Content
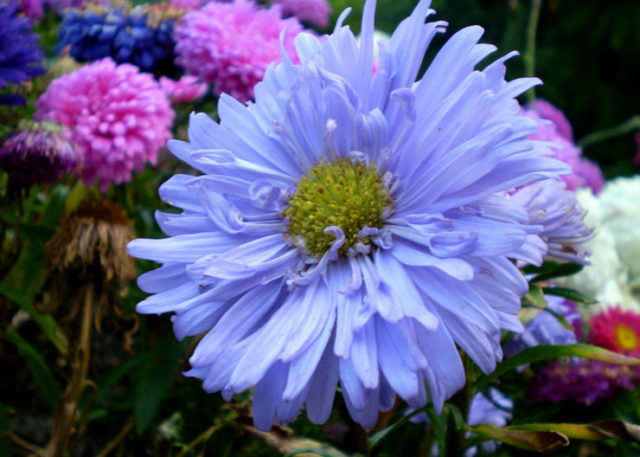
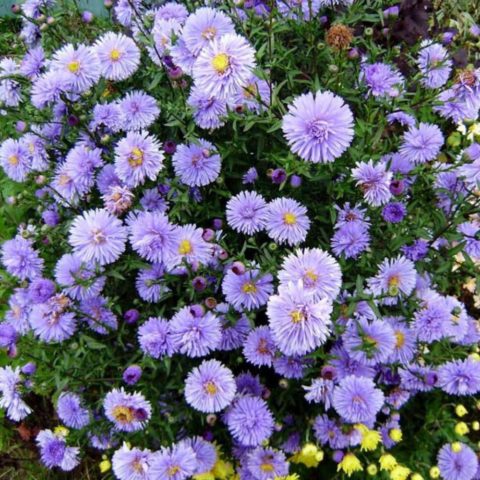
The annual aster is one of the most popular garden flowers. With great success in Russian latitudes, the plant is used for landscape design of various stylistic directions. During the times of the former Soviet Union, on the first day of school on September 1, smartly dressed students went to school with bright and colorful bouquets of asters. The variety of colors, varieties and types of this crop is truly impressive.
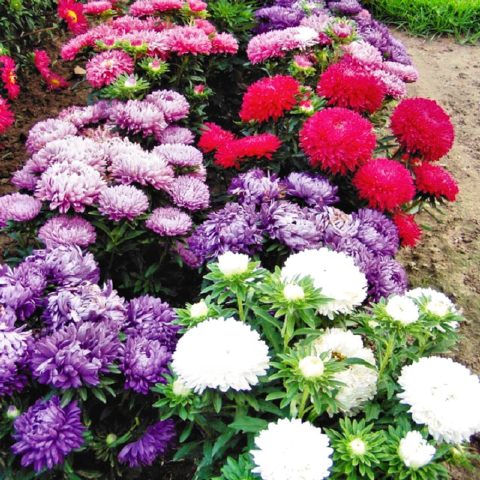

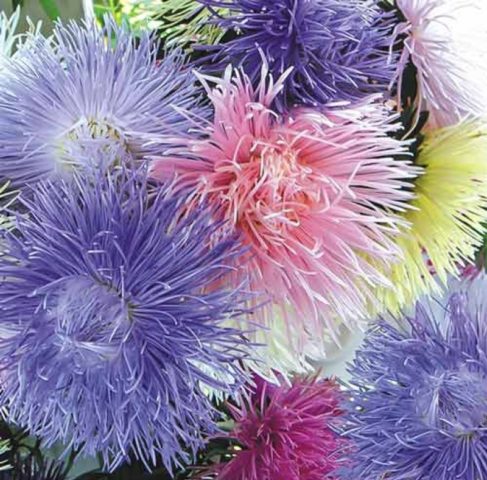
The riot of colors of annual asters allows you to create impressive landscape areas
General description of annual aster
Asters are annual flowers, numbering more than 200 different species, which are characterized by the following general characteristics:
- plant height 30-100 cm;
- fibrous root system;
- erect, branched green stems with short hairs (sometimes with a reddish tint);
- number of leaves on the stem - 10-15 pieces;
- oval-diamond-shaped, lanceolate, petiolate, slightly pubescent leaves of green or dark green color;
- basket-shaped inflorescences;
- petals in the form of tongues along the edges of the inflorescences;
- petals in the shape of small tubes in the middle of the inflorescences;
- flower diameter is from 3 to 18 cm (depending on the variety).
In China (the plant's original habitat), the aster is compared to a star. In the Celestial Empire, this representative of the world of flora is associated with elegance and beauty, a priceless gift from heaven.

Astra - “star living on earth”
Classification of varieties of annual asters
Classic annual asters are a decoration for any flower bed. Currently, there are more than 40 groups of annual Callistephus chinensis, varieties (more than 4000 different names) of which are divided into the following main categories:
- by inflorescence size: large and medium;
- by height and size of the bush: dwarf (up to 25 cm - Monpasier, Olympiada, Border, Pinocchio), short (up to 30-35 cm - Triumph, Lilliput, Scarlett, Milady), medium-sized (up to 50-60 cm - Pompom Princess, Laplata , Comet, Needle, Victoria), tall (up to 80-85 cm Blue Frost, Artistic, Rose-shaped, Peony-shaped), giant (up to 100 cm Pink King, Cutting, Royal);
- according to the shape of the bush: pyramidal, oval, columnar, wide dense, wide spreading;
- according to the structure of the bush: highly branched, spreading, weakly branched, compact;
- by inflorescence size: small (up to 4 cm in diameter), medium (up to 9-11 cm), large (up to 9-12 cm), giant (over 12 cm);
- according to the shape of the inflorescence: spherical, hemispherical, flat-round, flat;
- according to the texture of the inflorescence: densely double, double, semi-double and non-double;
- according to the structure of the flower: simple, transitional, tubular, reed, coronal, curly, spherical, hemispherical, needle-shaped, imbricated, pompom-shaped, peony-shaped, rose-shaped, “ostrich feather”;
- according to flowering dates: early (from the first ten days of July - Odarka, Ruby Stars, Carmen), middle (in the second ten days of August - Samantha, Cloud), late (at the end of August or the first ten days of September - Violetta, Anastasia, Venus);
- according to the color spectrum: single-color (except orange and green), multi-color (Gray Lady, Rainbow, Turm);
- by purpose: cutting (tall with large inflorescence), casing (short and medium-growing, for forming borders and planting flower beds), universal.
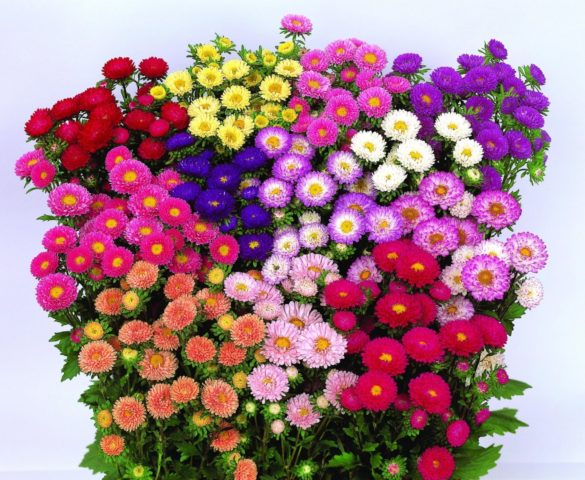

More than 4 thousand varieties and varieties of annual asters are known
Types of annual asters
Amateur gardeners have different taste preferences regarding the choice of plants. Annual bush aster is classified into the following varieties:
- tubular;
- reed;
- transitional.
Tubular group
Tubular annual asters cannot but amaze with the uniqueness of the inflorescences of each species:
- feathery - semi-double plants, with a flower diameter up to 7 cm, with long petals along the edge of the inflorescence (Oktoberfest, Rose Marie, Rosette);
Tubular, feathery annual asters - simplicity and grace in every inflorescence
- midget - double asters, up to 4 cm in diameter (Summer, Montpensier, Pinocchio);
Terry annual Lilliputian asters will decorate the flowerbed with bright wave-like patterns
- tubular - chrysanthemum type with petals in the form of neatly rolled tubes (Chocolate Girl, Memory).
On one bush of tubular asters “Memory” up to 12 magnificent inflorescences bloom, up to 10 cm in diameter
Reed group
The reed group of annuals is the most extensive and is divided into the following types:
- curly - terry, with a tubular center, with reed and curled petals at the edges (Early Miracle, Californian Giant, Ostrich Feather);
“California gigantic” from the reed group of curly asters pleases every summer with a variety of magnificent shades
- hemispherical - with inwardly curved, boat-shaped, wide petals (Duchess, Shenheit, Triumph);
The hemispherical aster “Duchess” from the linguistic group is distinguished by the widest range of colors
- radial - double asters, with narrow petals rolled along the entire length (Khudozhestvennaya, Unicum, Radio);
Ray aster “Artistic” from the reed group amazes the imagination with the beauty and modesty of pastel shades
- needle-shaped - with fused reed petals, reminiscent of needles or cat's claws (Krallen, Valkyrie, Radiant);
The beauty and grace of the needle-shaped annual reed aster "Valkyrie Brynhilda" sparkles in every tightly curled petal of the plant.
- sphericale - double with wide, short reed petals (Milady, Old Castle, Dragon);
The spherical reed aster “Dragon” from Chinese breeders is the height of perfect nobility
- tiled - with wide, short reed petals, shaped like correctly laid tiles (Royal, Dwarf, Victoria).
Reed annual asters are magnificent natural creations, delighting with a riot of shapes and colors
Transition group
The transitional (mixed) group of annuals is represented by several main species:
- coronoid - double asters with petals in the form of tubes in the center and with marginal petals in the form of reeds (Ambria, Laplata, Aurora);
The crown aster "Aurora" from the transitional group will decorate any flower garden
- simple - non-double, with two-row petals and a yellow core (Edelweiss, Margarita, Sonnenkugel);
Annual simple asters “Margarita Bogatyreva” from the group of transitional ones delight with riotous flowering almost all summer
- semi-double - with a yellow center (Anmuth, Victoria Baum, Madeline).
Transitional group of annual asters - mysterious and mysterious creations of nature
Varieties of annual aster
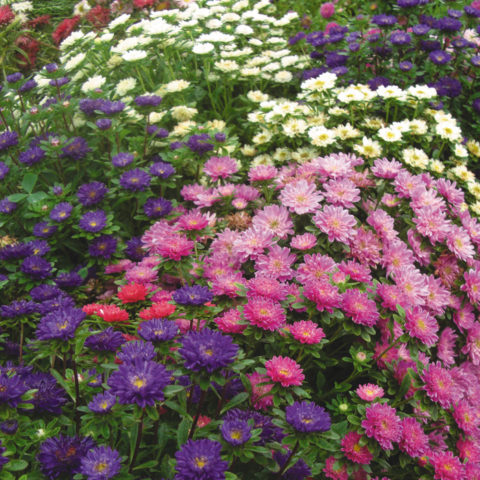
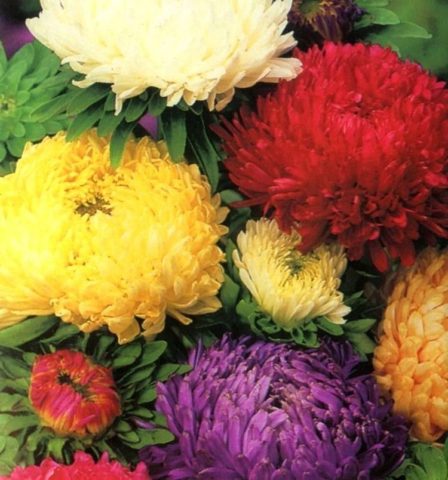
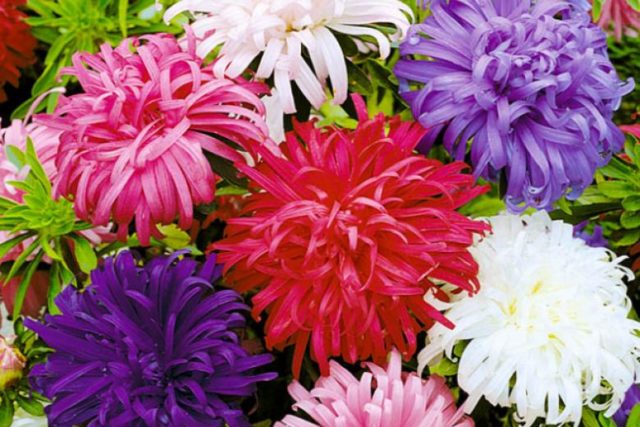
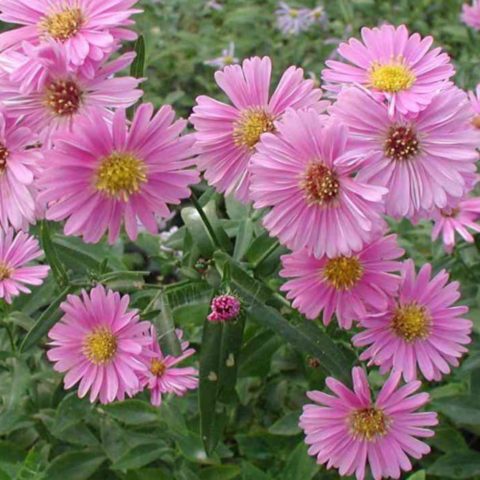
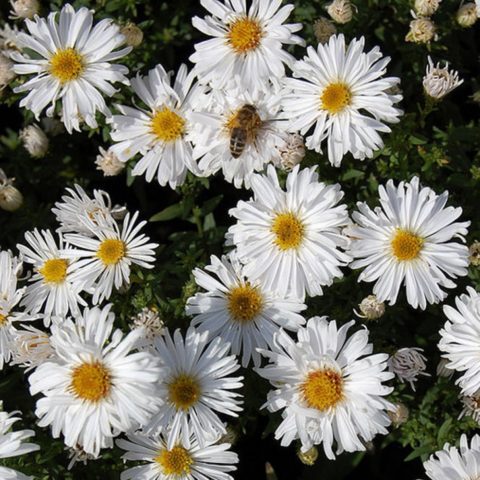
The variety of asters is the result of many years of work by professional breeders. The color palette of representatives of the world of flora varies from white to almost black tones of red, blue and purple. Annual asters differ not only in the intensity of their color, but also in the size, shape of the inflorescences, structure of the petals, and flowering time. The different varieties of annual asters in the photo allow you to visually appreciate all the splendor and diversity of natural colors and shapes.
The best varieties of annual aster
Chinese annual asters are considered the best in their category, there are more than 600 different subspecies and varieties, among which the following are mega-popular:
- Peony-shaped “Red Tower” distinguished by large inflorescences up to 10 cm in diameter. The plants look amazing in bouquets, since the height of the bushes reaches 70 cm.
The rich carmine color of the peony aster “Red Tower” will help make a bright accent on any part of the flowerbed.
- Pompom “Winter Cherry” produces up to 25 inflorescences, up to 9 cm in diameter and exhibits exceptionally lush flowering. The variety is in demand both for cutting and for group, strip, and pot plantings in landscape design.
Two rows of ruby-red petals of the “Winter Cherry” turn into a soft pink center with a yellow center, evoking associations of snow flakes on cherry berries; the flat-round flowers belong to the category of densely double
- "Princess Rita" characterized by rounded-flat inflorescences with a diameter of up to 10 cm. The plant reaches a height of up to 80 cm, so it is ideal for cutting, planting in rows and groups in flower beds, flowerbeds and ridges.
The pink-silver color of "Princess Rita" has a characteristic creamy hue and an invariably yellow core.
- Pink "Lady Coral" reaches a height of 70 cm, so it is not only a decorative decoration for flower beds, but is also used to create bouquets. Inflorescences with a diameter of up to 12 cm belong to the group of densely double, pink-shaped ones.
The luxurious salmon-pink color of the “Lady Coral” inflorescences amazes with its delicate petals arranged in the shape of a rosebud
- Needle aster "Unicum" - a unique flower, the height of which reaches 70 cm, therefore it is used for cutting and for landscaping. Pyramid-shaped bushes can have up to 30 inflorescences with a diameter of up to 15 cm.
The color range of the needle variety “Unicum” is extensive: coral, pink, red, yellow, white, purple
Bush varieties of annual asters
Bush annuals are characterized by a smaller diameter of inflorescences (about 5 cm), sufficient height of the bush (up to 70 cm). Plants are unpretentious and disease resistant. They are distinguished by lush flowering from the last ten days of July to September.Among the popular bush varieties of annual asters are:
- Variety "Bon Paris" - bushes, of various colors and shades (with thick and strong peduncles, up to 60 cm high, flower diameter up to 5 cm).
Bush aster "Bon Paris" is distinguished by a wide range of flowers and many inflorescences on one plant
- Variety "Matsumoto" - cut flowers, with semi-double inflorescences, various color combinations (white, blue, white-pink, pink, yellow, red, apricot), up to 70 cm high, diameter - up to 5 cm.
The bush aster “Matsumoto Scarlett” from Chinese breeders pleases the eye with the rich scarlet color of each petal.
- Variety "Duchess" It is distinguished by large inflorescences, ideal for decorating flower beds and borders.
New for 2019 - variety “Allure” with scarlet reed-type inflorescences
The newest varieties of annual asters
In 2019, the State Register of Breeding Achievements of Russia was replenished with the following newest varieties of annual asters:
- Variety "Allure" belongs to the Khudozhestvennaya variety, characterized by an average flowering period (up to 30 days). Plant up to 60 cm high, columnar, medium leafy. Inflorescences up to 10 cm in diameter are ligulate, double, flat-round, of medium density. Their color is bright red, the tubular core is light yellow with a green tint.
New for 2019 - variety “Allure” with scarlet reed-type inflorescences
- Variety "Nostalgia" The Radio variety is characterized by a height of up to 90 cm and an average flowering period. Bright red inflorescence up to 10 cm in diameter. The plant is intended for cutting and landscaping areas.
The newest variety “Nostalgia” (2019) was awarded a decorative score of 99
- Variety "Nochenka" belongs to the Radio variety.The universal plant is characterized by an average flowering period of up to 65 days. The height of the bush is up to 50 cm. Inflorescences with a diameter of up to 8 cm are hemispherical in shape, terry, medium density, dark purple in color.
The latest novelty “Nochenka (2019) is a specially bred variety for creating harmonious bouquets and compositions
Varieties of annual reed asters
Annual reed asters are characterized by particularly unforgettable, luxurious flowering. The structure of the inflorescences is needle-shaped, hemispherical, spherical, imbricated, curly. The most popular varieties of reed asters among gardeners are:
- Curly "Ostrich Feather" - the best annual variety with large inflorescences for decorative cutting into bouquets. The height of the bush is up to 60 cm, up to 15 inflorescences on one plant. Buds of various colors with curly petals.
Inflorescences of annual reed asters "Ostrich feather" can reach 13 cm in diameter
- Curly "California Gigantic" - a cut, beautiful annual flower with flat-round, non-drooping, double inflorescences with wide, ribbon-shaped petals curved at the ends. The height of the bush is up to 80 cm, up to 20 inflorescences on one plant.
The fabulously beautiful inflorescences of the “California Gigantic” reach a diameter of 15 cm, the ribbon petals look like curled curls and completely cover the central part of the flower
- Needle “New” - an improved variety of annual aster with double inflorescences. Bush height up to 50 cm.
Graceful needle-shaped reed petals of an amazing smoky blue hue reach a diameter of 12 cm
Varieties of tubular annual asters
Tubular annual asters are characterized by the presence of exclusively tubular petals, which form the main visual decorative effect. The most popular varieties:
- "Oktoberfest" - a plant up to 100 cm high, with pale blue semi-double inflorescences. Flowering period August-November.
Small blue inflorescences of tubular annual Oktoberfest asters reach a diameter of 3.5 cm
- "Patricia Ballard" - an elegant annual plant up to 100 cm high with pink peduncles, which is characterized by a pronounced yellow center. Flowering period is early autumn.
Refined pink inflorescences of tubular annual asters "Patricia Ballard" with a diameter of up to 3 mm delight with exuberant flowering almost before the onset of frost
- "Sam Banham" - tall plants, 140 cm in size, bloom in the second ten days of September and delight the eye with snow-white buds for more than 35 days.
The diameter of the white inflorescences of tubular annual asters "Sam Banham" reaches 3.5 cm
Planting and caring for annual asters
Planting annual asters is carried out in two ways: preparing seedlings from seeds and sowing seeds in open ground. Both methods are successfully used by flower growers in regions with different climatic conditions. Growing asters from seedlings is a more labor-intensive method, but the plants will delight you with flowering several weeks earlier than when sowing seeds in open ground.
Growing annual aster from seeds using seedlings
In prepared containers with soil, seeds are sown in grooves up to 1 cm deep and covered with plastic film to create a greenhouse effect. After the first shoots appear, the plants are placed in a place with sufficient lighting.
Aster seedlings are fertilized weekly with complex preparations. When planting seedlings in the ground in May, the seedlings are carefully separated from each other. By this time, the seedlings are characterized by strong stems up to 10 cm high and 2-3 leaves. The seedlings are transferred into the ground in the evening into prepared and fertilized soil. For this you can use dolomite flour, wood ash, humus and compost. The step (distance) between seedlings is up to 30 cm.
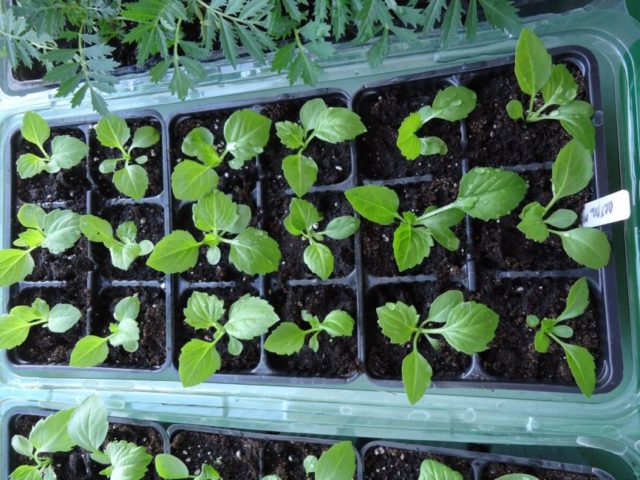

The planted seedlings are watered abundantly, then the planting area is sprinkled with dry soil.
Sowing annual aster seeds directly into the ground
Since the annual aster is a herbaceous plant for open ground, a place for sowing annual aster seeds is chosen in the fall. These should be well-lit areas, slightly alkaline or neutral soils. The beds are dug up in the fall with the addition of compost or humus at the rate of 4 kg per 1 m², potassium salt, ammonium sulfate and superphosphate. Sowing work is carried out in May when consistently warm weather sets in.
The seeds are sown in grooves 0.5-1 cm deep, after which they are sprinkled with earth. The sowing area is watered with water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate (0.5-1%), mulched with peat or special agrofilm.
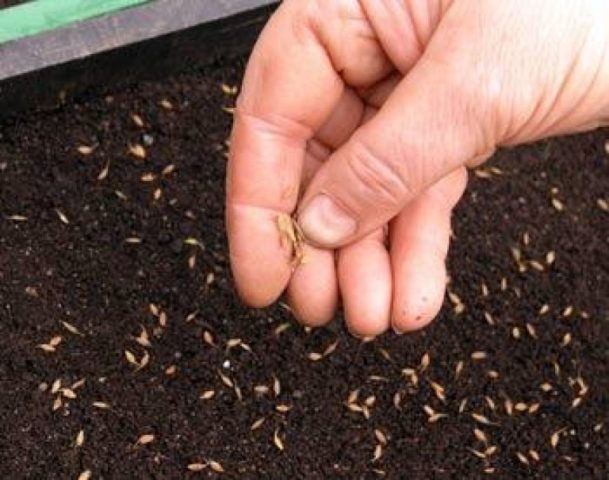

When two leaves appear, young plants are thinned out, leaving healthy and strong shoots at a distance of about 20 cm from each other
Growing annual aster in open ground
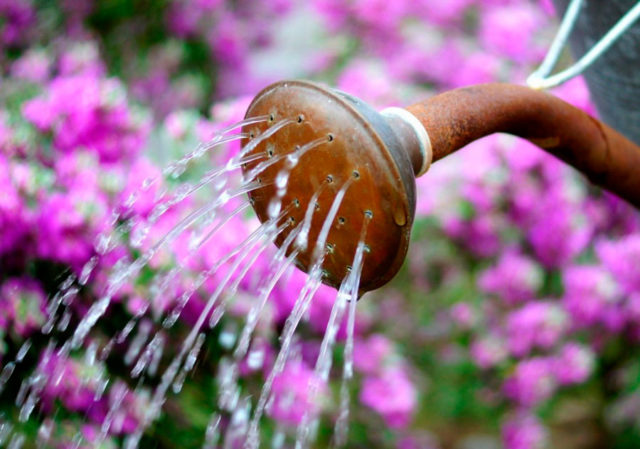
Planting and caring for annual asters is not difficult, since the plant is unpretentious and fully adapted for cultivation in Russian latitudes.Growing annual asters in open ground comes down to complete universal care: watering, loosening the soil, fertilizing, disease prevention and treatment, and pest control.
Asters are moisture-loving plants that require sufficient watering at the rate of up to 30 liters per 1 m². Experienced gardeners combine regular watering and loosening.
During the growing season, plants are fed several times:
- on the 15th day after the seedlings have rooted and the stem height reaches 15 cm, it is necessary to apply complex fertilizer;
- during the formation of buds, complex and nitrogen-containing fertilizers and ammonium nitrate should be re-applied;
- During the flowering period, fertilize the soil with wood ash, mixtures with potassium (without chlorine) and phosphorus.
For annual asters, periodic watering of plants with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (0.5-1%) is recommended.
How to collect annual aster seeds
Aster seeds are collected independently after the final wilting, drying and darkening of the inflorescences. The fluff in the center of the flower is removed and stored in paper containers. In order not to lose the distinctive features of the variety, you should buy seeds in specialized stores.
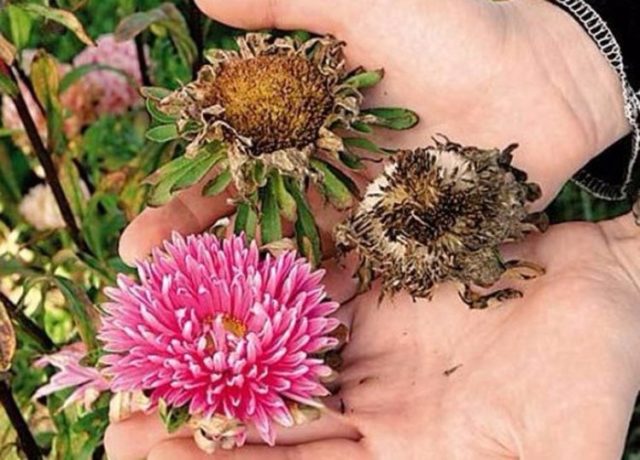

Experienced gardeners recommend collecting seeds in dry weather
Pests and diseases
Most often, annual asters are susceptible to infection by carriers of diseases such as fusarium, jaundice, gray leg, rust:
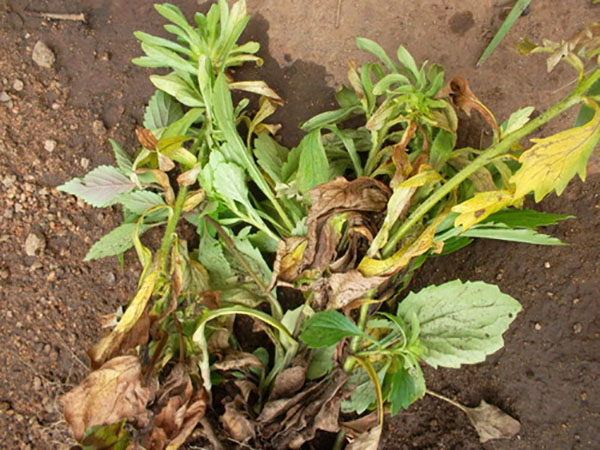
- Fusarium affects the plant during the flower formation phase. The leaves curl, turn yellow, the bud heads wither and droop. Infected plants must be destroyed. If the disease is detected in a timely manner, surviving seedlings can be treated with Fundazolom solution.
The causative agent of fusarium is the fusarium fungus, whose thick-walled spores are found in the soil
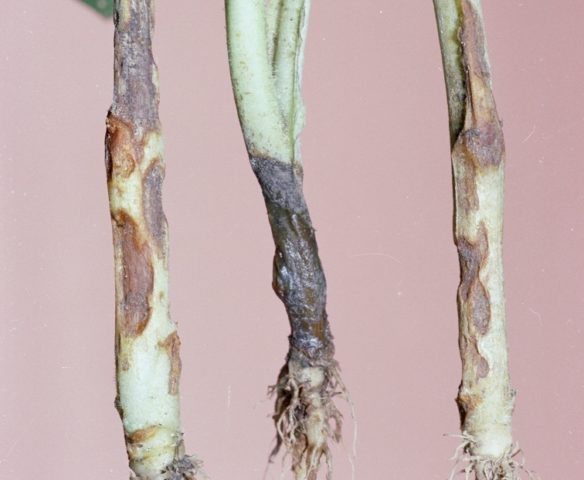
- Gray leg - fungal disease. Fungal spores colonize the aster's root system, clog the stems, causing the plant to wither, turn yellow, and the root to dry out and turn black. As preventive measures, you can use soil disinfection before sowing seeds or planting seedlings, early picking of seedlings, and complete and timely destruction of diseased plants.
Fungi that cause gray leg are present in any soil and can infect above-ground and underground parts of asters
- Rust characterized by the appearance of swellings on the lower part of the leaf, as a result of which the aster withers and dries out. To cure the plant, infected asters should be treated (sprayed) with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture or a mixture of lime and ground sulfur for 10 days.
To prevent asters from becoming infected with rust, plants must be planted away from pine trees.
- Jaundice is a viral disease transmitted by cicadas and aphids. The leaves on the asters become lighter, plant growth slows down, and the flowers acquire a characteristic green color. To combat jaundice, a set of measures is being implemented to destroy vectors.
Plants affected by jaundice must be completely destroyed
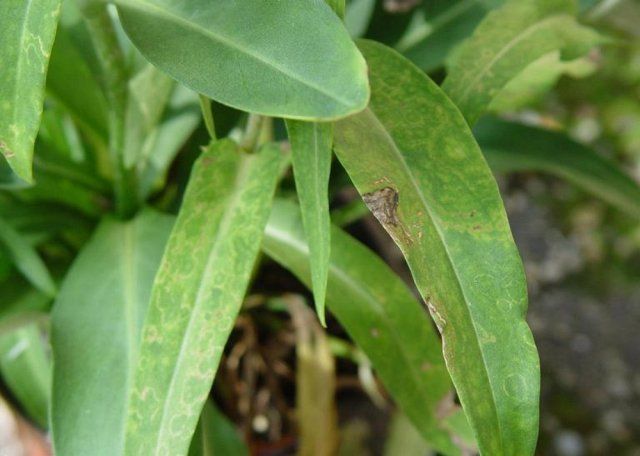
- Sepriosis, or "brown" spot, manifests itself in humid and especially hot weather at the stage of inflorescence formation. Light brown spots appear at the bottom of the plant, which will spread throughout the entire bush. To combat the disease, asters are treated with Bordeaux mixture or copper oxychloride 2-3 times with a 2-week break.
Over time, sepriosis affects the entire bush, which affects the attractive appearance of the plant
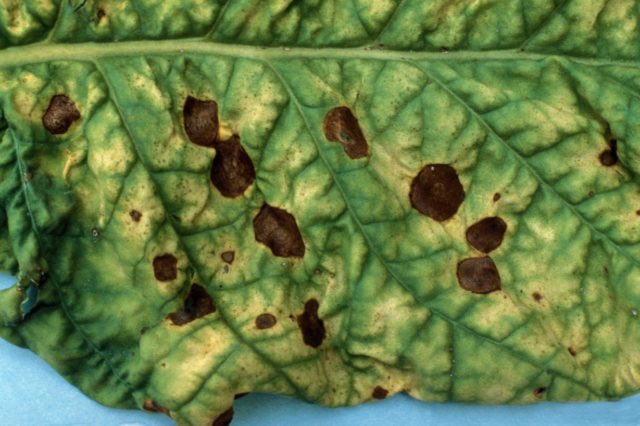
- Bacterial spot appears as brown and yellow spots up to 2 cm in size on the leaves. When the first signs of a disease are detected, plants should be provided with a dry habitat and the soil should be treated with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate and copper sulfate.
For bacterial spotting, asters are treated 3-4 times in a row, the course of treatment is repeated after 21 days
In addition, asters can be harmed by insects such as aphids, arable slugs, spider mites, and meadow bugs. If pests are detected, the flowers are treated with Metaldehyde, Fundazol, Fosfomycin, Karbofos:
- Aphid feeds on plant sap, so shoots and stems are deformed, leaves and inflorescences are twisted and secured. Aphids reproduce in dry and hot weather. Experienced gardeners recommend treating infected plants with a soap solution, infusion of garlic, onion, wormwood, a decoction of tomato tops, and Inta-Vir.
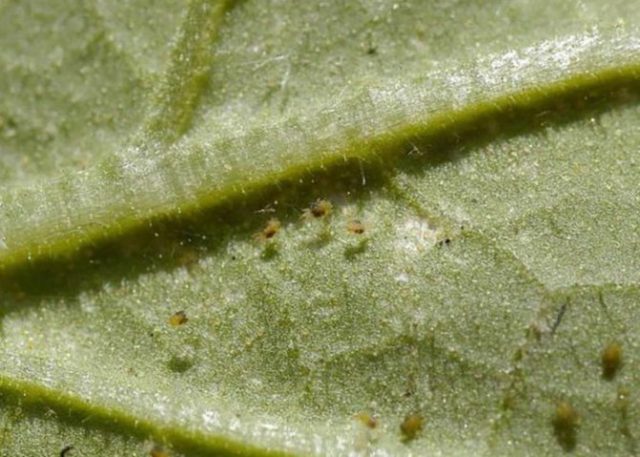
Huge colonies of pests can be found on infected asters
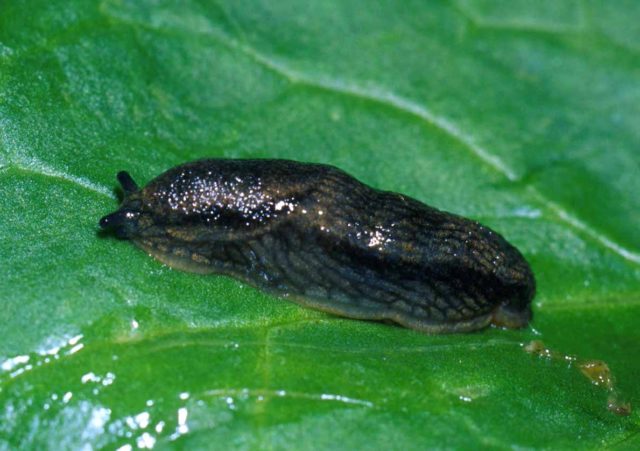
- Tilled slug eats foliage and inflorescences, multiplies quickly in a humid and warm environment. If pests are detected, visible individuals are collected manually, asters are sprayed with a solution of “Metaldehyde”, and after a week - with “Superphosphate”.
The length of the gastropod mollusk slug reaches 5 cm
- Spider mite attacks plants in hot weather. A brown cobweb appears on the bottom of the leaves; after a while they dry out and wither. As a treatment, an infusion of onion peels, garlic, dandelion, yarrow, and potato tops is used. Spraying is carried out 2-3 times every 5 days.
You can get rid of spider mites on annual aster using the insecticidal preparation "Skor" or a mixture of sulfur and lime
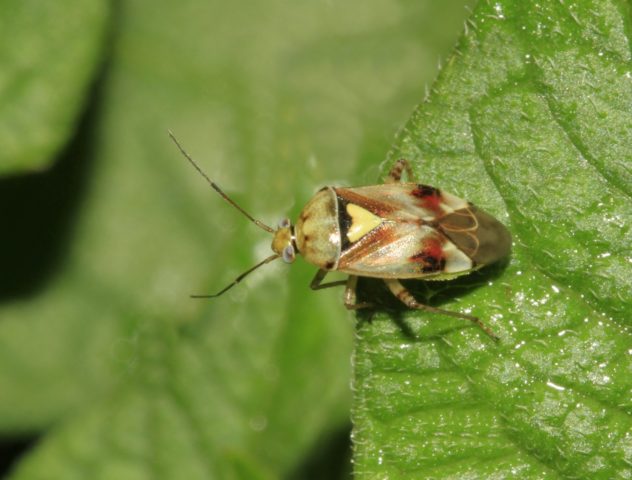
- Meadow bug feeds on the juice of buds, leaves, stems. The puncture site of the meadow bug dries up and the flowers take on an ugly appearance. For treatment, asters are treated with soapy water and insecticides.
The meadow bug is characterized by a dark brown or greenish-yellow color of the abdomen
- Sunflower moth is a small butterfly whose caterpillars eat various parts of plants in a short period of time. To combat the pest, insecticides and tobacco infusion are used.
The sunflower moth is a small butterfly with inconspicuous gray wings.
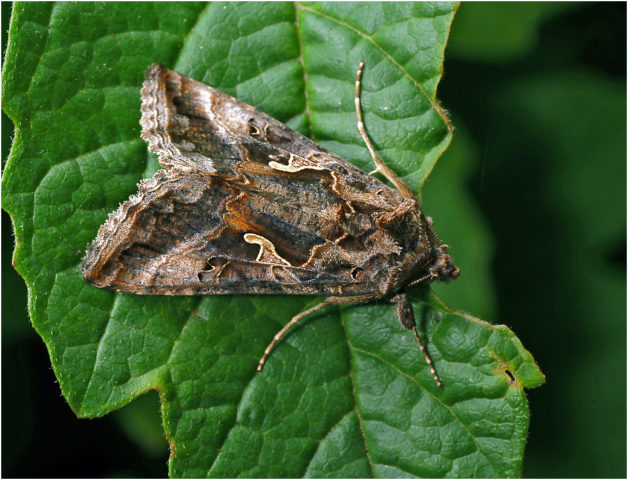
- Gamma moth caterpillars They eat the stems, leaves and inflorescences of asters. The caterpillars are collected by hand, the plants are sprayed with a soap solution of laundry or green soap, and treated with insecticides.
The length of the Gamma moth reaches 5 cm
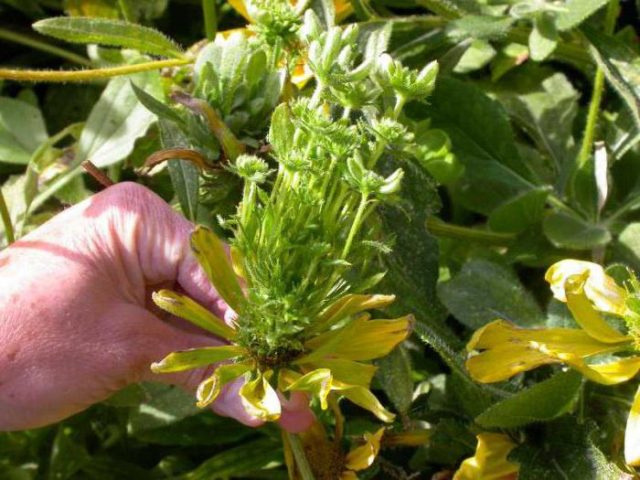
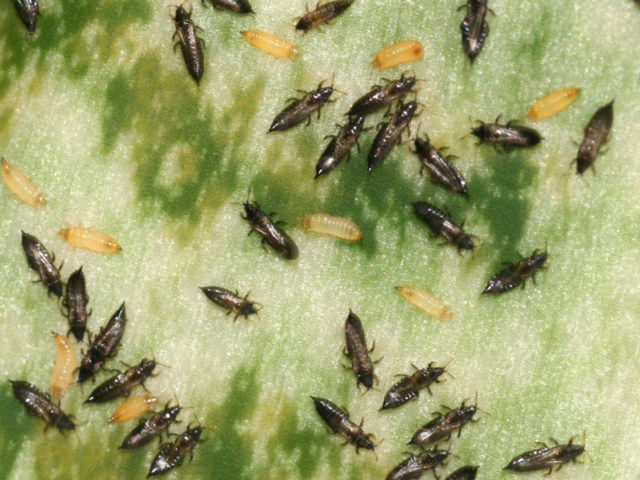
- Thrips provoke bending of the stems. The leaves of aster affected by thrips dry out and the buds fall off. To get rid of insects, damaged plants are treated with Fitoverm.
The sucking mouthparts of thrips are sharp, and several pairs of legs have characteristic teeth at the ends.
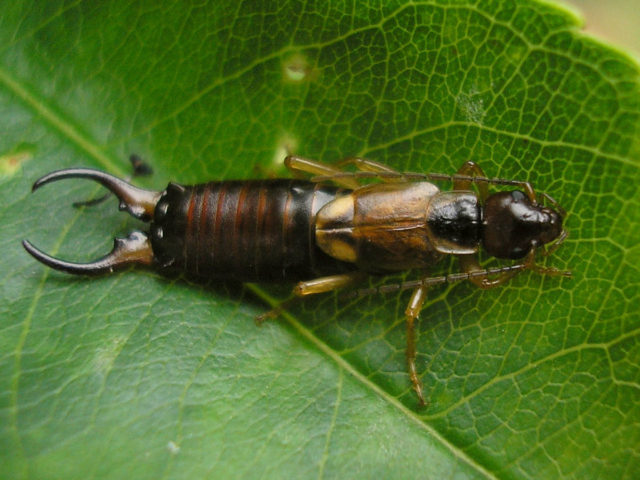
- European earwig nibbles castings, stems, and inflorescences of aster. To combat insects, a solution of potassium permanganate and insecticides are used.
The European earwig is nocturnal and avoids sunlight.
To prevent diseases and prevent the appearance of pests, you should follow simple rules for caring for annual asters:
- regularly dig up the ground for asters in the fall;
- in late autumn, after harvesting dry plants, it is necessary to completely burn faded flowers;
- Regularly fertilize the soil with complex mixtures.

If you ensure timely implementation of measures to combat diseases and pests, you can grow impeccably beautiful annual asters - real stars living on earth
Conclusion
The annual aster is a delightful natural creation that impresses with its variety of colors, shapes and sizes of inflorescences. Thanks to the different parameters of the bushes, you can create unique landscape areas and arrange bouquets with amazing design solutions.