Content
Rosehip propagation is one of the labor-intensive procedures when growing shrubs. The owner of the crop can hope for a successful outcome if he is familiar with the principles of agricultural technology. The choice of method depends on the personal preferences of the gardener, the age of the bush and its condition.
Features of propagation and planting of rose hips
Most often, owners see the crop as a powerful, tenacious shrub. In fact, the plant does not develop well in marshy and rocky areas and does not like clayey and sandy loam soils.
The ideal place for planting and vegetative propagation of rose hips is fertile black soil, whose acidity is close to the “neutral” mark. The area should be well lit, protected from winds and melt water.
Basic principles of planting rose hips:
- Young shrubs that have reached two years old are recognized as the best seedlings.
- A distance of 1.5 m should be maintained between plants so that the varieties do not interfere with each other’s development.
- If you plan to root a seedling in the fall, then preliminary soil fertilizing is required. To do this, you need to dig up the entire area and add compost to a depth of 30 cm. Fertilizer consumption is 6-7 kg per 1 m2.
- The hole for the seedling must be at least 30 cm deep. If the area has not been previously prepared, then the hole should be dug in a large size, at least 80*50 cm.
- The plant needs abundant watering and a good drainage system. For each bush, allocate at least eight buckets of water at room temperature.
- Compact the soil around the trunk and mulch using peat chips. The layer thickness should be no more than 3 cm.
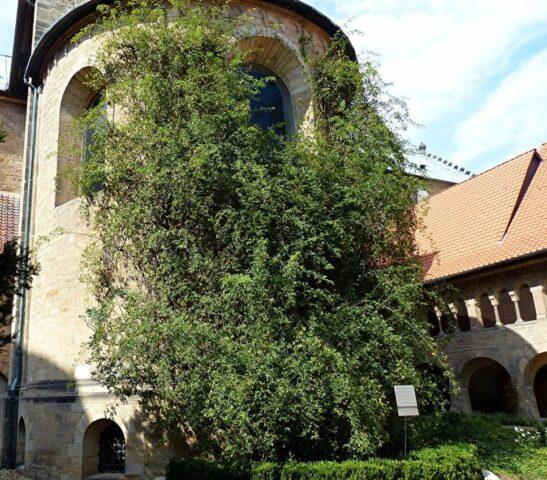

The oldest rose hip grows in Hildesheim in Germany, while its age has crossed the border of 1000 years
The peculiarity of the culture is its demanding care and good survivability during transplantation. It should be borne in mind that shrubs will be as aesthetically pleasing as possible only for those owners who do not spare water and fertilizers.
How does rosehip reproduce?
The method of planting and propagating the crop depends on the choice of the owner of the plant. At home, rose hips successfully reproduce by grafting, green cuttings, dividing bushes, and growing from layering.
How to propagate rose hips by layering
Most often, the most optimal time for the procedure is spring or summer. To propagate rose hips by layering, you need to select young flexible shoots. They need to be bent to the soil and buried in holes up to 10 cm deep. The ground needs to be watered abundantly.
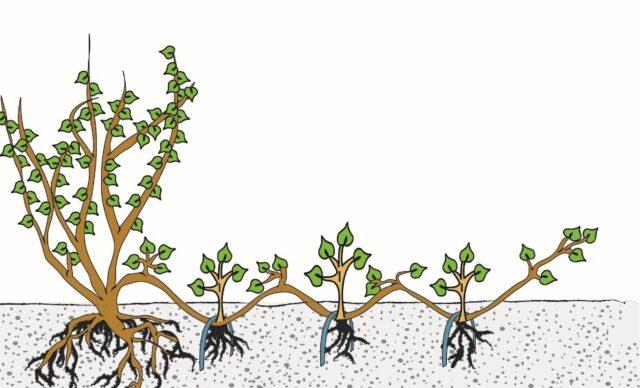
The cuttings are ready for separation after complete rooting: they need to be dug up and planted in prepared holes
Young shrubs can be transferred to a permanent place of residence in both spring and autumn, but this process should not be delayed.Plants older than 2.5-3 years will not respond well to transplantation.
Dividing the bush
This method is not popular among gardeners. This is due not only to the need to master special skills and knowledge, but also to the complexity of the process. Only adult rose hips that have reached 5-6 years of age can be propagated.
The division of the bush is carried out when replanting the plant. To propagate, you need to dig up and cut the rosehip roots into 3-4 parts so that 2-3 shoots go to each plot. It is mandatory to treat young seedlings with a growth stimulator. It is important to transfer the divisions to a permanent place immediately to prevent them from drying out.
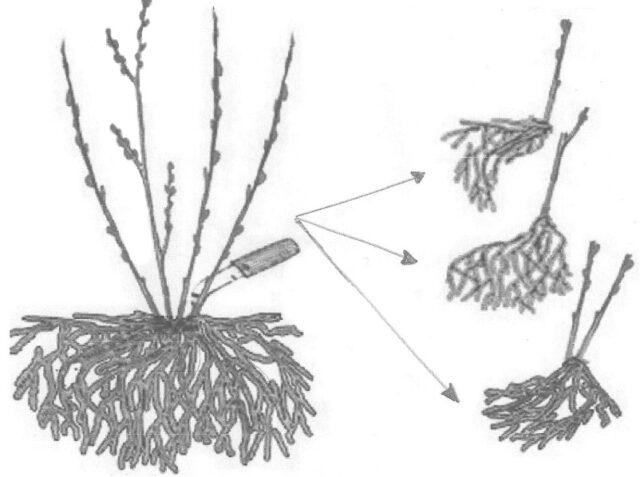
When cutting roots, use clean, disinfected tools, as the culture is sensitive to fungi and bacteria.
Reproduction by root suckers
This method is only possible if a root offspring has appeared next to the mother bush. You can prepare it in several ways:
- Dig up the plant in spring or autumn, cutting off the common root with the mother bush. Then transplant the rose hips to a new place.
- Do not remove the shoot from the soil, but hill it up using humus. If you propagate a rosehip bush using this method, then gradually adventitious roots will form around it. In the second year after the procedure, the maternal roots must be separated and the plant left in the same place for another year. Only then place the young rosehip bush in the hole.
If you choose the first method of reproduction, then in the future it is recommended to grow the offspring and form them in the nursery for another 1-2 years. Strong, healthy specimens with strong roots should be transferred to a permanent place of residence.
Propagation by seeds
This method is very time-consuming and labor-intensive; it is preferred mainly by breeders. If you propagate a plant in this way, you need to be prepared for the fact that the appearance of the variety will be different. The shape of the leaf, the height of the shoots and the berries change.
The main task of a gardener is to prepare seeds. They are collected from ripe fruits and processed. In the fall they need to be planted in the ground. It will not be possible to propagate rose hips right away: the material takes a long time to germinate, is sensitive to care, and can be easily confused with weeds. But if a couple of true leaves appear, then the crop can be transferred to the site.
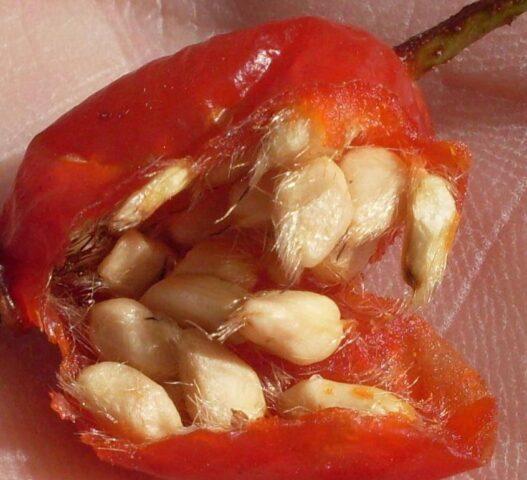

Despite their large size, rosehip seeds are difficult to germinate and have a dense skin that does not allow water to pass through well.
Propagation by cuttings
This method is one of the most accessible. Its advantage is the high survival rate of the culture.
To propagate rose hips, you need to prepare lignified cuttings and place them in a growth stimulator. Change the water in the container periodically until roots appear. It is important to prevent it from blooming. In this case, the cuttings will be unsuitable for propagation. “Ripe” specimens can be transferred to the garden bed, first under the film, and then into open ground.
Conclusion
Rose hips can be propagated in several ways. The least labor-intensive are root suckers and layering. Propagation of the plant by seeds will require a lot of time and physical effort. The survival rate of a crop is influenced by climate, proper care and planting.








