Content
- 1 What does a blooming rosehip look like, what color does it bloom?
- 2 What year does rosehip bloom?
- 3 When and in what month does rosehip bloom?
- 4 How long does rosehip bloom?
- 5 How many times does rosehip bloom?
- 6 Why doesn't rose hips bloom in the garden?
- 7 What to do if rosehip does not bloom
- 8 Does a rose hip bloom from a rose?
- 9 Conclusion
Rose hips bloom from the end of May to the second ten days of June. However, the timing may shift slightly in both directions depending on the climatic conditions of the region. Some types of plants bloom again. This happens in late August - early September. There are also varieties that bloom almost continuously from late May to early October. But if a rose hip does not produce inflorescences, it is most often due to poor care, for example, excessive fertilization or lack of pruning.
What does a blooming rosehip look like, what color does it bloom?
Rosehip produces large flowers, the diameter of which reaches 7–10 cm. It is a monoecious plant, i.e. On one bush there are both male and female flowers. The pedicels are small - up to 1.7 cm. The receptacle is ovoid or spherical, tapering towards the pharynx.
The corollas consist of 4–5 petals of equal size. The color is varied: pure white, pink, yellow, red, with a cream tint.
The photo of the bush shows how the rosehip blooms.
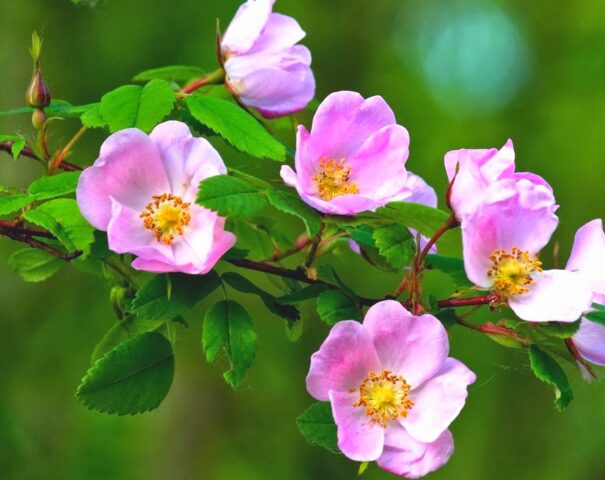

Rose hips have 4–5 sepals and petals, many pistils and stamens
The anthers are bilocular, they grow on the receptacle ring. The ovaries are fleecy, they are single-locular, located closely or on a stalk. Rosehip pollen is yellow, the grains are oval-elongated (visible under a light microscope).
What year does rosehip bloom?
Normally, rose hips bloom the next season after planting, i.e. in the second year of life. If you plant an adult seedling in April and it takes root well, flowers will appear within 1–2 months. If planted in the fall, the bush will have time to adapt, so flowering in the coming summer is guaranteed.
When and in what month does rosehip bloom?
The flowering period of rosehip occurs at the end of spring - beginning of summer. In most regions, bushes bloom from mid-May to the first ten days of June inclusive. Depending on climatic conditions, this period can shift either to later or earlier periods.
When does rosehip bloom in the Urals?
In the Urals, rose hips bloom from the last days of May to the second ten days of June. Sometimes these dates can shift by several days, since May can be cold. For comparison: in the southern regions the bush begins to produce flowers in mid-May. Moreover, it is here that it most often blooms again (from the end of August).
When does rosehip bloom in the middle zone?
In the middle zone, the flowering period of rose hips occurs at the end of May - beginning of June. Flowers appear en masse in early summer, when there is virtually no risk of return frosts. Therefore, all types of rose hips produce a stable, high yield of tasty and healthy berries. In favorable conditions, the plant blooms again in late summer - early autumn.
How long does rosehip bloom?
Rose hips do not bloom for a long time: even with good care, sufficient lighting and warm weather, the period lasts only 20, less often 25–30 days (certain varieties). Each flower lives 1–2 days. The inflorescences begin to bloom in the early morning, and in the evening the petals close to prevent moisture from reaching the pollen.

Rose hips bloom lasts 3 weeks
How many times does rosehip bloom?
Usually the plant blooms only once per season - in early summer. But there are exceptions to this rule. Remontant varieties are able to bloom more or less consistently throughout the entire season - from late May to early October. There are also types of rose hips that form buds twice during the summer.
For example, wrinkled rosehip, found in the Russian Far East, blooms for the first time from mid-June to early July, and the second from mid-September to early October. However, this is only possible under favorable weather conditions (warm and sunny autumn). In some varieties, the second wave may begin in late July - early August.
Why doesn't rose hips bloom in the garden?
Rose hips do not bloom for various reasons. For example, plants planted this season will produce flowers only next summer. This is considered the norm. But most often the plant does not bloom due to improper care, as well as due to diseases and pests:
- Unfavorable place for landing. The plant needs plenty of light, like most types of roses.If the bush is planted in the shade, there may be few or no flowers.
- No pruning - excess branches are removed in early spring and mid-autumn. It is also necessary to remove growth regularly. The best option is to identify several strong branches and maintain their active growth.
- Insufficient watering: this reason is rarely observed, since the plant is highly drought-resistant. However, during the hot period, the crop needs additional moisture.
- Violation of the dosage and timing of fertilizing. For this shrub, both a lack and an excess of fertilizers are bad. At the same time, overfeeding is always worse than underfeeding.
- Invasion of pests (aphids, moths, mites, moths, sawflies). Plants should be periodically inspected and, if necessary, treated with folk remedies or chemicals.
What to do if rosehip does not bloom
To grow a beautiful bush of flowering rosehip, as in the photo, you must follow the basic rules of planting and care. Seedlings are purchased from nurseries and responsible suppliers. When purchasing, you need to inspect and make sure that the roots and shoots are completely healthy and have no signs of disease.

Rose hips will not bloom in a shady place
It is better to choose the autumn period for placing the crop on the site. Then the bush will take root by spring and will actively grow, and in the second year it will produce the first inflorescences. In order for the flowering to be abundant, you need to choose the right place. Site requirements:
- completely open lawn (only light shading is allowed);
- dry (better a slight elevation than a lowland with stagnant moisture);
- protected from the wind (for example, along a fence or next to the house).
Suitable soil is light, fertile loam with a slightly acidic reaction (pH about 6.0).
Plants that are planted too densely will not be able to bloom normally.
After placing the crop on the site, you need to organize proper care. Young seedlings should be watered 2 times a month (if there is no rain, give a bucket of water). Adult bushes are drought-resistant, so they only need additional moisture when it’s hot (3-5 buckets per bush). In this case, excessive watering is excluded - the soil must have time to dry out.
In order for the plant to produce lush flowers, it must be fed 2 times per season. In April, they give urea (15–20 g per bush), and in the summer, during flowering, organic matter. An infusion of fresh manure, diluted 10 times, or chicken manure (20 times) is suitable. You can water it with water in which freshly cut grass has been standing for several days. Wood ash is added to this infusion (200 g per 10 l). It is necessary to carefully observe the dosage - otherwise, even on fertile soil, the bush will stop producing flowers.
After each watering (including fertilizing), as well as heavy rains, the soil in the tree trunk circle must be thoroughly loosened. Weeding is done regularly. To prevent the growth of weeds, the soil can be mulched with straw, sawdust, and pine needles. Before flowering, it is optimal to use black peat, humus and other organic matter as mulch.
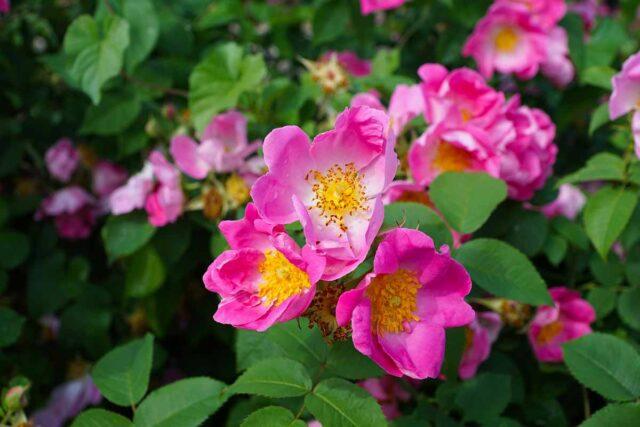

Rare watering and fertilizing guarantee the timely formation of rosehip buds
Often plants stop producing flowers due to pests and diseases.To avoid this, it is recommended to choose species and varieties with the strongest immunity, for example, wrinkled rosehip. In the spring (before the leaves appear), treatment is carried out with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture or another fungicide: “HOM”, “Fundazol”, “Topaz”, “Skor”, “Ordan”, “Tattu”.
In summer, shrubs are inspected and affected leaves and shoots are removed. If an invasion of aphids and other pests is observed, treatment is carried out with folk remedies:
- infusion of wood ash with laundry soap, garlic cloves and arrows, onion peels, chili pepper;
- solution of tobacco dust, mustard powder;
- decoction of potato tops.
You can also use special preparations, for example, “Fufanon”, “Fitoverm”, “Aktara”, “Decis”, “Confidor”, “Iskra” and others.
Pruning is another important measure to ensure lush and long-lasting flowering. It is done in early spring (early April) and late autumn (end of October). If pruning is needed for decorative purposes, then densely growing shoots are removed in the summer (as needed).
Main tasks of pruning:
- In the spring, before the buds begin to swell, you need to remove all frozen, broken and dried branches. They will not recover, but will take away water and nutrients from the plant. All shoots of a young seedling are cut off annually (up to 5 years), leaving a third. Thanks to this, active growth of the bush is stimulated.
- In autumn, formative pruning is carried out. The schemes may be different, but there is a general idea: it is necessary to identify several strong shoots, and remove the rest.Along with this, you will need to regularly shorten the branches, pinching the upper growth points. Thanks to this, all shoots will grow relatively evenly, which will ensure not only good flowering, but also an attractive appearance of the shrub.
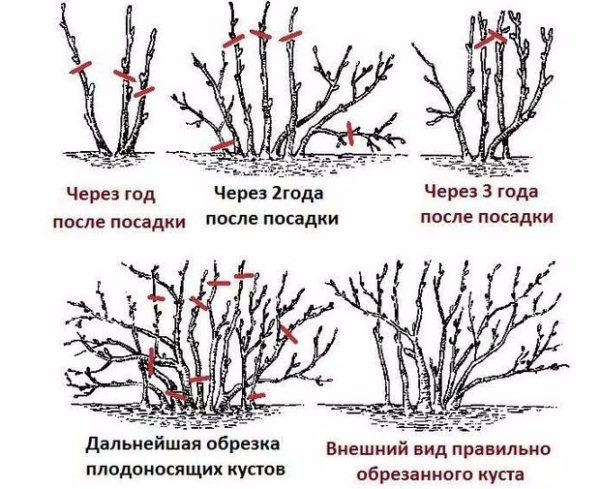
The classic rosehip pruning scheme will help to properly form the bush.
Does a rose hip bloom from a rose?
Any variety of roses can be grafted onto a seedling, for example, hybrid tea, standard, climbing and others. This is done so that the roses can withstand unfavorable climatic conditions and produce their flowers.
Sometimes the graft dies without surviving the frosty winter. If rosehip buds remain under the grafting, they will sprout. And already in the second season, white, pink or red flowers will appear on them. Those. Flowering of the rosehip to which the rose is grafted is possible if the buds of the rootstock remain.
Conclusion
Rose hips bloom from the second season after planting. The shrub is unpretentious, grows on different soils (except for waterlogged or alkaline soils). The culture develops well even with minimal watering and rare fertilizing. Therefore, the lack of flowering is most often associated with improper care or a poor planting location. Another possible reason is diseases and pests.








