Content
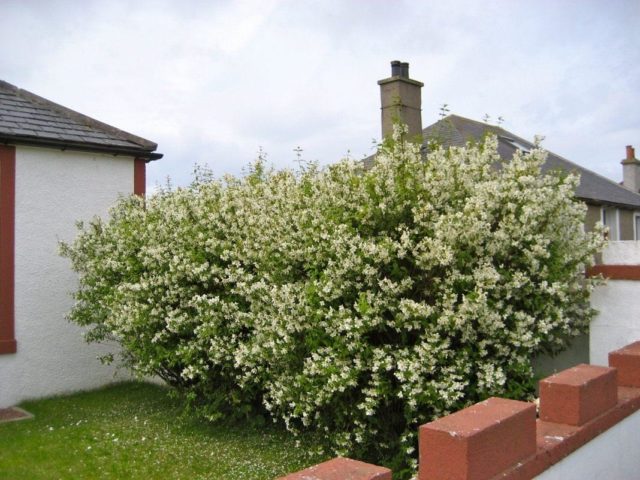
Chubushnik Komsomolets is a bright hybrid representative of its species. In the fifties of the last century, Academician N.K. Vekhov developed a new frost-resistant variety based on the famous French jasmines: Komsomolets surpassed the mother varieties in its decorative qualities.
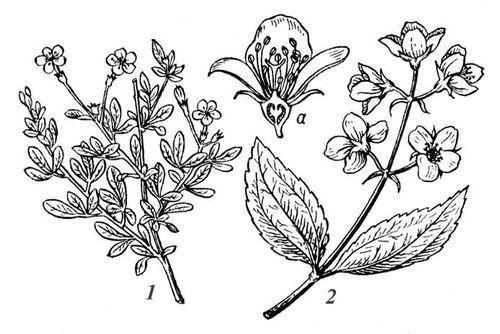
Mock orange is often called jasmine. It is possible that this is due to the external similarity and aroma of the plants. In fact, mock orange and jasmine belong to different families. Mock orange belongs to the Hydrangeaceae family and is a true shrub. Jasmine is classified as Olive and is an evergreen vine. But the main difference between the two types of plants is the different winter hardiness and requirements for growing conditions.
Description of jasmine Komsomolets
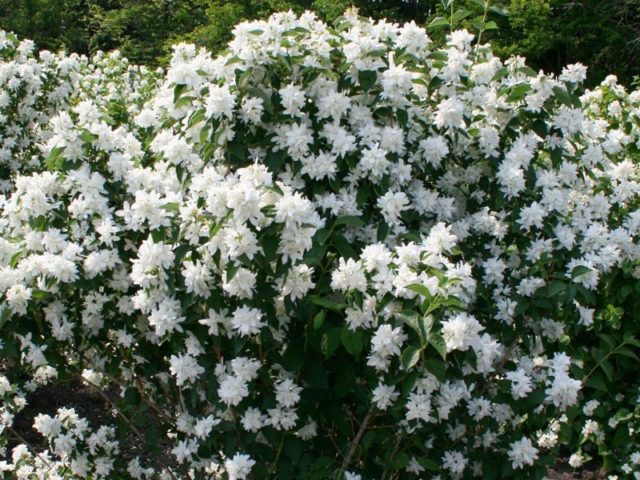
Chubushnik Komsomolets is a compact bush reaching a height of one and a half meters.Its erect stems and slightly curved flowering shoots fall apart and retain their shape during development.
Petiolate, on top - dark green jagged leaves in the axils of the veins are covered with small hairs. The bottom of the leaf is much lighter than its top side. The color of the foliage does not change with the seasons. Sometimes by autumn the leaves turn a little yellow.
Jasmine (1) and Chubushnik (2) in the picture:
How the mock orange Komsomolets blooms
Mock orange flowers are located on rejected flowering shoots. At a distance of half a meter, up to 11 strong shoots can develop, ending in dense bunches of inflorescences that contain up to 9 white double flowers.
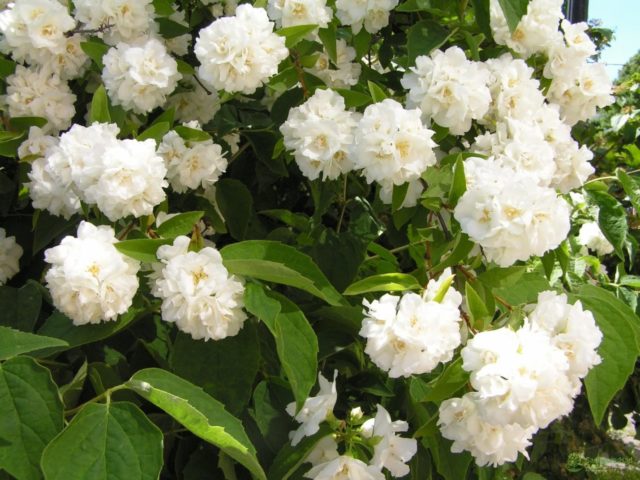
The flowers of the Komsomolets mock orange are very beautiful. The lower petals are thin lanceolate. The middle ones are twisted into a ball, through which light yellow stamens are visible. Fragrant inflorescences are located along the entire length of the flowering shoot.
Mock orange (jasmine) flowers Komsomolets in the photo:
Chubushnik Komsomolets is an early flowering crop. Snow-white flowers strew the bush from early summer to mid-summer.
Komsomolets can be grown in areas with low light. But in order for the flowering to be lush and long-lasting, you need to plant the shrub in a place illuminated by the sun most of the day.
Main characteristics
A special feature of the Komsomolets variety is its frost resistance. In central Russia, Siberia and the Urals, you can grow ornamental shrubs without shelter for the winter.
The Komsomolets mock orange is not afraid of returning spring frosts and sharp continental winds.Occasionally, in winters with little snow, young shoots may suffer from frost. But this has almost no effect on the decorative qualities of the shrub.
The Komsomolets variety is highly resistant to diseases that often affect mock orange. With proper care and timely thinning of damaged shoots, remedies for fungus and other diseases will not be required.
Features of reproduction
To propagate Komsomolets mock orange, all methods are used. But given that Komsomolets is a hybrid variety, when growing a new plant from seeds, its main varietal qualities may be lost.
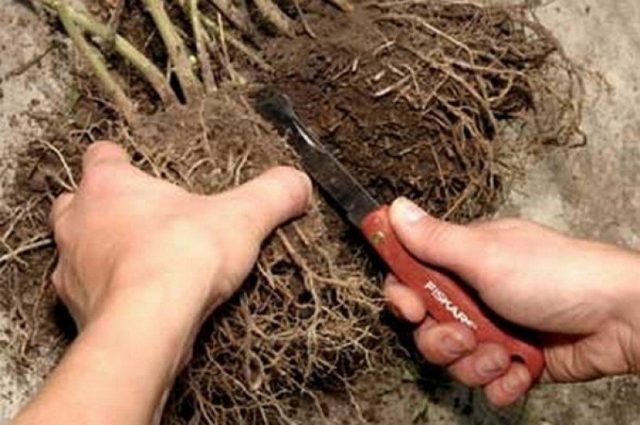
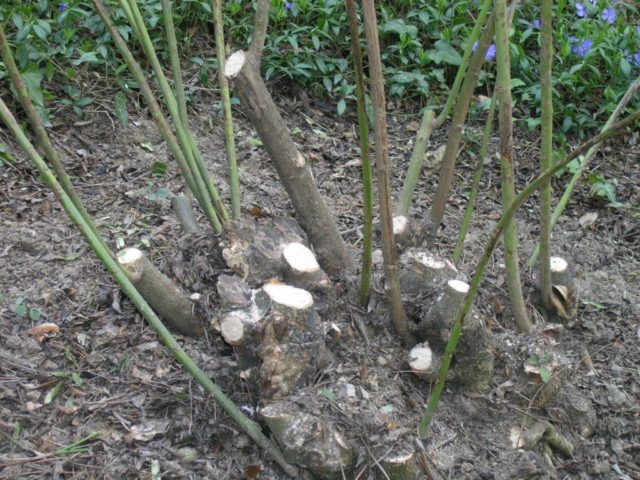
Dividing the bush is carried out on old, heavily overgrown bushes. The dug up plant is divided into several parts so that enough roots remain on the new seedling. This method is labor-intensive. It is difficult to dig up a powerful branched root system without damaging it.
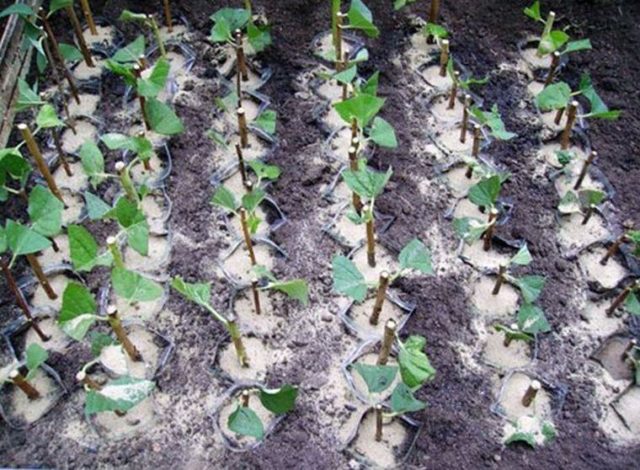
It is easy to propagate Komsomolets mock orange from cuttings. Shoots of both the first year of life (green) and older, woody ones are suitable for this. The cuttings are cut and rooted. Young healthy seedlings can be planted in a permanent place within 2 - 3 months after cutting the cuttings.
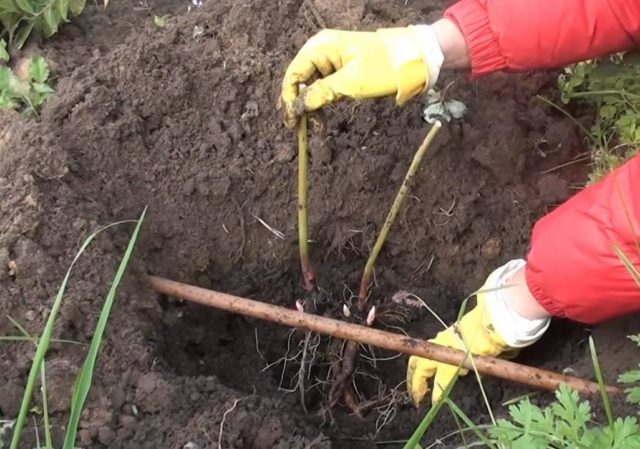
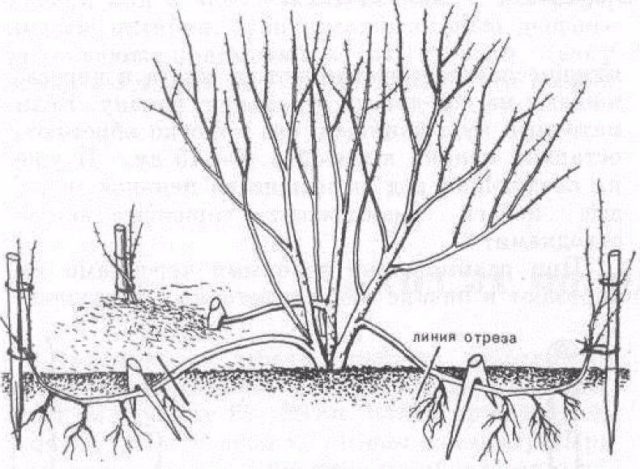
It is very easy to breed Komsomolets mock orange in a plot of cuttings. This method does not require special effort or care. The lower branches are dug in in early spring and watered throughout the season along with the main plant. By autumn, seedlings can be separated from the mother bush and planted separately.
Planting and care
Planting and caring for mock orange is not particularly difficult. The main thing is to take into account the requirements specified in the description of the mock orange variety Komsomolets.
Recommended timing
Mock orange can be planted in both spring and autumn.An autumn procedure is preferred, which is usually carried out from early September to mid-October, depending on the climate in the region. A young mock orange seedling needs time to take root before the onset of frost.
The spring planting period for mock orange is very short. It is necessary to identify the seedling in a permanent place before the first leaves appear on the trees.
Site selection and soil preparation
Gardeners classify mock orange as a crop with minimal requirements for growing conditions. But even for this unpretentious shrub it is worth choosing the right place in the garden in order to reveal the full potential of the jasmine (mock orange) Komsomolets, indicated in the description of the variety. Photos and reviews of Komsomolets owners indicate that the shrub requires a lighted area with fertile soil.
Mock orange is too free-loving to grow next to large trees and shrubs. Garden jasmine does not tolerate thickening. As a result, its inflorescences become smaller and its decorative effect is lost.
Mock orange does not like close proximity to groundwater. In a damp area, the root system of the crop may suffer from root rot or other diseases caused by high humidity.
Mock orange can grow on loams. But flowering when grown in dense soil will be poor. To plant shrubs in the garden, you need to prepare a fertile soil mixture of turf soil and high-quality humus. On clay soils, sand may need to be added. You can use an artificial soil loosener (vermiculite) to improve soil breathability.
For normal development, young mock orange will need a lot of nutrients. To improve the quality of the soil, add a glass of wood ash and 1 - 2 tablespoons of superphosphate to the soil mixture.
Landing algorithm
The planting hole must be prepared in accordance with the size of the seedling's root system. When planting several bushes, they should be placed no closer than half a meter from each other. The depth of the hole should be 50 - 60 cm.
The prepared hole must be filled with a coarse drainage mixture. You can use broken bricks, pebbles or artificial drainage. The layer should fill the hole about a quarter.
Mock orange takes root well when planted “in the mud.” The hole is filled with water and the seedling is placed vertically along with a lump of earth.
The evenly poured soil mixture must be compressed to avoid the formation of air cavities around the root. You need to observe the condition of the tree trunk circle for several days. If the soil shrinks significantly, the soil should be added until it is level with the surrounding area. After this, you can mulch the tree trunk circle.
The depth of the root collar can reach up to 2 - 3 cm. This will speed up the growth of shoots, but will slightly delay the start of flowering.
To speed up the growth of shoots, gardeners cut off most of the shoots from the seedling.
Growing rules
The unpretentiousness of mock orange allows you to grow the shrub with virtually no maintenance. But for hybrid varieties, such as Komsomolets, this method is not suitable. In order for the hybrid variety to appear in all the glory of its flowering, it requires regular feeding and watering.
Watering schedule
Mock orange needs to be watered regularly.The shrub is especially demanding of soil moisture during the flowering period. Lack of moisture can cause the delicate snow-white flowers to drop early.
After flowering has finished, you can water the mock orange as needed during the dry period. Excess moisture is harmful to the plant.
Weeding, loosening, mulching
As when caring for any plants, it is necessary to remove weeds from the tree trunk. The mock orange will then not have to share the nutrients it needs for normal development with the weed.
Loosening is carried out 3-4 times per season to a depth of about 5-6 cm. This technique will prevent caking of the soil and provide air access to the root system.
It is recommended to mulch the tree trunk circle every time after watering. A layer of mulch around the tree trunk will help maintain moisture levels.
Feeding schedule
If the composition of the soil during planting was sufficiently saturated with useful substances, then the first fertilizing can be carried out in the third year after planting the mock orange in the garden.
Mock orange is fed no more than twice a season. In spring, more nitrogen fertilizers are required. You can use organic matter or mineral mixtures with a high nitrogen content.
Fertilizers can be applied in the spring using a dry method or in the form of a solution. Nitrogen-containing preparations are scattered on the snow cover around the bush in early spring. The disadvantage of this method of feeding is the inability to correctly calculate the dose of the drug due to the action of melt water.
Gardeners with experience in growing ornamental shrubs advise adding a bucket of mullein solution (1 to 10) or bird droppings (1 to 20) under the mock orange bush.
Autumn feeding should prepare the bush for wintering.To ripen young shoots and increase frost resistance in September - early October, mock orange is fed with complex preparations of potassium and phosphorus.
Trimming
Formative pruning is carried out gradually, starting from the third year of the bush’s life. Within 2 - 3 years, the required shape of the bush is formed. Subsequently, the crown is adjusted by trimming overgrown branches that have strayed from the composition.
Sanitary cutting is carried out in early spring. Remove all damaged and dried branches. In rare cases, shoots that grow inside the bush and interfere with the movement of air in the crown are removed.
The main pruning is recommended to be done after flowering. During this period, you can remove the tips of flowering shoots, cut out excess young growth and remove old branches (more than 8 years).
Preparing for winter
Mock orange bushes require special preparation for winter for 1 - 2 years. Older Komsomolets bushes winter well in open ground without shelter.
The young bush needs to be tied with twine and covered with cloth. The tree trunk circle can be mulched with a thick layer of peat or rotted manure. In this case, you should not feed the bush in the spring to avoid fattening.
Pests and diseases
Komsomolets is particularly resistant to diseases. Only with improper care, planting in a wetland or excessive watering can the root system suffer from rot. This disease is easier to prevent than to cure.
For treatment, it is necessary to drain the area around the bush and treat it with standard fungicides. If the disease is neglected, the bush will die in a short time.
Among the pests, legume aphids, leaf weevils and spider mites like to feast on the sap and foliage of shrubs. Insects are especially dangerous for young seedlings. To control pests, it is recommended to use systemic insecticides for universal use.
Conclusion
Chubushnik Komsomolets goes well with flowering shrubs of different colors. You can create a unique fragrant corner in the garden if you plant mock orange, lilac and weigela nearby.