Content
In Russia, few people can be surprised by fir. After all, these trees make up most of the Siberian taiga forests. But white fir differs from its closest relatives in being more picky about growing conditions. Therefore, even in the Moscow region, and even more so in the vicinity of St. Petersburg, it takes root with difficulty. But in Europe, these trees can be found everywhere, both in the wild and as decoration for parks and gardens.
Description of European fir
Like most of its relatives, white fir is a powerful, tall tree. This is a typical representative of evergreen coniferous species. It is monoecious and dioecious. It also has other names - European fir, which characterizes the main areas of its growth. And comb fir - according to the growth form of its needles.
White fir trees reach a height of 30-50 m, and this is far from the limit. In natural conditions they can grow even up to 65-80 m.
In the first years of its life, white fir grows in the form of a pointed pyramid. With age, the crown becomes more oval, and the tip begins to dull.At an advanced age, the shape of the tree from above looks more like a huge nest. The crown can be spread over a diameter of 8-12 m.
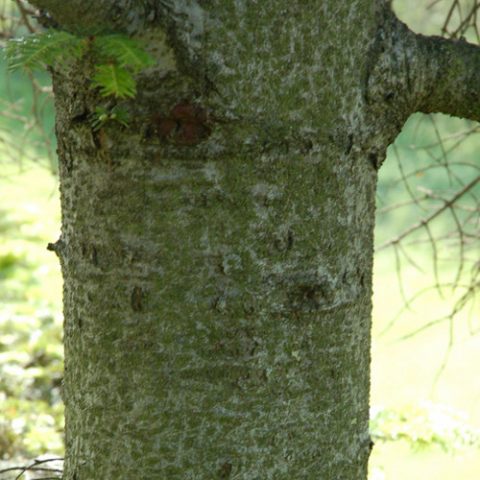
European fir has smooth bark of a silver-gray hue, which is clearly visible in the photo.
It remains smooth for a very long time and only with age can characteristic scales appear on it.
The central trunk is straight, and the side branches grow almost horizontally, only their ends are slightly raised upward.
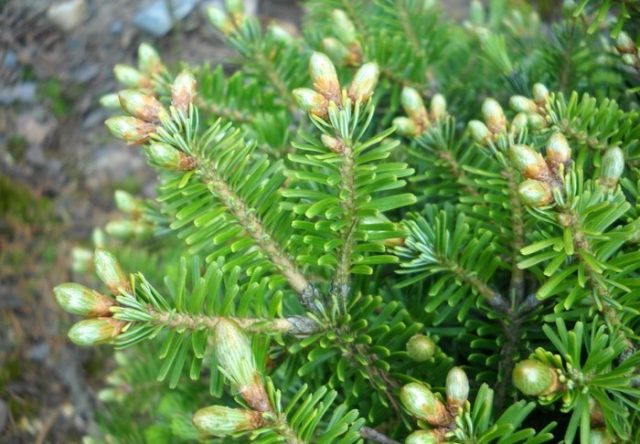
The shoots at a young age are green and pubescent, then turn brown and black, warty spots appear on them.
The buds are brown, ovoid, and lack resinousness.
White fir needles look very attractive: dark green and shiny on top, and have two white stomatal stripes below. The needles are not very long (up to 3 cm), but rather wide and flat (2.5 mm). Their tips are blunt or have a small notch. And they are arranged in the form of a comb, which served as the basis for one of the species names of white fir. The lifespan of individual needles ranges from 6 to 9 years.
The cones of the trees are quite large, reaching 10-15 cm in length and 3-5 cm in width. They grow straight up on white fir, slightly resembling candles, as in the photo.
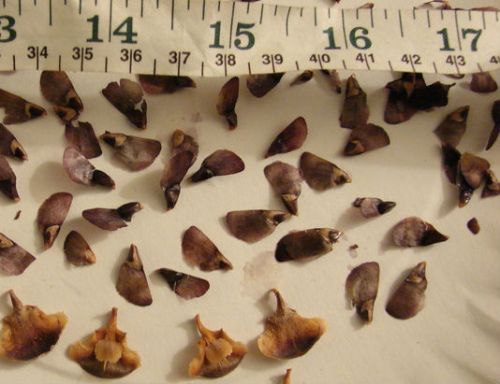
When unripe, they are greenish-brown in color. When ripe, they turn reddish-brown. The triangular seeds are large in size, reaching a length of 1 cm. The shade of the seeds is dark brown, and the wings are light and twice as large in size.
In the climatic conditions of the Moscow region, white fir does not produce pollen or fruit.
Trees can safely be classified as long-livers. Their lifespan is 400-600 years, and according to some sources they live up to 700-800 years.
White fir is characterized by the presence of a deep root system. In addition to the central root, large and strong lateral roots grow. However, the trees do not tolerate drought well and prefer to grow in well-moistened, fertile soils. At the same time, swampy soils are also not suitable for its successful growth.
Trees also have difficulty withstanding gas and smoke in the air.
In its natural growing conditions, white fir can be classified as a fast-growing tree species. Its growth especially accelerates after the tree reaches 10 years. But in the conditions of the Moscow region it grows and develops very slowly. The growth per year is no more than 5 cm. Thus, a tree at the age of 15 years does not exceed two meters in height.
According to European standards, white fir is a fairly frost-resistant tree, but at temperatures less than -25 ° C it can freeze. Young plants and the tops of branches formed in the previous season are especially susceptible to frost. Therefore, these trees are rarely used in landscaping areas located at the latitude of Moscow and to the north. But in the territory of Ukraine, southern Belarus and the Baltic states they are quite widespread.
White fir in landscape design
In nature, white fir most often grows in mixed forests along with beech and spruce.
In culture, it is actively used to decorate forested areas and other long green spaces. Goes well with larch, birch, maple and spruce.
However, given the decorative nature of white fir needles, as well as its cones, it can decorate a space in the form of a lonely tree.
Planting and caring for white fir
European fir planted in climatic conditions favorable for its growth will not require particularly careful care.
Preparing seedlings and planting area
White fir does well in open sunny areas, but can also tolerate semi-shaded conditions.
It grows best on loose, fairly moist sandy or loamy soils. The soil reaction is preferably slightly acidic, but can also be neutral. If there are waterlogged, heavy or poor dry sandy soils, some measures must be taken to improve them. For heavy soils - add sand or high peat. Poor sandy soils will require the addition of humus, at least to the planting hole.
On the one hand, the soil must retain moisture well; on the other hand, it is important to ensure good drainage so that the water does not stagnate.
Young white fir plants are planted in the ground in the spring. Although the planting hole can be prepared in the fall. In size, it must fully correspond to the volume of the root system with a lump of earth.
Humus, peat or sand are added to the hole depending on the properties of the original soil.
Landing rules
The roots of white fir seedlings, like those of many conifers, cannot withstand even a short stay in the air, much less in the sun. Therefore, plants should be replanted only with a ball of earth to ensure good survival in a new place.
The planting depth should match that at which the seedling grew in the nursery.
After planting the fir, the ground is thoroughly compacted and covered with a layer of coniferous bark or litter from the nearest pine or spruce forest.
Watering and fertilizing
European fir is a fairly moisture-loving tree, so it needs to be watered at least 3 times per season. Depending on the age of the tree and the volume of its root system, each plant can require from 5 to 15 liters of water. During dry periods, watering is required more often - up to 5-7 times per season.
Since white fir does not tolerate dry air well, it is advisable to spray its crown regularly at a young age, at least once a week.
In the first year after planting, European fir does not require special feeding. As a rule, the plant needs the nutrient medium that was provided to it during planting. In the second year, once a season, you can use fertilizers specifically designed for coniferous plants for feeding. They can be in the form of granules, which can be applied under a layer of mulch, or in liquid form.
As a last resort, Kemira-universal is used for fertilizing in a proportion of 150 g per 1 sq.m. There is no longer any special need to feed mature trees over 10 years old.
Mulching and loosening
White fir grows and develops best when using a layer of organic mulch placed in a one-meter diameter circle around the trunk. Any organic substance is suitable as mulch: straw, hay, sawdust, chopped bark, peat, nut shells.
Trimming
White fir does not need formative pruning; moreover, it does not react too positively to it.But sanitary pruning, which consists of trimming the frozen ends of branches in May, will be most welcome. It is also good to regularly remove any dry or yellowing branches to prevent and protect against possible pests or diseases.
Preparing for winter
It is especially important to prepare young, newly planted white fir trees for winter. In the fall, the circles around the trunk are additionally covered with a layer of dry leaves, at least 8-10 cm thick.
And the trunks and branches are covered with spruce branches. This shelter can also be used during repeated frosts in late spring, when young branches are especially vulnerable to frost.
Reproduction
White fir reproduces both by seeds and vegetatively (by semi-lignified cuttings, layering or grafting).
Seeds can be sown before winter. For sowing in spring, they are stratified in a cold room for 1-2 months, after which they are germinated in moist, light soil at a temperature of about + 20 °C.
When propagating white fir by cuttings without the use of special stimulants, about 25% of the cuttings collected in winter take root.
Diseases and pests
White fir is rarely affected by diseases and pests. But if there are any problems, you can use spraying with solutions of phytosporin and fitoverm.
Use of white fir
White fir is a valuable plant that is used for a variety of needs. For medical purposes, resin is very important, which is extracted from a tree trunk in the summer. From one fir you can get up to 50 g of healing substance.
The needles are rich in ascorbic acid. And the most valuable fir essential oil is extracted from the bark, young shoots and cones.It is used to cure respiratory diseases, heart problems, and rheumatism. It is also widely used in the production of various drinks, in perfumes and cosmetics, and in printing.
Fir wood can be used for construction and making musical instruments.
Conclusion
White fir is an interesting tree that is especially attractive when young. But it is better to plant it in regions with a relatively mild climate.