Content
Apricot Russian is one of the best frost-resistant varieties, adapted for cultivation in the cold regions of the middle zone. This crop is distinguished by its medium-sized tree, high yield and excellent taste of the fruit.
History of selection
The Russian variety was bred on the basis of the North Caucasus Zonal Research Institute. But to date it has not yet been included in the State Register of the Russian Federation.
Despite the fact that the crop was bred in the south, Russian is excellent for growing in regions of central Russia characterized by unstable weather conditions.
Description of culture
The plant can reach 4-4.5 meters in height, the crown of the tree is spreading, which greatly facilitates the process of collecting fruits. The apricot root system is powerful, so you need to ensure that the roots do not protrude above the ground.
In appearance, Russian is practically no different from other apricot varieties. The bark on young shoots has a characteristic red-brown tint and many lentils. The leaves are round in shape, slightly elongated towards the apex, and have a finely toothed edge.
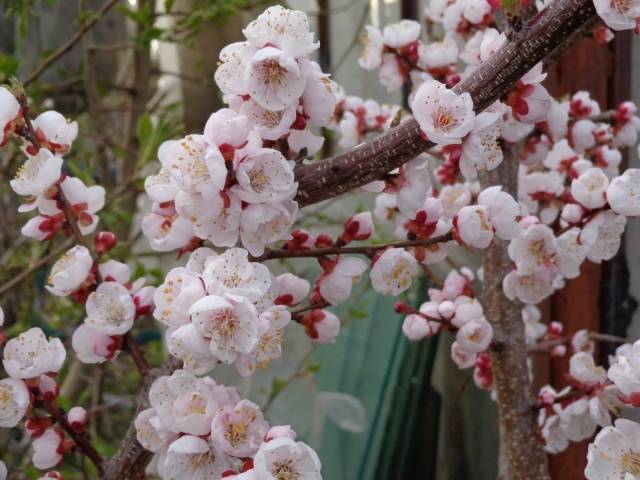
Apricot flowers are single, the petals are white or pink with reddish veins. The flowers bloom before the leaves appear.
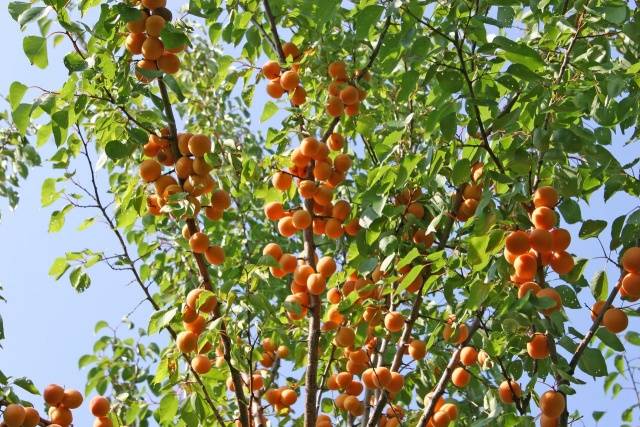
The variety is characterized by large, slightly flattened yellow-orange fruits. The weight of one apricot can reach 60-65 g. The pulp of the fruit is juicy, aromatic, and easily separated from the stone.
The frost resistance of the Rossiyanin variety allows the crop to be grown in the regions of the middle zone, including the Moscow region, Ryazan and Samara regions.
Characteristics
Characteristics of the Russian apricot variety has several features. First of all, the crop is distinguished by its ability to tolerate unfavorable conditions of the region in which it grows, and also has immunity to a wide range of diseases and pests.
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
The frost-resistant Russian apricot variety can tolerate temperatures down to minus 30-33 °C. The crop's resistance to dry periods is average. For favorable growth of apricot, it needs to be provided with proper watering.
Pollination, flowering period and ripening time
The variety is a self-fertile crop, but to increase productivity, it is better to plant pollinators nearby for the Russian apricot. These are, first of all, other apricot varieties that have similar flowering periods. The tree begins to bloom in May, and the fruits ripen in mid-July.
Productivity, fruiting
One of the main advantages of the Russian variety is its high yield rates.From one mature tree you can collect more than 70 kg of fruit. At the same time, the fruits ripen very large and juicy.
The harvest can be harvested starting from the 3-4th year after planting the seedling in a permanent place. Regular pruning of the tree will increase the yield.
Area of application of fruits
Apricot fruits of the Russian variety have excellent taste. They are ideal for both fresh consumption and for making various preparations.
Resistance to diseases and pests
The variety is resistant to most pests and diseases that affect stone fruits, and apricots in particular.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of the Russian variety are:
- high productivity;
- large and juicy fruits;
- resistance to frost, drought and parasites;
- self-fertility.
This culture has practically no disadvantages. However, the variety does not tolerate stagnant moisture in the soil.
Landing Features
Growing Russian apricots in the middle zone requires compliance with a number of conditions. It is important to choose the optimal place for the seedling, as well as determine the timing of planting.
Recommended timing
It is best to plan apricot planting in the middle - end of April. By this time, the soil will have warmed up enough and the root system will not be damaged by frost.
Choosing a suitable location
Successful cultivation of Russian apricots also depends on the planting location. The selected area should be sufficiently illuminated, but at the same time protected from north winds by some kind of building or fence.The groundwater level is not of great importance for the Russian variety.
What crops can and cannot be planted next to apricots?
An adult tree, due to its spreading branches and powerful roots, takes up quite a lot of space and creates a large shadow. Therefore, only early spring flowers, such as tulips or daffodils, can be planted next to apricots.
Undesirable neighbors for apricots are raspberries and currants. Also, you should not plant the crop in a place where other stone fruit trees previously grew.
Selection and preparation of planting material
You should purchase seedlings from trusted nurseries. Planting material should not show signs of disease, the root system and shoots should be intact, without breaks, cracks or damage. No preparation of apricot seedlings is required, but if desired, the root system can be treated with mullein solution.
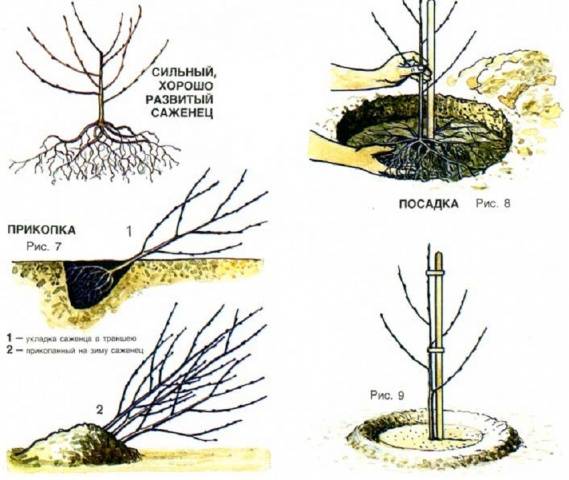
Landing algorithm
The main stages of planting apricot Russian:
- In the fall, you need to dig a hole, the size of which is 70 cm deep and about 75 cm wide.
- A layer of crushed stone or pebbles is placed at the bottom of the pit. Clay performs the drainage function for sandy soils.
- The top layer of dug soil must be mixed with humus, compost and ash, and then a complex of mineral fertilizers must be added.
- The hole is filled to the top with the prepared substrate, a stake is driven in, and a seedling is placed on top of the ground.
- It is necessary to fill the apricot root system and form a hill, compacting the soil.
- The seedling is tied to a peg. A roller is formed around the plant, which is necessary to retain water.
At the end, you need to water the apricot with 10-15 liters of water.
Subsequent care of the crop
Many reviews about the Russian apricot contain information that the culture is completely unpretentious in care, and this is true. You need to water the apricot early in the morning or after sunset and make sure that water does not stagnate around the tree. Since the variety tolerates drought well, 1-2 times a week will be enough.
Apricot feeding is carried out according to the following scheme:
- before planting, fertilizers are applied three times with an interval of 10-14 days;
- starting from the second year of the plant’s life, mineral fertilizers are applied every year in spring and autumn;
- Organic fertilizers are best used no more than once every 4 years.
To increase productivity, you need to prune the crown every spring. In this case, all shoots are shortened by half, and only 5-7 main skeletal branches remain. In the fall, sanitary pruning is carried out, as a result of which all damaged, broken or diseased shoots are removed.
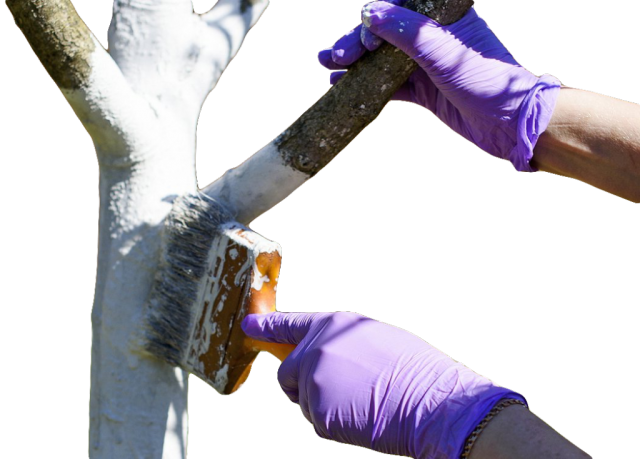
Preparing apricots for the coming winter involves removing all weeds, digging up the soil and spraying with insecticidal preparations. To protect against rodents, it is recommended to cover the trunk and lower shoots with spruce branches.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
The plant is resistant to many diseases and pests, but it is necessary to periodically carry out preventive measures.
Diseases | Methods of prevention and control |
Coccomycosis | Spraying the tree with a 3% solution of Bordeaux mixture until the buds open |
Leaf holeiness | Treatment in spring with “Fundazol” |
Pests | Methods of control and prevention |
Fruit moth | Digging the soil in the fall, destroying damaged parts of the tree |
codling moth | Treatment with insecticides, removal and burning of affected fruits |
Conclusion
The Russian apricot is considered one of the best frost-resistant varieties of the crop. It is characterized by high yield, ease of care, strong immunity, and most importantly, large and sweet fruits.