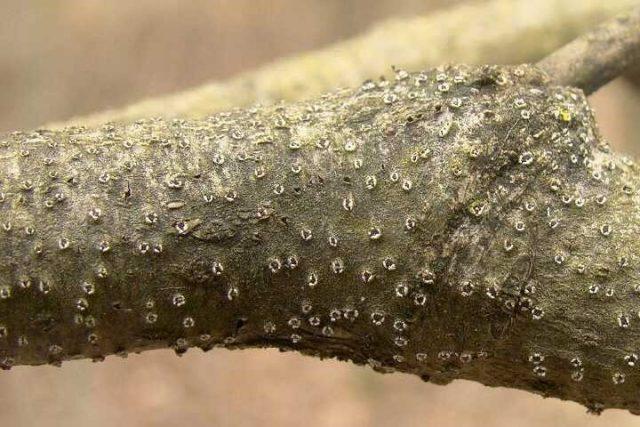

The containers for developing spores are sometimes called “goose bumps.”
Soon the signs of the disease become more obvious: the flowers dry out, the petals change their color to rusty brown, but do not fall off the tree. Brick-red (less often copper-green) spots appear on the bark, covered with ugly “swellings” resembling tumors, consisting of individual “pads”. They quickly increase in size, “girdling” the shoots and trunk.

Cytosporosis spots on apple trees in severe cases turn into “ulcers” or “scabs” with a cracked surface
Causes of infection
Spores of the fungus that causes cytosporosis are carried by wind and insects. The gardener himself can provoke infection of apple trees and other fruit trees by transferring pathogenic microflora on tools, gloves, and clothing that have not been disinfected.
For the spores of the fungus that causes cytosporosis to penetrate into tissues, any minor mechanical damage, including microcracks, is sufficient. The following factors contribute to the activation of the pathogen:
- long-term heat;
- frequent and heavy rains, providing increased soil and air humidity;
- “poor” substrate that does not contain enough macro- and microelements and other substances necessary for the normal development of the apple tree;
- “massive” insect attacks;
- “abandonment” of an apple tree by a gardener.
Consequences
Apple tree cytosporosis can occur in two “scenarios”:
- Almost instantaneous development. The pathogen infects the trunk or main skeletal branches of the tree. The apple tree dies within 1-2 months from the moment of infection. Less often, it is able to “stretch” until the end of the active growing season.
- Gradual, rather long infection. The process of death of an apple tree from cytosporosis lasts for a year or more. The fungus consistently attacks small branches and moves through the “vessels” of the sap flow system into the tissue of skeletal shoots.
However, in both cases, if nothing is done, the tree will inevitably die. Due to “global” changes in the texture of the bark during cytosporosis of the apple tree, it practically loses its ability to pass juice.

Not only the infected branch, but also the entire part of the crown suffers from a deficiency of nutrients “pulled” by the roots from the soil.
Methods for treating apple cytosporosis
Cytosporosis is very difficult to treat.It is difficult to notice the disease at an early stage of development, and in severe cases, success is not guaranteed, even with the use of modern antifungal agrochemicals, not to mention biological products and folk remedies.
Chemicals
Having detected signs of cytosporosis on an apple tree, the tree and the soil in the tree trunk circle are sprayed with a solution of fungicides. The drug is selected depending on the stage of the active growing season. Many chemicals are prohibited for use during flowering and shortly before fruit harvest. However, the situation often develops in such a way that it is necessary to sacrifice the current season’s harvest in order to cure the apple tree from cytosporosis.
To combat the disease, gardeners use:
- copper sulfate;
- Bordeaux mixture;
- HOM;
- Topsin-M;
- Horus;
- Alirin-B;
- Baktofit;
- Topaz;
- Fitosporin-M;
- Abiga Peak.

Copper compounds are “killer” for any pathogenic fungal microflora
Another option for combating cytosporosis on the trunk of an apple tree is to entrust it to professionals. Using special equipment, they “pump” an antifungal composition based on zinc sulfate and boric acid under the bark.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies against cytosporosis on apple trees are ineffective even in the early stages of the disease. However, they can be used for prevention throughout the season. Solutions have antiseptic antifungal properties:
- potassium permanganate (bright pink);
- baking soda or soda ash (25-30 g/l);
- fermented milk products in combination with iodine (100 ml and ten drops per liter of water).

Potassium permanganate is an effective antifungal agent available to any gardener
Agrotechnical methods
Treatment of an apple tree for cytosporosis using an agrotechnical method involves radical pruning of the tree and removal of all its parts affected by the disease. In this case, you need to capture another 3-4 cm of tissue that looks healthy: in most cases, the fungus managed to penetrate there too, it just hasn’t manifested itself outwardly yet.
Small branches of an apple tree with signs of cytosporosis are immediately cut into rings. The same is done with any shoots that are “girdled” around with “tumors” characteristic of the disease. They also get rid of all branches that show signs of damage to the layers of tissue under the bark - cambium and wood.
If the shoots are partially damaged, you can try to save them. All areas of the apple tree bark affected by cytosporosis are cut off, also capturing 3-4 cm of healthy tissue around the perimeter.
The resulting “wounds” are washed with a 3% solution of copper sulfate (30 g/l) or 5% solution of iron sulfate (50 g/l). Any modern fungicides will do. Then the sections are “covered” with garden varnish.
When cytosporosis on the branches of an apple tree is noticed at an early stage, you can try to do without pruning. Areas covered with characteristic “bumps” are generously sprayed with copper naphthenate (a mixture of copper sulfate, rosin and kerosene in a ratio of 3:1:1) or applied with a brush. After this, several treatments with fungicides are carried out.
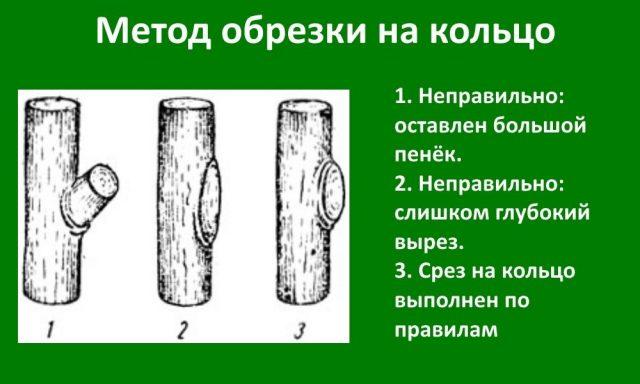
Improperly cut branches can be another factor that negatively affects the condition of the tree.
Prevention measures
Preventing infection of an apple tree with cytosporosis is immeasurably easier than curing the tree. Accordingly, it is obvious that prevention in this case becomes extremely important.
Simple measures:
- Regular sanitary pruning of the apple tree twice a year. Trees also need formative and rejuvenating pruning as needed. “Wounds” must be disinfected, washed with a solution of any fungicide, and covered with garden varnish.
- Timely treatment of all mechanical damage.
- Keeping the tree trunk clean. The causative agent of cytosporosis successfully overwinters in plant debris under an apple tree.
- Timely application of fertilizers. “Saturation” of the soil with the macro- and microelements necessary for the apple tree ensures its normal development, increases immunity and overall endurance.
- Preventive treatment of apple trees and soil in the trunk circle with fungicides. Spraying against fungal diseases, including cytosporosis, must be carried out in early spring and mid-autumn. During the season, the treatment is repeated if signs of cytosporosis are detected in neighboring garden plots or other fruit trees.
- Disinfection of garden tools after any work.
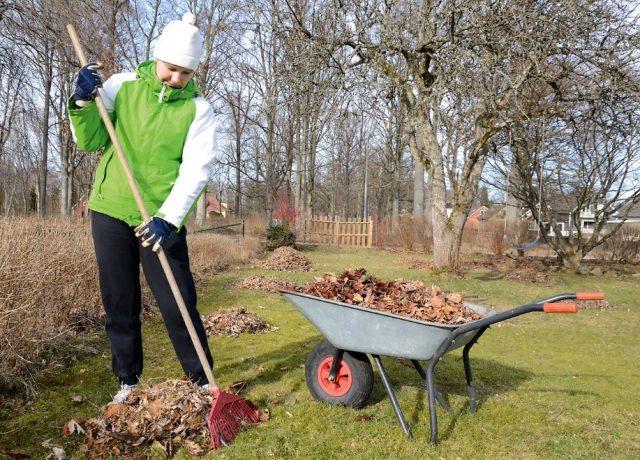

In addition to autumn cleaning, regular weeding is necessary - insects that carry spores of the fungus that causes cytosporosis of apple trees often settle on the weeds
Conclusion
Apple tree cytosporosis is an extremely dangerous and often tree-killing disease from the category of necrosis-cancer, treatable only in the early stages of development. In order not to have to think about how to save the apple tree, it is better to reduce the risk of infection with cytosporosis in advance by providing the tree with high-quality care and not forgetting about simple prevention.








