Content
You can often hear the sad stories of summer residents that the purchased seedling was pleased with good yields of large fruits for only a couple of years, and then the fruiting deteriorated sharply. In such situations, gardeners blame a low-quality variety, bad weather, and look for reasons in other external factors. If you look at such a tree close up, you can see a thickened crown, many old shoots, bare branches - all this is evidence of incorrect or completely absent pruning. Pruning fruit trees and shrubs is the most important part of care, responsible for the growth and health of the plant, its yield, quality and size of the fruit. It is necessary to prune the garden several times a year, but the most important stage of this process occurs in the spring.
How and when to prune fruit trees in the spring will be discussed in this article. The basic rules for pruning, its types and methods of implementation will be listed here.
When to prune your garden
First of all, the gardener must understand that any, even the most correct and gentle, pruning is an injury to the tree. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right time for this event, when the plant will tolerate trauma less painfully and can quickly heal the wounds.
In principle, it is necessary to prune the garden several times a year. Some gardeners recommend starting pruning fruit trees and berry bushes at the end of winter, as soon as the severe frosts have subsided.
Spring pruning of fruit trees and shrubs is the most important part of garden care. It is in the spring that old and dry branches are removed, damaged and diseased parts of the plant are cut out, the crown of young trees is formed and old trees in the garden are rejuvenated.
The optimal time for pruning an orchard is in early spring - in most Russian regions this is done from mid-March to early April. After winter, the gardener should go out into the garden as soon as the snow begins to melt, around the end of February, early March. This is the best time to inspect the trunks and crowns, remove winter shelters and protection from rodents, and cut out dry and broken branches.
When the air temperature stabilizes and the thermometer does not drop below -5 degrees, you can begin major spring pruning of trees. This must be done in dry weather in the absence of strong wind.
Basic Rules
When pruning your garden for the first time, it is very important not to harm the trees. It is better to first familiarize yourself with specialized literature, consult with more experienced gardeners, look at photos of pruning schemes or video lessons from professionals.
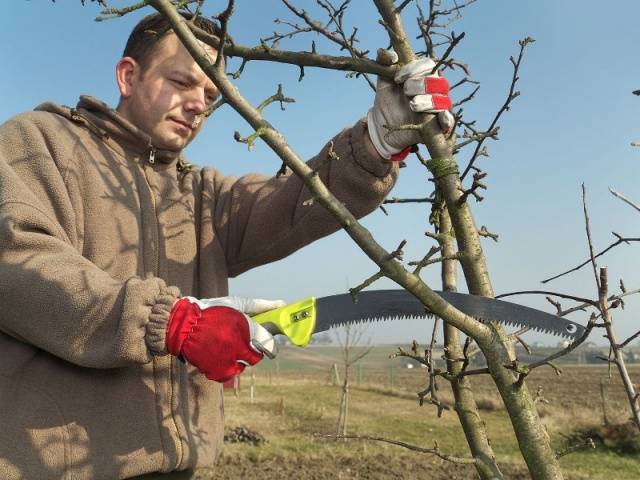
After this, you should prepare the necessary tools: a garden knife, a saw, pruning shears, and garden pitch for covering large wounds. It is recommended to disinfect and sharpen the tool before work.
To do everything right, you need to adhere to the following recommendations:
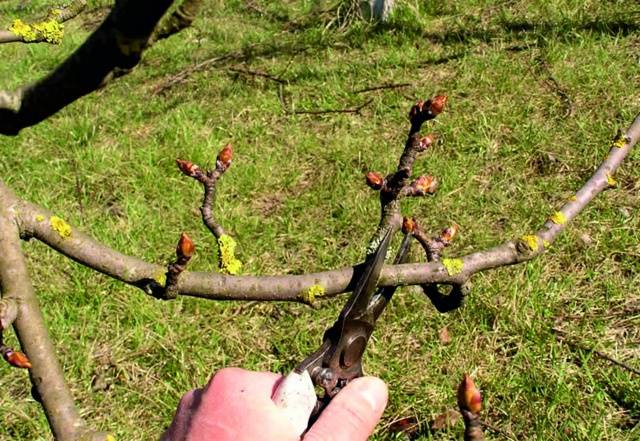
- The cuts should be even and smooth. If the cut is not immediately perfect, you need to trim and clean it with a sharp knife.
- It is recommended to trim young shoots above the buds, which are located on the outside of the branch. The cut should be oblique; it is made from the center of the tree outward.
- The shoots, which are a continuation of the trunk, after pruning should remain 20-30 cm longer than the others.
- If the tree is weakened by disease or other factors, it should be pruned as short as possible - by 2-3 buds.
- It is better to prune normally developing fruit trees above the fifth or sixth eye.
- When the fruit variety is vigorous, you can use long pruning - leaving 7-8 buds on the shoots.
- If a branch needs to be removed completely, it is cut out close to the trunk, leaving no stumps.
- When cutting out thick branches, they begin to saw them from the bottom so that, if they suddenly break off, they do not damage the bark of the cut. Then the same cut is made from above, connecting the two cutting lines into a ring.
- It is better not to touch trees that have frozen this winter, but to prune them only next spring.
- During pruning, the secateurs are held so that its narrow part is directed towards the shoot.
- There should be only one conductor - the central shoot - and all its “competitors” should be cut out.
- Shoots of small diameter must be trimmed so that the lower edge of the cut is at the bottom of the bud, and the upper edge coincides with the top of the eye.
- It is important to adhere to the same pruning pattern throughout the life of the tree. For most fruit trees with normal growth, a sparse-tiered pruning scheme, which involves the formation of a powerful frame of skeletal branches, is most suitable.
- While the tree is young, its pruning should not be excessive, as this can lead to stunted growth and deformation of the plant.
Methods and schemes
The pruning technique chosen by the gardener at the time of planting the seedling should depend on several factors. The most important of them is the age of the tree and its type. If you look globally, then All methods of pruning fruit trees are divided into three types:
- Thinning. This method involves the complete removal of entire branches, where the shoots are cut close to the trunk or larger branch from which they arise. Thinning does not affect the size of the tree in any way; it is necessary to reduce its mass. You should not get carried away with such pruning, because it does not stimulate the formation of young branches and increased fruiting. The thinning method is used to remove diseased, dry, old and excess shoots.
- Non-selective pruning. This technique is applicable to all young shoots, which are shortened by making an oblique cut above the bud. The non-selective method is used both for crown formation and for tree rejuvenation. The result of this method is the active stimulation of dormant buds and the growth of new shoots.
- Selective pruning. In this case, the shoot is cut to a bud or to a side branch. It is important here that the diameter of the remaining side branch is half the thickness of the shoot being removed.Young shoots up to 3 mm thick are cut off at one eye. The selective method helps to reduce the height of a shrub or tree without disturbing its shape. In other cases, it is better not to use the technique, as it is very aggressive and will negatively affect the amount of harvest.
Crown formation
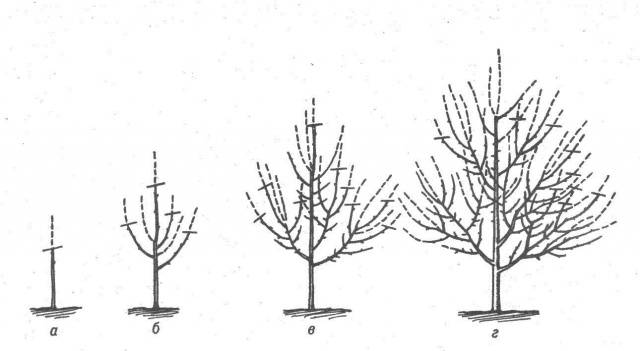
Formative pruning is necessary for all young trees. It begins from the second year of the seedling’s life and continues for at least 4-5 years. Knowledge of the characteristics of some fruit trees will help the gardener to correctly form the crown of the tree. Thus, apple and pear trees, for example, bear fruit on perennial shoots. And the fruits of plums and cherries appear on two-year-old branches a couple of years after planting.
The most common options for formative pruning are: tiered and sparsely tiered. Most often, gardeners use a sparse-tiered scheme for pruning cherries, cherry plums, and plums. The tree looks like a trunk and side branches extending from it at intervals of 20-25 cm, the number of which usually does not exceed ten.
To correctly form the crown of a young tree, you must follow the instructions:
- Annual seedlings without side branches should be shortened to 80 cm in spring. At least ten buds should remain on the guide (this will be the central shoot or tree trunk). From these eyes, in subsequent years, side shoots will grow - tiers of the tree. The emerging leaves on the stem are cut off to a height of 40 cm from the ground.
- Two-year-old trees leave 2-4 shoots - over time, they form the lower tier of skeletal branches. You need to leave the strongest and healthiest branches.
- In the third spring, it is necessary to form a second tier, its skeletal branches should be 70-100 cm from the base of the first tier. In the second tier, only two shoots are left, located at an angle of 45 degrees: the first 50-60 cm from the trunk, the second 40-45 cm from the first. The shoots growing between these two tiers are shortened by half.
- The next few prunings will consist of thinning the crown by cutting out branches growing deep into the tree, twisted or weak shoots. If during this period the gardener notices stronger growth of a competitor to the conductor, then the current conductor will need to be cut into a ring. Otherwise, all competitors are removed.
- Formative pruning is completed when the tall tree reaches a height of four meters (for dwarfs, 2 m is optimal). At this stage, it is necessary to remove the conductor above the top shoot - this will stop the growth of the tree and complete the formation of its crown. The conductor should be cut into a ring.
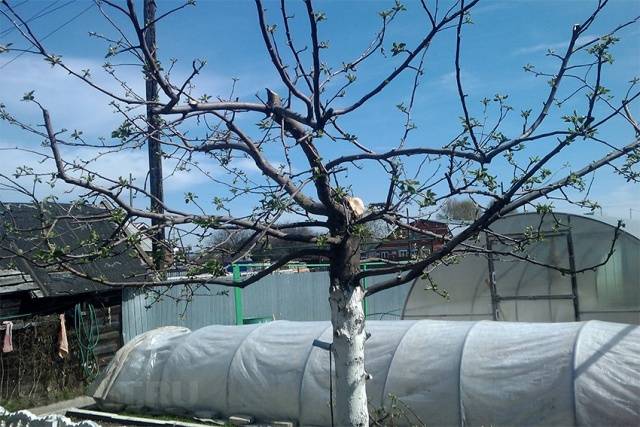
Caring for mature trees
For the health of the garden and abundant fruiting, it is important to prune not only young trees, but also mature trees that have been actively bearing fruit for several years. Pruning mature fruit trees is as follows:
- removal of old, dry and diseased shoots - annual sanitary pruning;
- thinning the thickened crown for better ventilation and lighting of branches and fruits;
- in trees with a pyramidal crown (for example, pears), it is necessary to lower all growing shoots down, that is, remove branches growing upward;
- the rest of the trees with shoots directed downwards require the removal of all branches directed downwards - shoots whose growth is directed towards the top are left;
- To rejuvenate old trees, the upper part of the trunk is cut out and the crown is thoroughly thinned out.
Conclusion
It is very difficult for a novice gardener to understand in words how to properly prune a fruit tree or shrub. That's why It is recommended that every beginner, even before the onset of spring, select a pruning scheme and become familiar with the technology for its implementation, so that with the onset of warm weather, they can competently improve their garden.
Spring pruning is very important for the health and productivity of the orchard, so you should not neglect it. You can learn more about the methods from this video.