Content
The gorse plant belongs to the legume family and has many subspecies native to North America and Eurasia. Most plant species have the form of a subshrub or shrub; rare varieties resemble vines. Some subspecies of this plant can be used to make yellow dye.
Description of gorse

Gorse is a small perennial ornamental tree, the size of a shrub.
Gorse is classified as a legume-like vine-like plant with fairly dense green oval-shaped foliage. Shrubs of this family love sunlight very much. They are of different types, have massive or even sprouts. The stems of the perennial plant are either erect or creeping. The average height of the bush is 30 cm, and the maximum bush can grow up to 1.7 m.
The plant produces a large number of thin branches, which are often covered with smooth green bark. Side shoots are formed along the entire stem.
The branches of the bush are quite tightly covered with small oblong-lanceolate leaves, which in different subspecies of plants can be ordinary or trifoliate. They are alternately distributed on small petioles. The leaf blades of the shrub are usually smooth, dark green in color, and small fluff periodically forms on them.
Shrubs begin to bloom at the age of 3-6 years. Racemose-shaped bright yellow buds form on the plant. The flowering period occurs in June.
The buds stay on the branches of the bush for 15-60 days. Axillary flowers cluster along the edges of young branches.
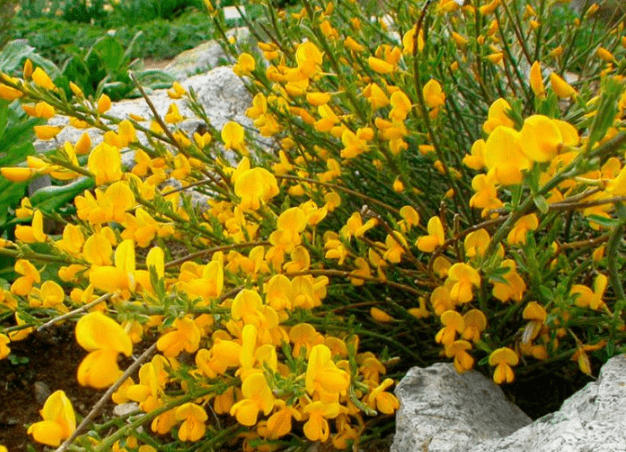

Blooming gorse is covered with a fairly thick yellow carpet, which almost completely hides the green branches and leaves.
The fruits of the plant ripen in August. On the branches of the bush, narrow large beans with elongated shiny grains are formed, which most often have a dark brown tint.
Gorse flowers are perfectly adapted even to poor soils, so shrubs of this family grow on almost any soil.
Types and varieties
The gorse plant includes 125 species of shrubs. Some subspecies are allowed for cultivation in mid-latitudes.
German gorse
According to the description, German gorse (German gorse) is an evergreen and fairly heat-loving ornamental shrub that is afraid of frost. Its bushes grow up to 60 cm in height and reach a diameter of 120 cm.
The surface of upright branches is covered with down and lanceolate leaf plates with felt pubescence on the underside. At the junction with the shoot, the leaf has a long green needle.
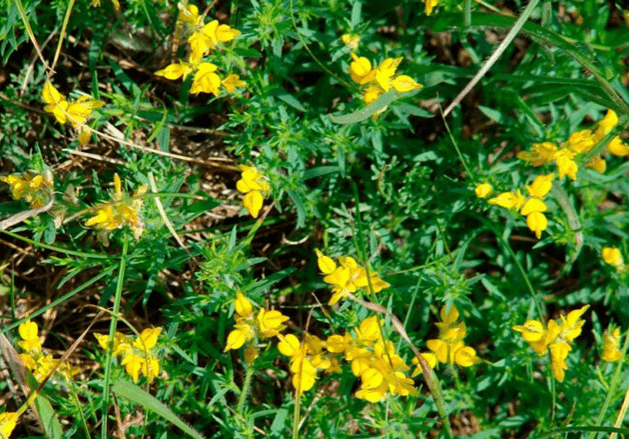

German gorse begins to bloom from the first days of summer and ends only in August
During this period, golden spikelets open on the tops of the bush branches. The fruits of the plant ripen in October.
Spanish gorse
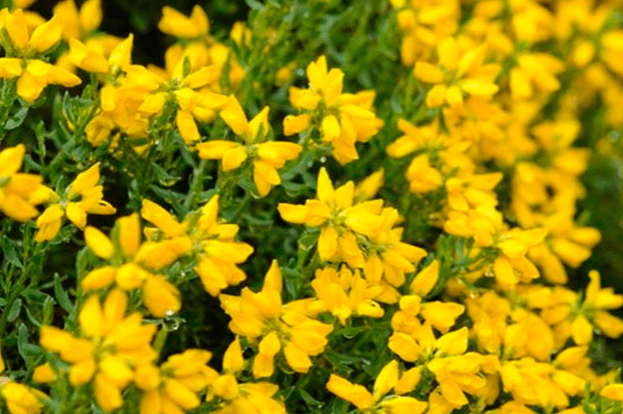

Spanish gorse bushes reach half a meter in height
Thorns and balls form on the bush. The dense crown of the plant includes glossy lanceolate leaf blades of rich green color. Their length is about 10 mm.
The Spanish bush blooms twice:
- at the beginning of summer the first flowering occurs, accompanied by the formation of many rich yellow inflorescences;
- at the end of August - the second, but less magnificent flowering of the plant.
Lydian gorse
Lydian gorse (Lydian gorse) grows in southern Europe. The stems of the plant are located near the surface of the ground and can fall very effectively from mountain slopes. Dense dark green foliage, small in size and oval in shape, covers the shoots.
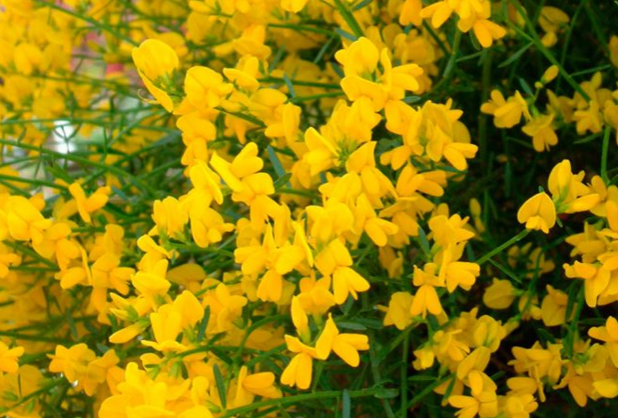

Lush flowering begins in April and ends in June
Gorse Don
Don gorse (Donskoy) is a perennial branched plant that grows up to half a meter in height. Lanceolate bluish-green leaves form on the bush.
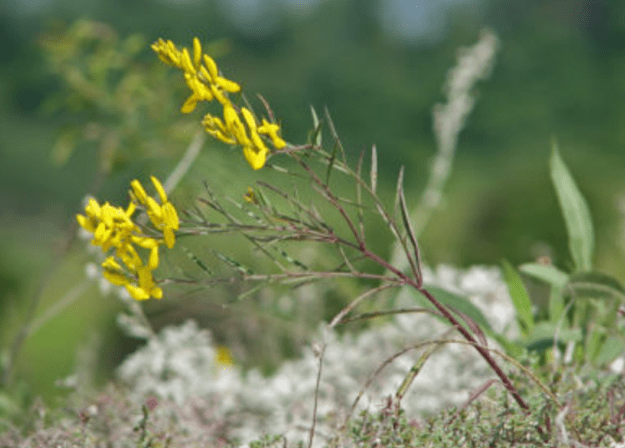

Flowering period – June-July
The inflorescences of the bush are loose, racemose, and yellow in color. After flowering is completed, bean seeds form on the bush.
Gorse yellow
Yellow gorse is a low-growing shrub that grows up to 1.5 m. It has thin, erect branches and dense bluish foliage.
The plant begins to bloom in June and ends in July.
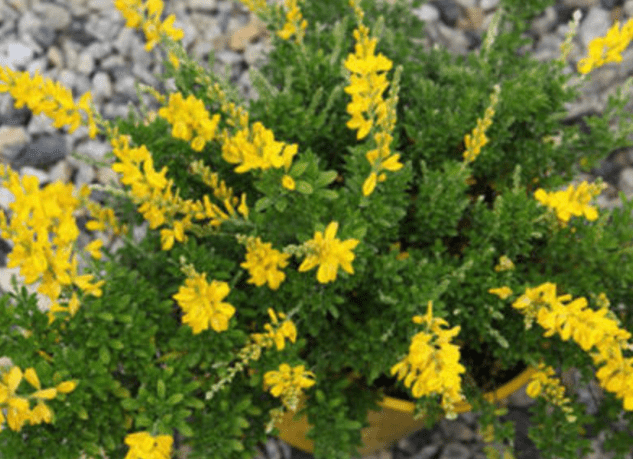

The beautifully flowering bush has racemose bright yellow inflorescences that form at the tops of the shoots
Gorse
Spreading gorse (Dyeing) grows up to 100 cm in height. The shrub is distinguished by weak branching of creeping stems and a complete absence of thorns.
The almost bare dark green leaf blades of the plant have an oblong narrow configuration.
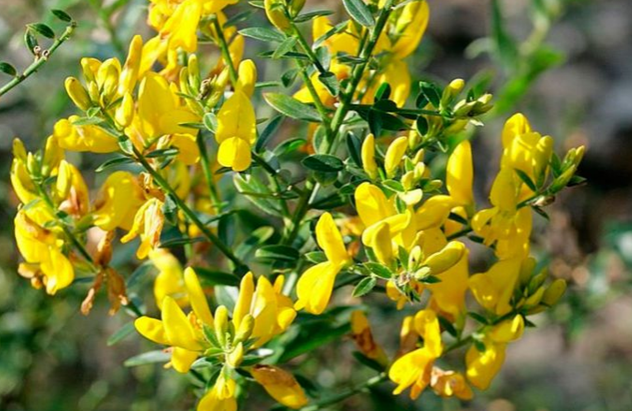

Gorse grows in the Middle East, Western Siberia and Kazakhstan
Useful properties and harm of gorse
The roots, shoots and flowers of the shrub contain essential oils, alkaloids, flavonoids and tannin components. The characteristics and properties of this plant have not yet been sufficiently studied by scientists, so it is not used in traditional medicine. But non-traditional healers use plant culture in many countries.
Based on the plant in question, various medicinal decoctions and tinctures are prepared. They have a laxative, diuretic, sedative and restorative effect. Decoctions and tinctures can effectively remove toxic components from the human body, treat infectious skin diseases and heal wounds.
Fresh juice of the bush is used to remove papillomas. Gorse-based products help in the treatment of malaria, rheumatism, hepatitis, sore throat, stomatitis, allergic dermatitis, and bronchial asthma.
The plant contains not only useful substances. It also contains toxic elements, so using gorse on your own for medicinal purposes is not recommended. It is strictly forbidden for pregnant and lactating women, children and hypertensive patients to take tinctures based on this plant.
Landing rules
Gorse bushes can grow even in poor soil.Not too dry, well-drained soil is more suitable for seedlings.
Rules for planting in open ground:
- The plant is planted in a hole dug to a depth 2 times greater than the diameter of the root ball. If the soil requires additional drying and fertilizing, the hole is made larger in both depth and width. After planting the sprout, it is filled with coarse sand and peat composition.
- Ground cover varieties require sufficient area for subsequent development and growth. Therefore, several plants need to be planted further away from each other, taking into account the approximate sizes of adult bushes. If you plan to form a living fence, then it is recommended to plant gorse sprouts more densely.
- To ensure that the substrate adheres well to the roots, the seedlings need to be watered abundantly after planting in the ground.
It is theoretically permissible to plant shrub seedlings in containers throughout the entire growing season, but it is best to do this in the fall (September-October). At this time, the plant recovers best.
Also, gorse can be planted after the end of frost in the spring, but before the heat of June. In this case, the young shrub needs to be watered regularly.
Rules for sowing seedlings:
- The seeds of this type of shrub have a fairly hard shell. Therefore, they are first dipped in boiling water for a couple of seconds, then soaked in cold water for two days. As a result, the seed shell will crack and become much softer.
- After preliminary soaking, the seed material is sown in deep containers or large flower pots with a pitch of 5 cm between grains.
- Containers with seeds are placed in a heated room in a greenhouse.
- The seedlings are watered daily, but not abundantly.
- In mid-May, the seedlings are thinned out.
- At the end of spring, seedlings are planted in open ground or in large decorative flower pots in a permanent place.
Frost-resistant shrubs growing in open ground are recommended to be covered for the winter.
Care instructions
Caring for gorse bushes in your backyard is easy. This is a fairly unpretentious plant that, in optimal climatic conditions, is capable of developing independently without human intervention.
Watering
After planting, young plants must be watered regularly. After each irrigation, the soil around the gorse bush is loosened and weeds are removed.
Mature acclimatized bushes no longer require regular irrigation; their resistance to drought increases. The volume of natural precipitation in the region is enough for the shrubs. If the summer is very dry, it is recommended to artificially feed the plant with water once every two weeks.
Top dressing

Humus added to the soil before planting seedlings is the first feeding of the plant.
The following compositions are applied monthly during the growing season of the bush. For this purpose, experienced gardeners recommend using phosphorus, potassium fertilizers or wood ash.
Trimming
To form the crown of the bush, the shoots are regularly pruned. The best period for this is early spring.Lush thickets can be given any shape.
Wintering
The plant can withstand hot summer weather very well, but severe frosts can destroy it. Therefore, in mid-latitudes, gorse bushes in late autumn are first covered with a layer of spruce branches and additionally covered with some kind of non-woven material.
In climatic regions with relatively warm, snowy winters, low-growing gorse bushes do not need to be covered, but there is a risk of freezing of the upper shoots.
Diseases and pests
Gorse bushes are characterized by increased resistance to diseases and also do not attract insect pests. The plant is adversely affected by chlorosis, which causes green leaves to turn yellow and fall off.
To prevent gorse chlorosis, special compounds are introduced into the soil. If signs of disease are detected, the bush is sprayed with iron chelate or Ferrovit solution.
Reproduction methods
There are two options for propagating gorse bushes: seeds and cuttings.
Growing from seeds
Gorse seeds are collected in August after they are fully ripened. The ripe fruit becomes brown and small cracks form on it.
The collected seed material is slightly dried and immediately sown in open ground, deepening the grains by 25-30 mm. After this, they are lightly watered with water.
Propagation of gorse by cuttings
Some varieties of gorse can be propagated by cuttings. To do this, in June, the apical cuttings of the plant are cut 12-15 cm long.
The cut cuttings are immediately planted in a moist sandy-peat substrate without prior preparation and covered with a transparent cap or placed in a greenhouse until the plant takes root.
Photos in landscape design

Ornamental gorse shrubs are highly valued by gardeners and modern landscape designers.
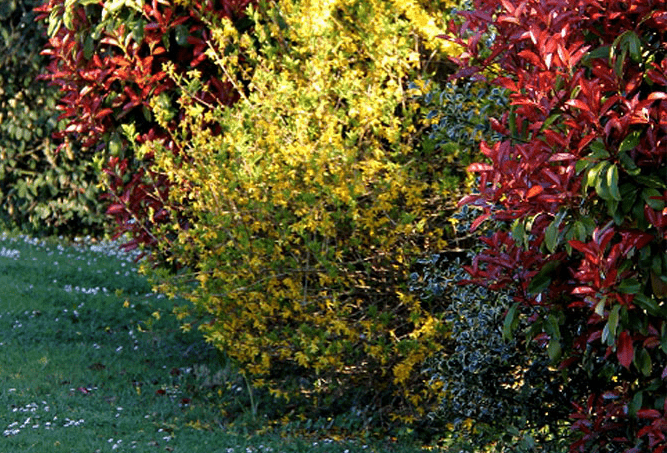
The plant has spectacular lush flowering
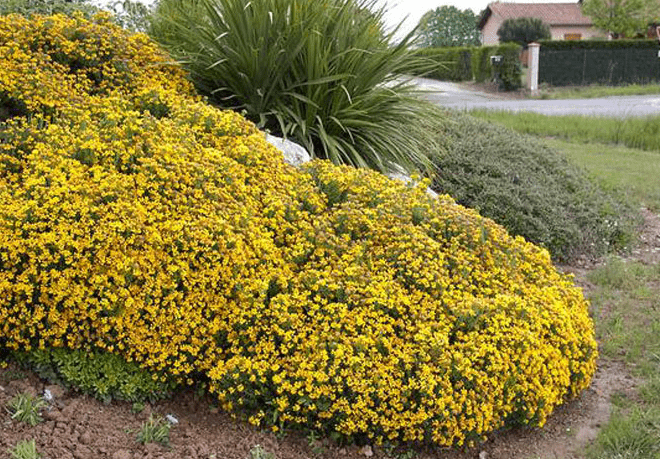

The shrub fits perfectly into the landscape design of personal plots, public parks and squares
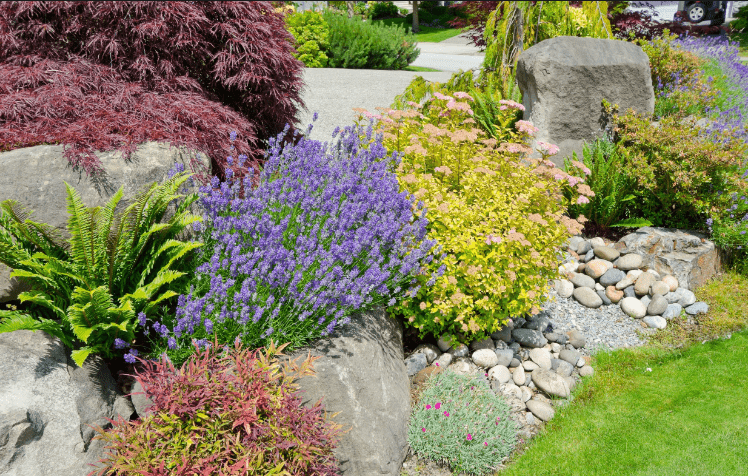

Yellow flowers go harmoniously with purple
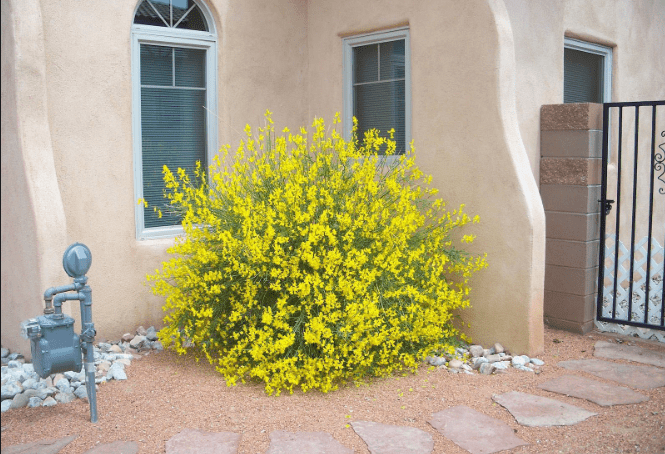

A bright shrub will help decorate any corner of the garden.
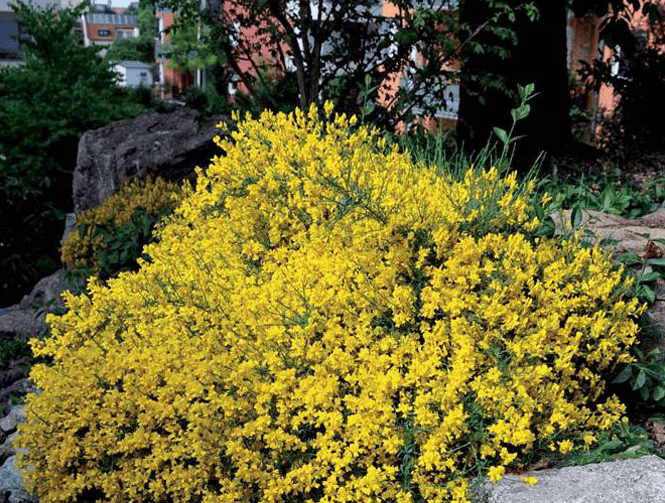

Lush blooms attract the eye to the flowerbed
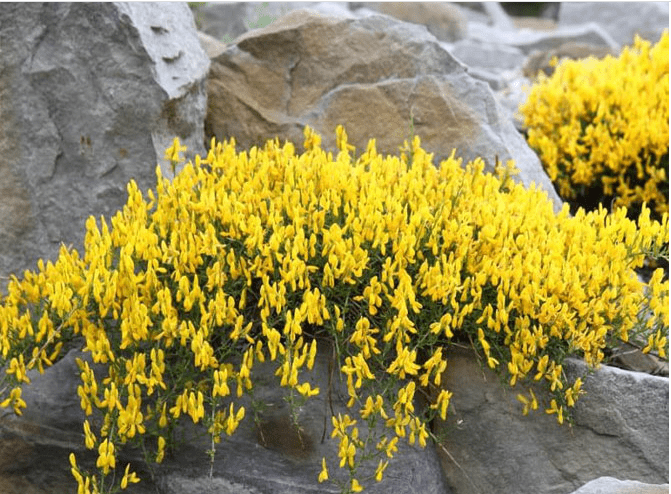

The plant looks advantageous against the background of stone blocks
Conclusion
The gorse plant is an ornamental plant of the legume family. This low-growing shrub with a spectacular solid yellow coat is difficult to miss during the flowering period. Today, about 125 subspecies of gorse shrubs are known, most of which grow in the southern regions. But there are also frost-resistant specimens suitable for northern regions. The plant is unpretentious in care, in optimal climatic conditions it is able to grow and develop independently. With proper pruning and shaping of gorse bushes in your garden plot, you can achieve any shape of bush.








