Content
The Teremoshka cherry was bred for the center of the country, it is winter-hardy and productive. The low and compact plant is convenient for picking berries. The variety is popular due to its good resistance to common stone fruit diseases: moniliosis and coccomycosis.
History of selection
Teremoshka is the result of breeding work by employees of the fruit growing department of the All-Russian Lupine Research Institute, which is located in Bryansk. M.V. Kanshina, A.A. Astakhov, L.I. Zueva worked on the new cherry tree. After field trials, the Teremoshka cherry variety has been included in the State Register since 2001.
Description of culture
The Teremoshka variety is recommended for cultivation in the Central region; now cherries have spread to the northwestern and southern regions. Gardeners fell in love with the tree for its compact, rounded and wide crown, the growth of which is restrained. The shoots of the Teremoshka cherry are large, spreading, and densely leafy. Fruit branches are noticeable with rounded tops.Vegetative shoots become pointed towards the apex. Elongated oval leaves of a dark green hue, the blade is jagged along the edges, the apex is sharp. They sit on a long petiole of medium thickness.
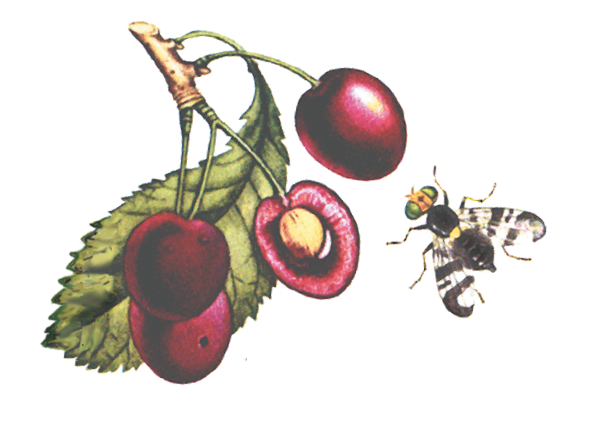
The fruit ovaries of the Teremoshka variety are formed from three large flowers with a free arrangement of white petals. The calyx with long stamens and pistil is shaped like a glass. The short, medium-thick stalk bears heart-shaped cherries with a blunt, rounded top and a narrow funnel. The size of the fruits of the Teremoshka variety is uniform, 2.1 x 2.2 cm, weight - 5 g, sometimes reaching 6.6 g. The dark red skin is dense, but pleasant when eating. The juicy flesh is fleshy, also dark red in color. The juice released is the same color.
The oval light brown seed weighs a quarter of a gram, which is 5% of the mass of the Teremoshka variety berry. It separates easily from the pulp.
- In sweet berries, 17.5% of sugars and the same amount of dry matter are determined.
- The fruit contains only 0.38% acids.
- 100 g of Teremoshka cherries contain 14.5 mg of ascorbic acid.
- Tasters rated the dessert taste of the fruits of this variety at 4.7 points.
Characteristics
According to its properties, the Teremoshka cherry variety is suitable for growing on personal plots or on farms in the middle climate zone.
Drought resistance, frost resistance
The Teremoshka variety tolerates frosty winters, which was proven in field tests. The wood was damaged by only 2 points after prolonged periods with low temperatures of -29...-34 °C. The buds of the variety suffered 40% damage, and after spring frosts of -5 °C, up to 30% of the flowers died.The Teremoshka cherry survives short droughts without consequences, but long periods without precipitation affect the next year's harvest.
Pollination, pollinating varieties, flowering period and ripening time
Like all cherries, the Teremoshka variety is self-sterile. Other cherries should grow nearby or on an adjacent plot for cross-pollination, up to 2-3 trees. It is believed that the following varieties cope best with this role:
- Ovstuzhenka;
- Revna;
- Bryansk pink.
In addition, cherries planted nearby, which bloom during the same period, have a positive effect on the fruiting of Teremoshka.
The Teremoshka variety blooms in the middle period, from May 10–15. The fruits ripen after 2 months, from the second ten days of July.
Productivity, fruiting
Teremoshka cherry trees bear fruit for 4–5 years. Up to 30% of ovaries are formed on bouquet branches. The main harvest is formed on annual shoots and fruit twigs. From a hectare of plantings of the Teremoshka variety, 50–55 centners of berries are harvested; if all agricultural technology requirements are met, the yield doubles. The berries are easy to pick, dry picking predominates. With improper, abundant watering and during prolonged rainfall, an acceptable small percentage of cracking is observed.
Area of application of berries
The variety is universal. Dessert-type Teremoshka berries are a wonderful fresh delicacy that saturates the body with vitamins. They are also used to make various homemade preparations and drinks.
Resistance to diseases and pests
The Teremoshka cherry variety has good resistance to moniliosis and coccomycosis. To an average extent, trees are affected by fungi that cause clasterosporiosis. Early spring preventive spraying is carried out against pests.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of the Teremoshka cherry variety is the possibility of cultivation in relatively cold regions. Also note:
- crown compactness;
- winter hardiness;
- stable yield;
- high consumer qualities of fruits;
- transportability;
- resistance to major fungal diseases.
The Teremoshka cherry variety has no pronounced disadvantages, except for general species properties: self-sterility and susceptibility to attacks by insect pests.
Landing Features
For a good harvest, you need to plant cherries correctly.
Recommended timing
In the climate of the middle zone, cherries are planted in the spring if the seedlings are bare-rooted. Plants in containers move throughout the warm season.
Choosing a suitable location
For the light-loving Teremoshka cherry, choose a sunny place. In regions with cold winters, trees are placed 4–5 m from buildings, on the south wall.
Follow the rules:
- groundwater does not lie higher than 1.5 m;
- do not plant trees in lowlands with melt or rain water;
- The best soils are sandy loams or loams with neutral acidity.
What crops can and cannot be planted next to cherries?
Berry bushes, other cherries and sweet cherries are quite favorable neighbors for the Teremoshka variety, but tall trees depress it. The distance between holes is up to 4–5 m.
- Raspberries suffer from close proximity to cherries.
- Tomatoes or eggplants should not be planted near cherries.
Selection and preparation of planting material
Buy Teremoshka seedlings with well-developed buds and elastic roots. The trunk and branches are without scratches or signs of disease.
Before planting, trees with bare roots are placed in a clay mash with a solution of a growth stimulator. The containers are soaked in large containers, the earthen lump is removed and the protruding roots are straightened.
Landing algorithm
- Dig holes measuring 60x60 cm, with the same depth.
- Having arranged the drainage, pour nutritious soil with fertilizers, forming it in a small mound in the hole, and install the seedling.
- A peg for garter is placed nearby.
- The root collar of the Teremoshka seedling remains 5 cm above the soil.
- The hole is filled with earth, compacted, sides are made and watered.
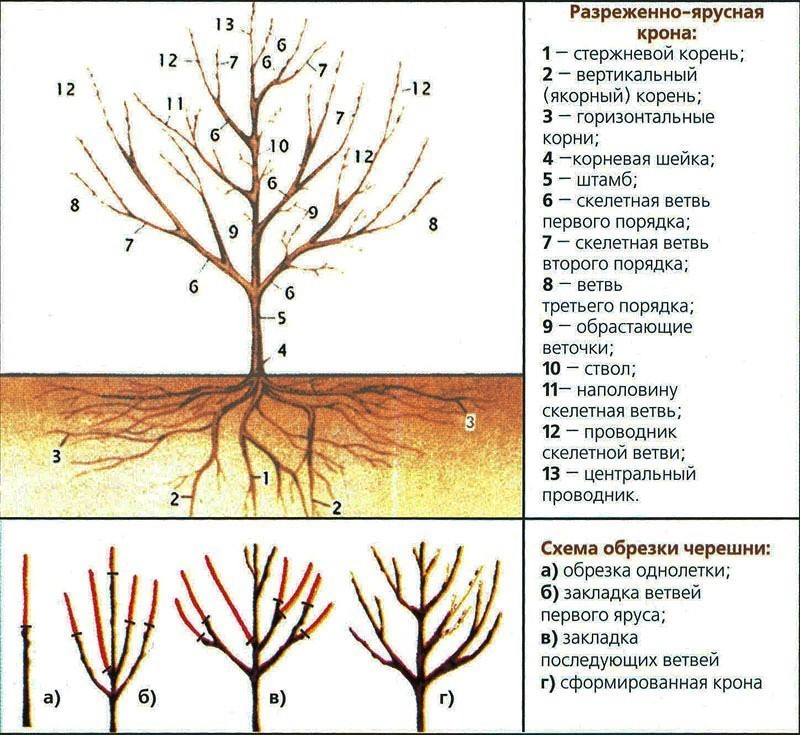
- A one-year-old seedling is pruned at a height of 1 m to establish a crown. In 2-year-old seedlings, growth is shortened by one third.
Subsequent care of the crop
Teremoshka cherries are pruned in March - April, before the sap flows. Remove damaged and barren branches by cutting into rings, without stumps. When branches appear over the summer that are located low on the trunk, they are cut off in August, like fast-growing young shoots.
The tree trunk is loosened, especially after watering, which is done every week, 20–30 liters per tree. Irrigation of Teremoshka cherries in May - June is important. From the beginning of July, watering is stopped to prevent the fruits from cracking. Then water in August and October.
- In April, the Teremoshka variety is fertilized with nitrogen fertilizers.
- In summer - superphosphate and potassium sulfate.
- Mulch with humus before winter or early spring.
In autumn, seedlings are wrapped in agrotextiles and rodent netting. Snow is thrown up to the trunk for insulation.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
Diseases | Signs | Treatment | Prevention |
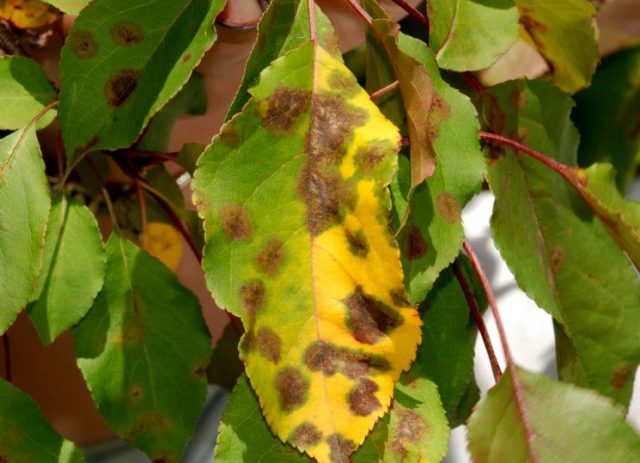
Clusterosporiasis | Leaves, shoots and fruits have brown spots. Later there are holes on the leaves | Spraying with Bordeaux mixture, fungicide "Horus" | Autumn leaf removal, pruning |
Bacteriosis (cancer) | Spots on leaves, fruits, cankers on shoots and stalks | The affected parts are removed | Nitrogen fertilization, moderate watering |
Scab | Spots on leaves | Fungicides | Cleaning leaves and fallen fruits |
Pests | Signs | Fighting methods | Prevention |
Aphid | Leaves curled | Soap/soda solution | Fufanon |
Cherry pipe maker | Beetles feed on flowers, buds, ovaries | Insecticides | Digging up the soil |
cherry fly | Fruits with a hole | Insecticides | Digging up the soil, picking berries in a timely manner |
Conclusion
Cherry Teremoshka is cultivated more and more widely due to the yield and winter hardiness of the variety. Gardeners only need to worry about pollinators and covering the seedlings for the winter. Simple tree care will bring sweet, delicious fruits to the delight of the owners.













What sport is best to plant cherry “Poetry” with?