Content
Frost cracks on apple trees and other fruit trees are also called frost cracks and frost cracks. Such damage to the bark violates the integrity of the trunk, increases the risk of crop diseases, and can lead to the death of the plant. They cannot be left without treatment; it is carried out in different ways.
What is a frost blaster?
Damage to the wood of trunks is called frost damage. This is a radial crack that can be open or closed. In addition to frost holes, swellings or ridges often appear. The length of the lesion can affect a significant part of the trunk, and the depth can reach the core.
The appearance of frost holes is accompanied by a strong cracking sound. When the temperature rises again, the previously compressed outer layers return to their original volume. As a result, the frost trap closes tightly. In summer it is difficult to detect.
Why do frost holes appear?
The main reason for the appearance of frost holes is sudden cooling. Wood is deformed in several directions, the difference between which is significant. This provokes critical tension and tissue rupture. The process is facilitated by water in the central part of the trunk, which expands when frozen.
The reason for the appearance of frost holes is also called the temperature difference in the central and peripheral parts of the trunk. This happens when it gets very cold. The outer layers of wood shrink more than the inner layers due to cooling.
Why are frost breakers dangerous?
It is necessary to treat frost damage on apple trees and other fruit trees. The appearance of cracks is fraught with the following consequences:
- premature aging of wood;
- decrease in yield;
- increased risk of trunk damage by fungi and pathogenic microorganisms;
- damage by pests that settle under exfoliated bark;
- core rot of the trunk with an open crack;
- violation of the conductivity of moisture and nutrients.
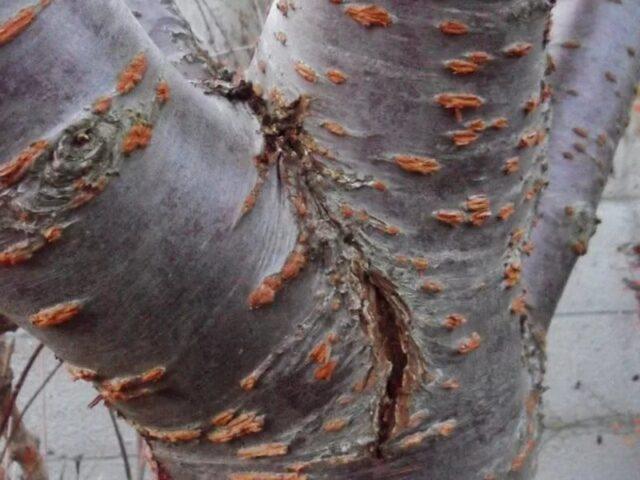

Frost holes usually appear on the south side of the trunk, where the temperature difference due to the daytime sun is more pronounced
On which trees do they most often occur?
Frost damage occurs more often on stone fruit and pome fruit trees. In the garden they suffer:
- apple trees;
- pears;
- plums;
- cherries;
- apricots;
- cherries.
How to treat frost damage on fruit trees
Treatment of frost damage on pear, apple and other fruit trees begins in the spring immediately after detection. The process is not interrupted until the crack is completely healed.
Treatment begins with stripping the frostbite down to healthy tissue.The instrument must be disinfected before and after treatment. Dead bark is removed. When the frost wound dries out, it needs to be treated with a fungicide. The following compositions are suitable:
- potassium permanganate solution (potassium permanganate);
- Bordeaux mixture (3%);
- inkstone;
- copper sulfate (5% solution).
For treating apple trees with frost, brilliant green and hydrogen peroxide are also suitable. The selected fungicide is best applied using a sprayer. Treatment is carried out on cloudy and windless days.
Covering up
After clearing frost holes on a plum tree, apple tree or other fruit tree and treating them with fungicide, the cracks are covered. They do this to create suitable conditions for healing, to prevent the evaporation of vital juices and the entry of moisture and pathogens inside. The following compositions are used as putty for frost protection:
- garden var;
- clay and mullein 3:2;
- fresh mullein, dry lime, wood ash and river sand 16:8:8:1 - prepare before use, cannot be stored.

When preparing garden varnish yourself, it is important to strictly follow the proportions.
You can use a store-bought garden brew or prepare it yourself. There are many recipes:
- Melt six parts of paraffin, add half the amount of dusty rosin, after boiling, add part of the liquid oil, heat for half an hour, cool and knead.
- Take rosin, beeswax instead of paraffin and pork fat 4:2:1. Prepare in the same way as the previous point.
- Melt equal parts of wax, interior fat and rosin separately, pour into cold water to form, and wrap in oiled paper.
- Melt 0.2 kg of wax in a water bath, add half the amount of rosin, 0.2 kg of turpentine and 43 g of melted fat.Pour into water to cool, knead and form into small balls.
- Take 0.2 kg of tree resin and mix vigorously with 1 tbsp. l. linseed oil.
- Melt 0.4 kg of pine resin, add 4 tbsp. l. alcohol, 4 g gum, 1 tsp. baking soda (dilute in water). Mix ingredients, cool.
Before applying garden varnish, tools and hands must be disinfected. This measure serves to prevent the introduction of fungi and other pathogens. After processing the fruit crop, repeat disinfection.
If the frost hole on the apple tree is large and a hollow has appeared, then it is filled with broken bricks and ash, and then secured with a mortar of cement and sand.
Wrapping
Frost breaks on cherry, apple and other fruit trees are wrapped to protect the surface treated with garden varnish. It is effective to use burlap by securing it with wire. This material is attractive because it dries quickly when wet. This prevents the trunk from rotting.
Other sources recommend providing humidity to speed up the growth of new tissue. To do this, the frostbite on the apple tree is tightly wrapped with film.
If the crack is large and deep, tying it tightly with wire will help. Small wooden spacers are placed under it. This procedure is carried out every spring until the frost wound is completely healed.
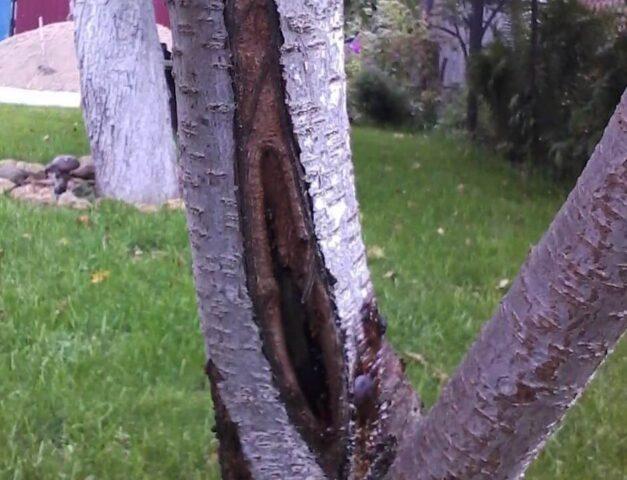

Every year, the apple tree and other crops with frost wounds are wrapped again, cleaning the wound and treating it with a fungicide and garden varnish.
Furrowing
This is an alternative method for stimulating the healing of shallow frostbites.The idea is to apply 3-4 intermittent furrows around the circumference of the trunk. They are made 0.3-0.4 m long, extending from the first branch down to the surface of the earth.
A sharp garden knife is used for furrowing. To control the depth of cuts, it is worth making a limiter on the tool.
Furrowing is carried out in May after the first upward sap flow. It is permissible to make recesses around the entire circumference of the stem.
Sorrel compresses
Sorrel helps in treating frost damage on apple trees and other fruit crops. It is used as compresses. Use freshly picked young sorrel. It is crushed, applied to the wound (a layer of 1.5 cm is sufficient) and bandaged tightly. Treatment of frostbite takes more than one year. During this period, the bandage is renewed several times.
Grafting cuttings with a bridge
You can heal severe frost damage on an apple tree by grafting with a bridge. It is also used when the trunk is damaged by rodents. The purpose of the procedure is to restore impaired sap flow, especially when the cortex is damaged along the entire circumference.
In addition to apple trees, bridge grafting is suitable for pears and plums with frostbites. The procedure is carried out at the beginning of sap flow. It is recommended to prepare cuttings in advance from late autumn (when leaf fall ends) to February. Select the length of the scion so that it is 10-12 cm greater than the width of the affected area. It is better to take annual shoots, adjusting the thickness to the extent of the damage. You can store the cuttings in the refrigerator, tightly wrapping them in plastic and placing a damp cloth inside.
The bridge grafting algorithm is as follows:
- Clean the area with frost damage.If it is covered with garden varnish, remove the entire composition.
- Wipe the wound with a damp cloth.
- Trim the edges of the bark with a sharp knife without touching the wood.
- Remove buds from the cuttings, cut both ends diagonally (cut length 3-4 cm).
- Make T-shaped cuts on the bark of the apple tree, leaving 1 cm at the top and bottom from the exposed wood.
- Carefully bend the edges of the opposite cuts and insert the ends of the cuttings. They should be slightly curved, the cuts should be pressed tightly against the wood. Be sure to position the workpieces correctly, without confusing the top and bottom.
- Distribute the cuttings evenly in a circle. Secure each with a strip of cotton fabric soaked in garden varnish.
- Secure everything with a washcloth tie.
- Treat the bare areas of the apple tree trunk with garden varnish (preferably a composition with rosin).
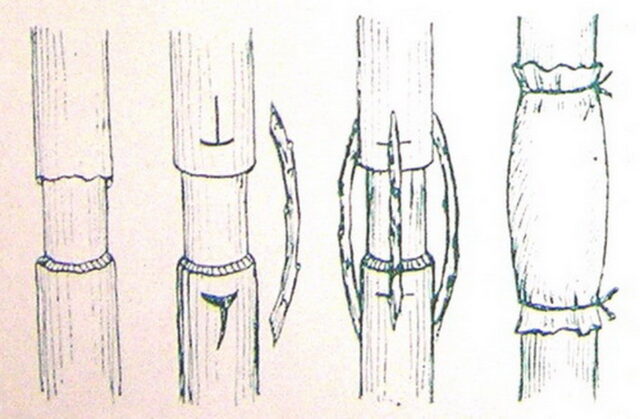
It is better to fix the cuttings with a cloth soaked in garden varnish, but you can replace it with twine, strips of polyethylene or grafting tape
The vaccination for the treatment of frostbite is checked after 2-3 weeks. The scions should become noticeably thicker, then the binding is loosened without interfering with their growth. Complete engraftment usually occurs within a month. It is permissible to leave the harness until autumn, but then be sure to remove it, otherwise the risk of disease increases.
After grafting, the apple tree needs special care:
- timely removal of buds from bridge cuttings in the summer;
- reducing crown height by a third for better nutrition and reducing moisture loss;
- tying a young apple tree to a support so that in a strong wind the trunk does not bend and the bridges do not fall out;
- regular watering and application of potassium-phosphorus compounds;
- autumn digging around the perimeter of the crown.
Comment! If vaccination to treat frostbite is unsuccessful, it can be repeated after a year.During this time, the wound should be treated with garden varnish.
Preventive measures
It is always easier to prevent a problem than to deal with its consequences. To prevent frost damage, the following measures are important:
- Select varieties of fruit trees so that their frost resistance corresponds to the climatic characteristics of the region.
- Choose the location for planting fruit trees wisely. Minimum exposure to dampness and cold air is important.
- When planting, do not bury the root collar of seedlings; this has a bad effect on their development and winter hardiness.
- Whiten trunks and large skeletal branches in a timely manner. This measure is needed in autumn and spring. The white color reflects the sun's rays, preventing the trunk from overheating - the temperature difference becomes smaller, the risk of frost damage is lower.
- Cover fruit trees for the winter. The trunks are wrapped in burlap or other material and tied with pine spruce branches.
- Apply fertilizers correctly and in a timely manner. Exceeding their dosage, especially nitrogen, enhances growth, because the tree does not have time to ripen, and the risk of frost damage increases.
Conclusion
Frost damage on apple trees and other fruit trees must be treated. Such cracks occur due to temperature changes, often when the winter hardiness of the variety does not correspond to the climate in the region, or when shelter or whitewashing of the trunks is ignored. There are several treatment options for frostbite, it is important to bring the process to complete healing.








