Content
The bee pavilion simplifies the process of caring for insects. The mobile structure is effective for maintaining a nomadic apiary. A stationary pavilion helps save space on the site and increases the survival rate of bees during wintering.
Advantages of pavilion beekeeping
The first pavilions appeared in European countries. In Russia, the technology began to develop later, and gained popularity in the Urals and the North Caucasus. Pavilion beekeeping differs from the traditional method. Bee hives are replaced by special cassette modules. Insects live in their houses all year round. Bees fly out into the street through their entrances. To make it easy for returning insects to find their entrance, beekeepers mark each entrance hole with colorful figures.
The popularity of pavilion content is due to a number of advantages:
- Good mobility of the mobile pavilion during migration.
- Easy to maintain. During the move, hives constantly need to be loaded and unloaded from the car trailer. It is enough to transport the pavilion to another location.
- The pavilion always maintains optimal conditions for hatching the uterus. There is no such possibility in hives. The process will depend on weather conditions.
- The presence of a mobile house helps to increase honey collection.
- An optimal microclimate for bees is created inside the pavilion. Insects overwinter and develop better.
- Bee families living in one large pavilion create less danger to humans and animals than insects whose hives are scattered over a large area.
Stationary and mobile pavilions are primarily compact. In a small area you can support a large number of bee colonies.
Types of beekeeping pavilions
If we talk about the fundamental differences between the pavilions, there are only two of them. Structures can be mobile or stationary. The minor differences are in size, design and other minor details.
Stationary pavilion for bees
The appearance of the stationary pavilion resembles a wooden utility block. The house is installed on a strip or column foundation. A stationary pavilion has several advantages over its mobile counterpart:
- lighting, water supply, sewerage can be installed in the house;
- For heating in winter, heating is supplied to the pavilion.
In fact, a stationary house is a full-fledged residential complex for bees. The supply of communications facilitates the process of servicing the apiary. Heating makes wintering safe.The bees do not weaken, and the stronger bees begin to work more intensively in the spring.
Stationary pavilions are convenient for wintering bees even without heating. There is enough natural heat inside the house. They try to place a permanent building on the site so that the long side wall faces southwest or southeast.
The roof for a stationary structure is made of two types. A less successful option is considered to be a gable one without opening hatches. Windows are provided on the walls, but in order to open them, free space must be left for access. The best option is a flat roof with opening hatches. Space is saved inside such a building, since cassettes with bees can be placed close to the wall.
Cassette (mobile) pavilion for bees
The main structure of a mobile pavilion is no different from a stationary bee house. The same wooden building with a flat or gable roof. The main difference is the lower part. If a foundation is poured for a stationary house, then the mobile structure is placed on a chassis.
Usually the chassis is a trailer of a truck or agricultural equipment. During construction, it is jacked up and placed horizontally on supports. The sides of the trailer are removed, leaving only the frame. It will serve as a foundation. The metal frame of the future house is welded to the size of the frame. Sheathing is done with chipboard, boards or other material.
For stationary use, the building can stand on supports. At the beginning of the season, the structure is raised with jacks. The supports are removed from under the trailer. The pavilion with the bees is hooked to the car and taken out to the field closer to the honey plants.
The cassette mobile design has many advantages:
- Increasing the harvest due to the access of the apiary directly to the seasonal flowering honey plants. Honey yield doubles. Overcoming a shorter distance, the bees bring 100% of the collected product to the honeycombs.
- The beekeeper is given the opportunity to obtain pure honey from one variety of honey plant. Bees will only carry the product from flowers growing nearby. During the season, with frequent moves, you can get several varieties of pure honey, for example: acacia, sunflower, buckwheat.
- The ease of maintenance of a mobile pavilion is the same as that of a stationary structure. The bees remain in their houses for the winter.
The only disadvantage of the mobile pavilion can be considered the impossibility of supplying communications. However, plumbing and sewerage are not so important for bees. Elements of comfort are in demand by beekeepers. As for lighting and heating, wiring is needed. During the winter, the house stands in the yard. The cable is connected to the home electrical network. Light appears inside the pavilion. Heating for bees is provided by electric heaters.
How to make a cassette pavilion for bees with your own hands
The construction of the pavilion itself is no different from the construction of an ordinary barn. In general terms: first, they prepare the base (a foundation or a trailer on wheels), create a frame, sheathe it, and install a roof, windows, and doors. Initially, you will need to think about the layout. If you make a mobile pavilion for bees with your own hands, then you need to position the change house correctly.
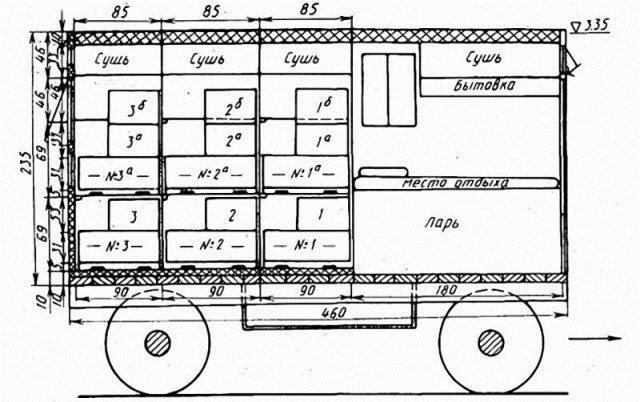
To accommodate many bee colonies, a standard size trailer for a large house is not enough.The frame is lengthened, which increases the load on the rear axle. To distribute it evenly, the cabin is located in front on the side of the coupling with the car. It is optimal to make a drawing before starting construction, think through all the nuances, and calculate the consumption of materials.
Drawings of pavilions for bees
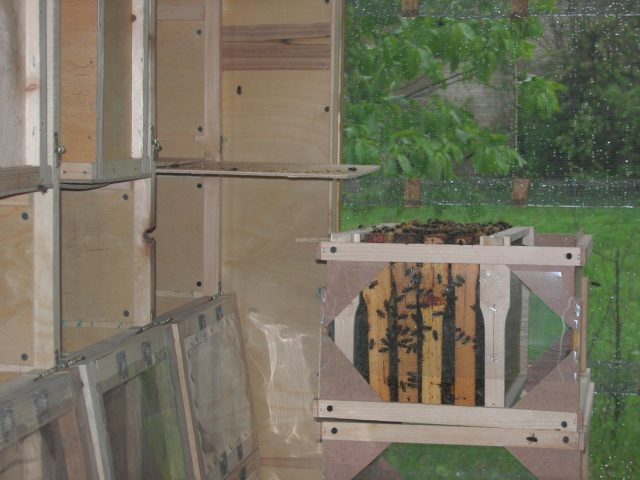
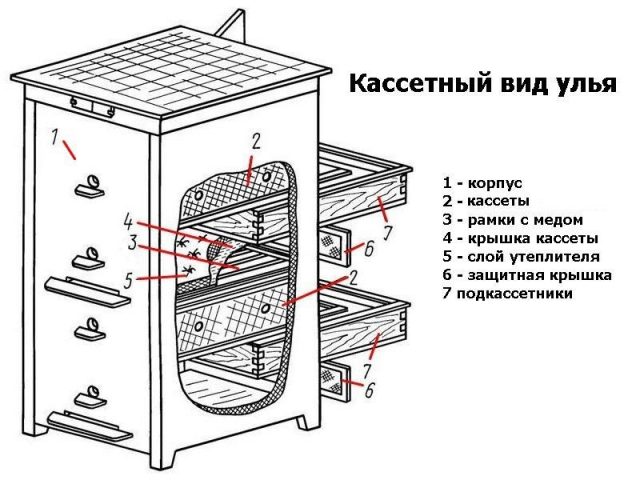
The interior of the large pavilion is separated by partitions. 5-12 cassette modules are installed vertically in each compartment. They must be the same size. Cassette modules are often made to fit 450x300 mm frames. It is advisable to install no more than 60 cassette hives inside.
The cassette module or hive consists of a housing. Cassettes with frames are inserted inside. They are closed with protective covers. The cassettes rest on the cassette pods.
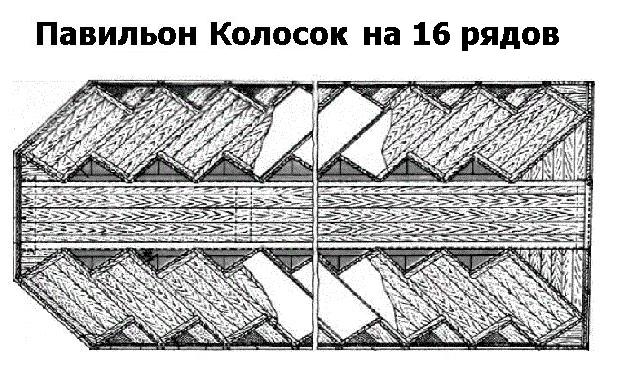
The Kolosok pavilion, which can accommodate 16 rows of cassette modules, is considered convenient for keeping bees all year round. They are installed at an angle of 50 to the passage O. The front of the spikelet is always placed on the south side. Then the cassette modules of the rows will be deployed to the southwest and southeast.
Required tools and materials
The materials for the base of the mobile structure will require a trailer. The foundation of a stationary building is poured from concrete, pillars are laid out from blocks or screw piles are screwed in. The frame of a mobile house is welded from a profile or pipe, and a stationary pavilion is assembled from timber. For cladding, the best material is board or wood boards. The roof is made of lightweight roofing materials.
For work you will need woodworking and construction tools:
- hacksaw;
- Bulgarian;
- electric drill;
- hammer;
- jigsaw;
- welding machine.
The entire list of tools is impossible to list.It will depend on the type of construction and materials used.
Construction of a pavilion for bees
In general terms, the construction process consists of the following points:
- Decor. In terms of size, the building is erected with a maximum of 20 compartments for the installation of cassette modules. With more numbers, the bees will crowd each other. For a permanent building, an optimally convenient location is initially selected, away from people and large numbers of animals. After assembling the frame of the house, it is optimal to start manufacturing and installing cassette modules. They are connected to each other and only then a common roof is erected.
- Compartments. The inventory compartment and change house in a stationary building are located at your discretion. On a mobile pavilion they are provided in front of the trailer near the coupling with the car. Compartments for keeping bees in modules are located in one or opposite directions. The Kolosok scheme is considered more convenient.
- Lighting. The bees and beekeeper will not have enough natural light through the windows. Wiring is laid inside the house and lights are connected.
- Change house. The design of a beekeeper's closet involves the installation of cabinets for storing clothes, bee feed, and work equipment. In the case of a mobile apiary, a place to stay for the night is provided.
- Thermal insulation. For optimal wintering of bees, all structural elements must be insulated. If the walls are made of boards, then additional thermal insulation is not needed. When using plywood, double skin the frame. The void is filled with insulation, for example, mineral wool. More attention is paid to insulating windows, doors, and ceilings, since it is in these places that large heat losses are observed.
The roof is made strong, but light.There is no need for extra load, especially if the apiary is of a mobile type.
More details about the pavilion for keeping bees are described in the video:
Ventilation in the pavilion for bees
Natural ventilation from spring to autumn is provided by ventilation through windows and doors. In winter, a lot of dampness accumulates inside and around the cassette modules. Humidity increases greatly in stationary houses on strip foundations. Based on reasonable considerations, it is better to install non-mobile buildings on columnar or pile foundations. Additionally, supply and exhaust ducts with adjustable dampers are equipped. Natural ventilation is arranged so that in winter moisture escapes along with stale air, and heat is retained in the modules.
Rules for keeping bees in pavilions
The first important rule for keeping bees is the presence of high-quality heating and ventilation inside the pavilion. In winter, death is detected by inspection. If a good microclimate is maintained inside the pavilion, the bees practically do not die. Feeding is carried out through feeders. They are attached to the doors of cassette modules. The amount of feed is checked by inspection through the transparent wall of the feeder. In February, Kandy is used for feeding. To prevent the food from drying out, it is covered with film on top.
Conclusion
A bee pavilion initially requires manufacturing costs. In the future, bee maintenance will be simplified, the beekeeper will receive more honey, insects will endure winter more easily, and the amount of death will be reduced.