Content
Planting and caring for loosestrife in accordance with all the rules of agricultural technology will guarantee a healthy plant with a full growing season. The crop is grown to decorate the landscape. An unpretentious herbaceous shrub will decorate any composition in the garden. To grow loosestrife (pictured), you must adhere to planting dates and crop care rules.
What does loosestrife look like?
In Russia, in addition to common loosestrife, there are 8 types of crops; decorative forms created on their basis are used in gardening.

Loosestrife prefers to settle on waterlogged soil of water meadows, along the banks of reservoirs or in wetlands
The characteristics of the plant depend on the type of crop:
- the biological cycle can be annual, biennial or multi-year, the latter option being the most common;
- herbaceous plant in the form of a bush with upright growing stems and drooping tops or a ground cover, creeping type;
- leaves are simple, with smooth edges, opposite, whorled or alternate;
- color green, maroon or variegated;
- The fruit is a round-shaped capsule.
The root system of all species and varieties is powerful, highly expanded, and creeping.
When and how does loosestrife bloom?
Flowering times depend on the variety. This is mainly June - August, the seeds of all varieties ripen in September.
How the culture blooms:
- inflorescences are corymbose, paniculate or single flowers located in the leaf axils;
- color yellow, white or pink;
- calyxes five-parted with a bright core.
The culture is characterized by intensive shoot formation, flowering is always abundant, and the bush forms are dense and dense.
Types and varieties of loosestrife with photos
Loosestrife (pictured) is a common plant in Russia, distinguished by a variety of varieties. Each of them has its own flowering period. All representatives are united by the same agricultural technology and biological requirements.
Common loosestrife
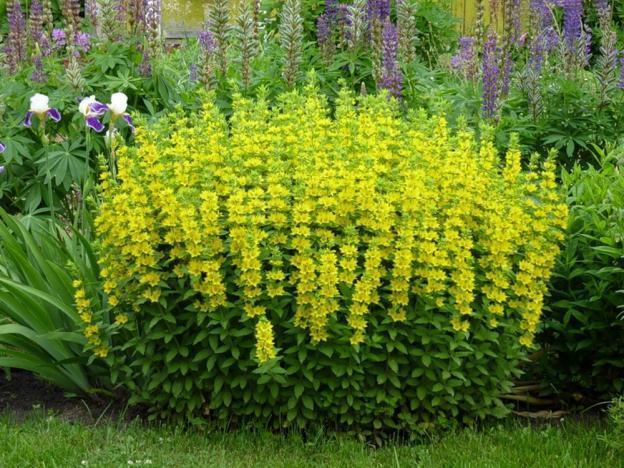
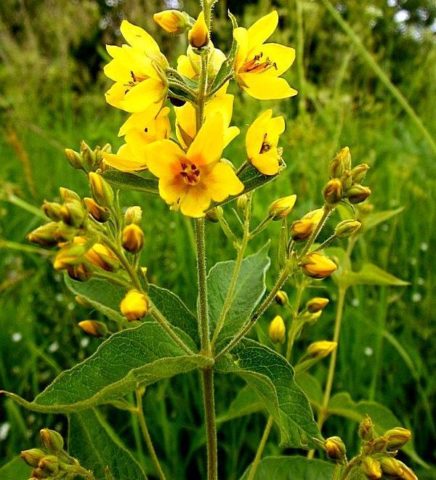
The most common species is common loosestrife, growing throughout the European part, in the North Caucasus. In the landscape it is used as a simple field plant to imitate a corner of wild nature.Common loosestrife is not used in breeding work.
Characteristics of the herbaceous plant:
- shoots are up to 1 m long, hard, pale green, with dense pubescence;
- leaves are entire, lanceolate, with smooth edges, light green, collected in whorls of 4 pieces;
- The flowers are five-petaled, bright yellow with an orange center, forming panicle inflorescences located on the tops of the shoots.
Blooms in mid-June. The plant has medicinal properties, so it is used in folk medicine.

The bush of common loosestrife is dense, blooms until early August
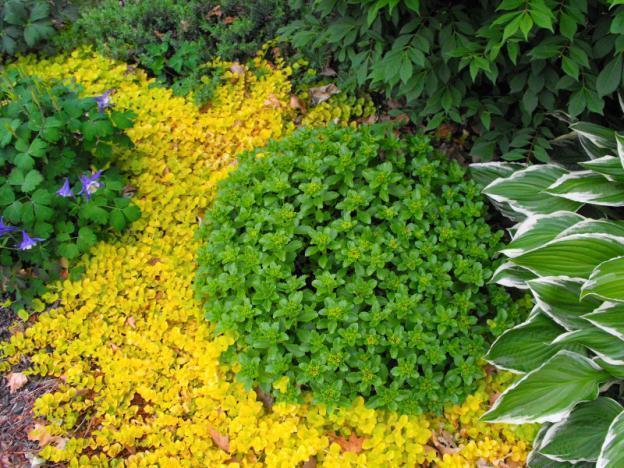
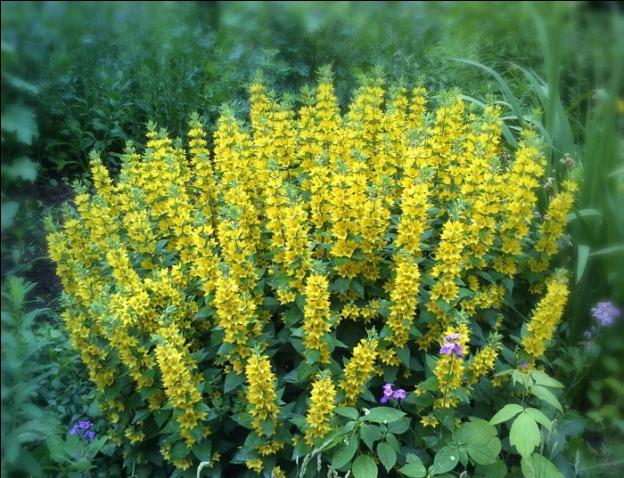
Monetary loosestrife
A ground cover variety up to 15 cm high, growing to cover an area of up to 60 cm. This is a perennial herbaceous plant with creeping stems. Root shoots are formed in the leaf axils, with which the loosestrife is attached to the surface and quickly takes root, forming a new bush.
External characteristics of the plant:
- the stem is smooth, knotty, completely covered with leaves;
- leaf blades are round, oppositely located, light green;
- the flowers are flat, reminiscent of a coin (hence the name of the species), consist of five petals with sharp tips, located singly in the leaf axils;
- the color is bright yellow, the anthers are beige, there is no obvious contrast in tone with the core.
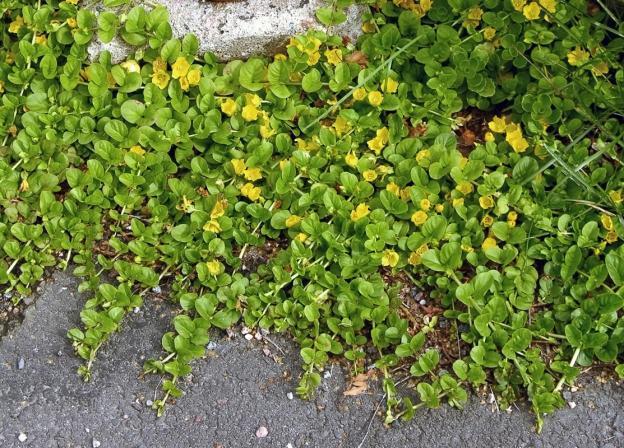

The coin variety blooms from late May to August
Presented in two varieties. Loosestrife Aurea with salad-yellowish leaves. The plant is more prostrate, the length of the stems is up to 30 cm. The flowers are single, bright yellow with black splashes.
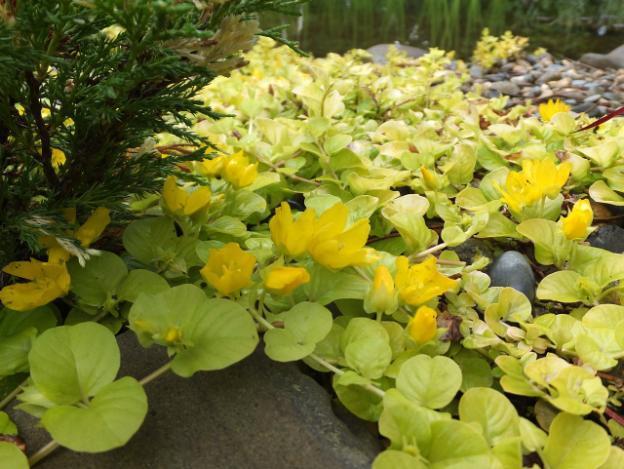

The Aurea variety is distinguished by abundant flowering, lasting from May to August.
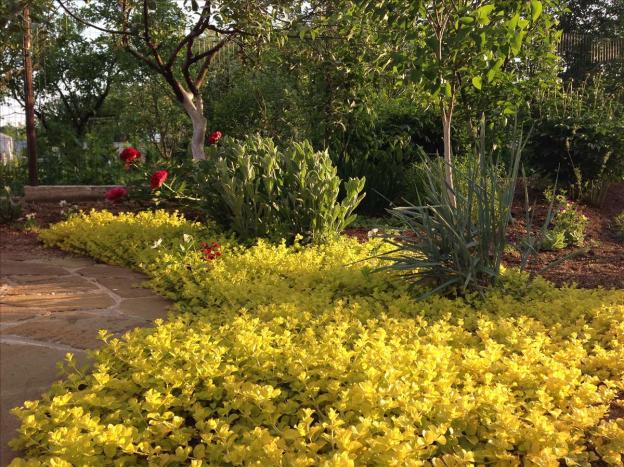
Variety Goldilocks (Goldiloks) is a groundcover perennial with long creeping stems and golden leaves.The flowers do not differ from wild plants; the species is valued for its decorative crown.
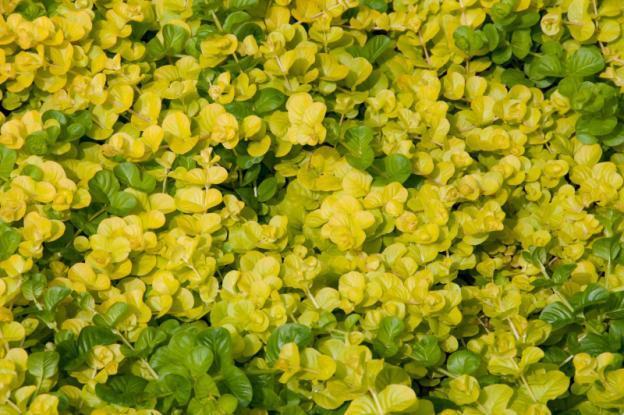

Goldilox is suitable for growing in pots for vertical gardening
Loosestrife point
Loosestrife grows in the form of a herbaceous shrub, the height of the stems is 1.2 m. The wild-growing species is characterized by yellow panicle inflorescences with drooping tops. The most common variety in gardens is Alexander. The exotic appearance of the bush is given by the unusual color of the light green leaves, which have a pronounced white border along the edge.
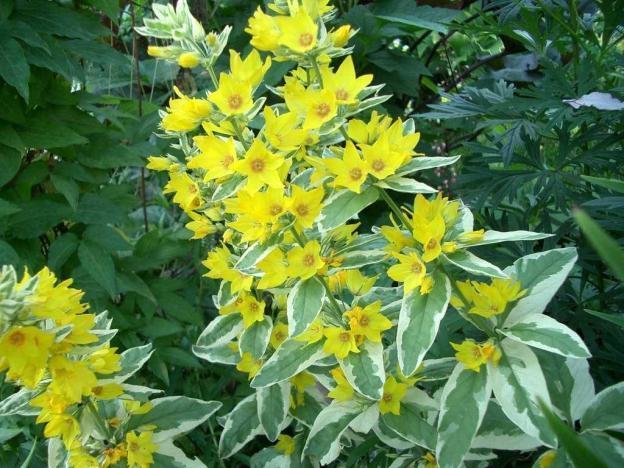

The flowering period of point loosestrife is from mid-June to the second half of August
Variety Goldilocks is a herbaceous shrub up to 1.3 m high with spike-shaped drooping inflorescences. It resembles curls of hair, hence the unusual name. The flowering of the variety is not too long, the first buds open in June, they do not bloom at the same time, so the process continues until the end of July.
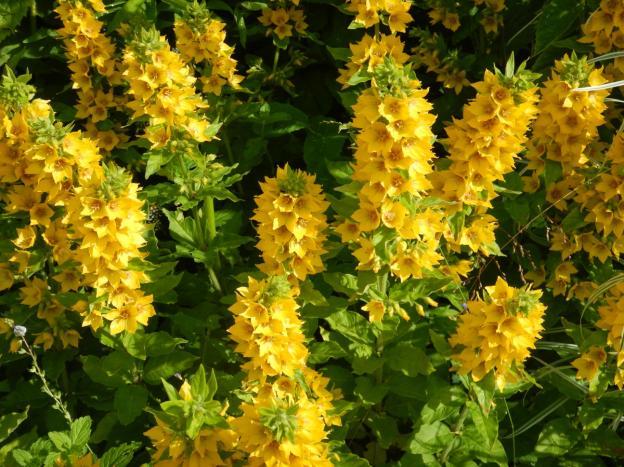

The flowers are large, orange, with a dark red or burgundy core
Loosestrife ciliated
A perennial herbaceous shrub found in the wild. Has an unattractive appearance. The bush is loose, the flowers are yellow, collected in paniculate, sparsely spaced inflorescences. The leaves are lanceolate with a brown tint.

Often found along the edges of swamps and on the banks of muddy ponds
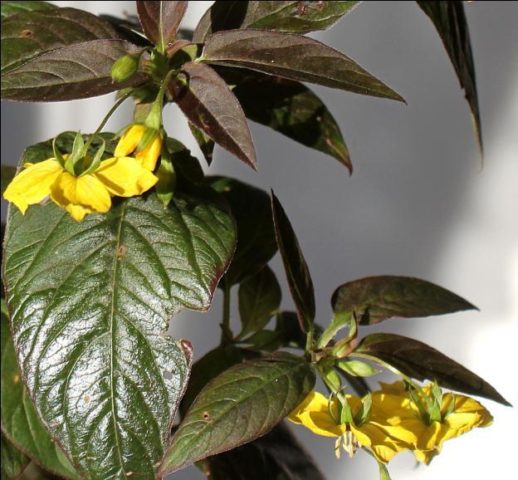
In ornamental gardening, the purple loosestrife variety Firecracker is used. Plant up to 50 cm in height with a dense crown. The leaves are dark burgundy in color, lanceolate, with a glossy surface, paired. The flowers are small, yellow, collected several times in inflorescences.
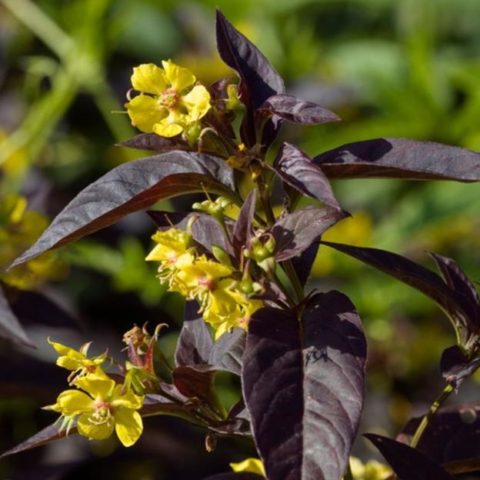

Firecracker – late variety, blooms from August to September
Loosestrife lily of the valley
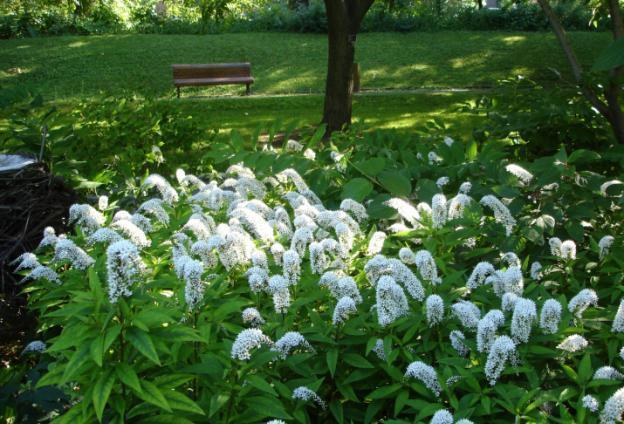
One of the rare varieties of loosestrife is considered to be the lily-of-the-valley or lily-of-the-valley.Distribution area - Primorsky Territory, less often the Far East. This is a good option for creating white gardens. Grows only in the shade on wet soil. The bush is tall, very dense, with intense stem formation. The flowers are milky white, forming a lush pyramidal inflorescence up to 30 cm high with a drooping crown.
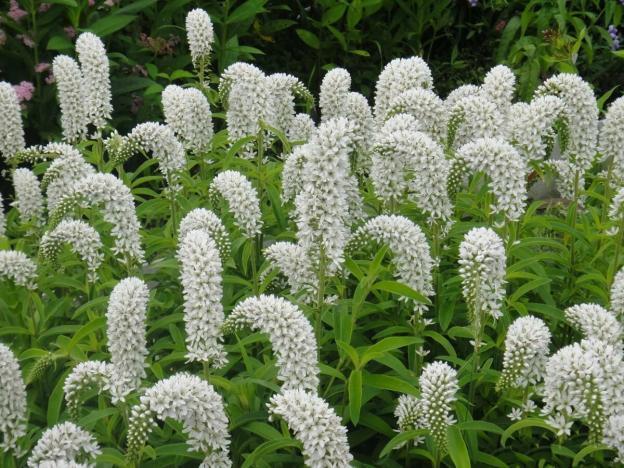

During flowering, the loosestrife bush attracts many butterflies with its aroma
The Lady Jane variety was created based on a wild crop. The bush is denser, up to 85 cm tall, the leaves are narrow, collected in whorls. The inflorescences are longer (up to 35 cm) and lush. The flowers are white with a pinkish tint and a red or crimson center.
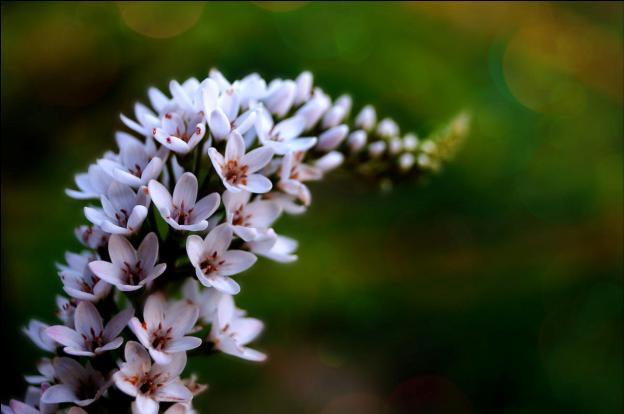

Lady Jane is characterized by late flowering: from August to late September
Loosestrife dark purple
In the natural environment, this type of loosestrife is rare; it can be found in northern latitudes. The gardens grow the Beaujolais variety, a rare seedless cultivar with dark purple flowers that form from the base of the stem and along its entire length. The shrub is 40 cm high, compact, the leaf blades are located in the lower part, oblong, with a blue tint.

Beaujolais grows only on soil with stagnant water, blooms in the second year
Loosestrife ephemerum
In nature, distributed in the Far East. The ephemerum is known as Dahurian loosestrife. The plant is endowed with medicinal properties. Rarely found in ornamental gardening. The plant forms a loose bush with long (up to 80 cm) stems, completely covered with small light red buds. When blooming, the petals appear white with a slight pink tint. The field species does not have an ornamental variety.
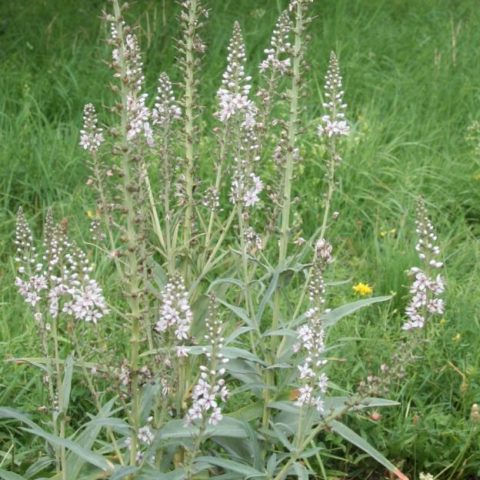

Loosestrife ephemerum is propagated on the site only vegetatively, the plant does not produce seeds
Loosestrife
The natural form of the wild species is quite decorative - it is a ground cover plant 15-20 cm high. The branches are outstretched, smooth, without root shoots. The leaves are round, large, collected in rosettes, and have a bright green color. The plant completely covers the soil with a dense green carpet. The flowers are solitary, formed on high stalks, and are rarely scattered throughout the crown. The petals are bright yellow with beige anthers.
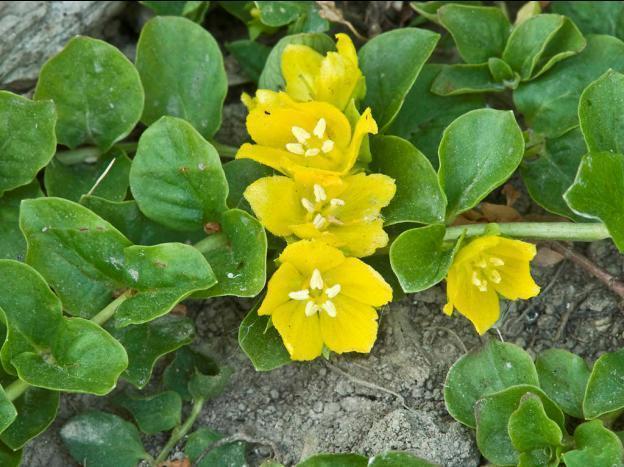

Dubravny is the earliest variety, blooming in mid-May and delighting with its beauty until the end of July
Loosestrife
Loosestrife is a perennial plant listed in the Red Book as an endangered species. Found in Siberia, Kamchatka, Chukotka, and the Urals. Does not grow in regions with warm climates. In design they are used to decorate the banks of artificial reservoirs.
A plant with a powerful branched root that produces single shoots that are not collected into a bush. The height of the stems is up to 1 m. The leaves are formed from the middle of the shoot. Inflorescences are round yellow racemes on long peduncles, growing in the upper part from the leaf axils.
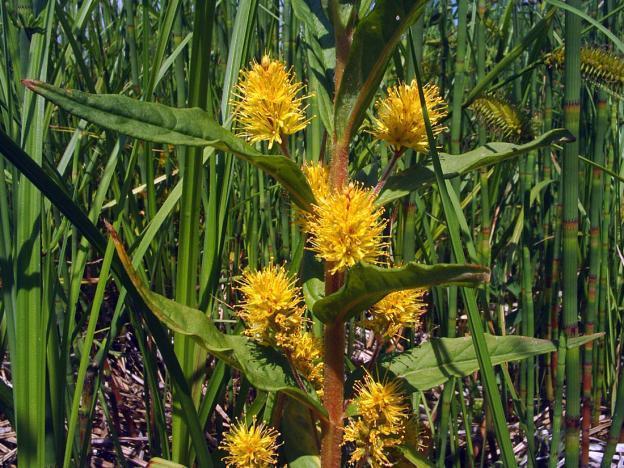

The brush-flowered variety is often found in shallow stagnant bodies of water (closer to the shore)
The use of loosestrife in the landscape
Several examples with photos of the use of flowers of perennial varieties of loosestrife in a flower bed and the design of the territory:
- planted for landscaping rock gardens and rockeries;
- in the foreground discounts near the fence;
Loosestrife blends harmoniously with tall plants with blue or light blue inflorescences
- to create a corner of wild nature;
- for the design of park areas;
- culture is included in compositions in flower beds;
- to delimit flowerbed areas;
A creeping variety of loosestrife with a brightly colored crown emphasizes color zones
- as a lawn covering near a garden path;
Ground cover loosestrife covers the soil with a continuous carpet, preventing weeds from growing
How to propagate loosestrife
All methods are suitable for propagating a species plant. When propagated from seeds, there is no guarantee that the crop will completely retain the appearance of the mother plant. More often they use the vegetative method or dividing the bush.
Seeds
The material is collected after it ripens in the fall. You can immediately sow in open ground, the seeds will undergo natural stratification and sprout in the spring; loosestrife will bloom only after 2 years. Planting can be done in the spring in the last days of May, after placing the material in the refrigerator for 2 weeks.
The generative method is possible using seedlings. The seeds are planted in a fertile substrate in February, the container is covered with transparent material and left at a temperature of + 150C. After the shoots appear, they are picked into separate containers and transplanted to the site in the spring.
Cuttings
Cuttings are a possible method, but not productive; gardeners rarely use it. Cuttings are harvested from the middle part of the shoots before budding. The material is placed in water until root shoots appear. Then they are placed in the ground in a shaded place, arcs are installed and covered with film to create constantly high humidity; the covering material is periodically removed to allow air circulation. In the fall, rooted seedlings are planted in a designated place and covered for the winter.
Dividing the bush
The optimal propagation option is for a well-grown loosestrife bush at least three years old. The work is carried out in the spring after the first shoots appear.
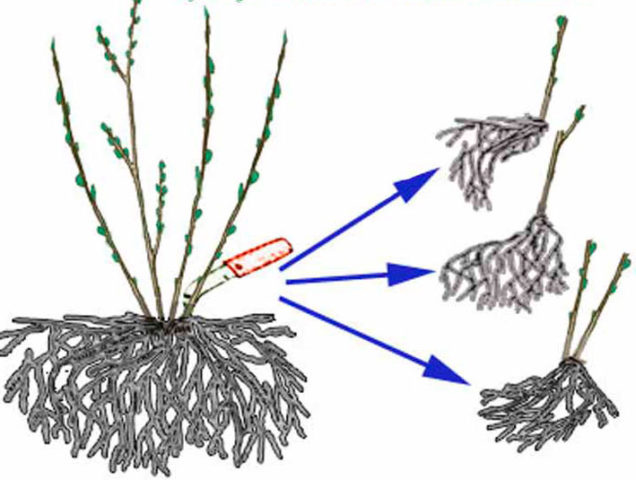
The plant is dug up and carefully divided into parts so that each plot has several vegetative buds
Ground cover varieties propagate well by rooted layering.
Planting and caring for loosestrife in open ground
Loosestrifes are completely unpretentious if conditions are created for them that meet biological requirements. If planting dates are observed and the location is chosen correctly, there will be no problems with cultivation.
When to plant loosestrife
Planting time depends on the weather conditions of the region; the ground should warm up to +150C. Seedlings are placed on the site in early or mid-May. By autumn, the loosestrife will take root and easily overwinter.
Dividing the bush is carried out after flowering or in the spring, when the condition of the soil allows you to dig up the plant.
Where to plant loosestrife
Loosestrife varieties with brightly colored flowers and leaves are best identified in a lighted or periodically shaded place. Varieties with white inflorescences are only in the shade; in the open sun, burns are possible, the flowers dry out, and the plant loses its decorative appearance. Ground cover varieties with green foliage thrive in the shade; varieties with a golden color without ultraviolet radiation lose their decorative qualities.
The soil composition is slightly acidic, fertile, the root system is superficial, soil aeration does not play a role.
In arid regions, regular root watering is necessary.
How to plant loosestrife
The pit is not prepared in advance for planting crops. On the day of work, mix peat and compost in equal parts.

Dry areas are cut off from the root and planted together with a lump of earth.
Landing:
- The depth of the hole is 10 cm, the width is determined by the volume of the root.
- 4 kg of substrate is poured onto the bottom.
- Place the plant and cover it with the rest of the mixture along with the vegetative buds.
Water abundantly and mulch.

If there are young shoots, they are left on the surface
Transplanting loosestrife
If the loosestrife displaces more valuable cultivated plants or the place for the species is not chosen correctly, the bush is moved to another area. In other cases, transplantation for culture is not necessary.
When can loosestrife be replanted?
You can replant loosestrife in the spring, before budding, but at this time there are some disadvantages: it will not be possible to do the work early, because the ground is not warmed up enough. After the transfer, the adaptation period may affect flowering; it will not be very abundant, in some cases the crop will not bloom at all. The optimal time for replanting is when the plants have finished flowering, so the time depends on the variety. The procedure is carried out in the fall, but no later than September.
How to transplant loosestrife to another place
The root system of the crop is not deep, but has grown greatly; it will not be possible to replant varieties without damaging the root. The main thing is not to damage the young shoots.
How to move a bush to another area:
- The stems are tied with a rope so that they do not fall apart; this applies to both the bush and ground cover forms of the crop.
- They retreat about 25 cm in a circle, go deeper on the bayonet of the shovel, and carefully dig out the bush.
- A cloth or polyethylene is spread nearby and the plant is transferred onto the material along with the soil by transferring it.
- The hole is dug in accordance with the size of the lump so that it fits tightly into the recess.
Features of growing loosestrife
All varieties and varieties quickly increase their root mass; it can double in size over the course of a season. The plant is absolutely unpretentious if the space is properly allocated. Varietal representatives are less stress-resistant; to maintain a decorative form, it is necessary to adhere to agricultural technology.
Watering and fertilizing schedule
Fertilizing is done in the spring with nitrogen-containing agents necessary for intensive growth of green mass. Tall shrubs are fertilized with Agricola during flowering; for ground cover varieties this fertilizing may not be given. To establish new buds, add organic matter in the fall.
Watering depends on the location; in a wetland or near a pond, the crop is not watered; the root system will fully provide the plant with moisture.

In a dry area, you will have to moisten every day, covering the area around the loosestrife up to 2 m
Weeding, loosening, mulching
Mulching is mandatory for the crop; the covering material retains moisture, and the layer is renewed in the spring. Weeding is necessary for seedlings; weeds do not grow under mature ground cover bushes. Loosening is carried out if there is no mulch; the procedure is relevant only for young crops. Aeration for plants older than 3 years is not important.
Rules for pruning loosestrife
Regardless of the shape of the bush, loosestrife must be cut off completely for the winter. But this should not be done too early; the plant forms vegetative buds for replacement and does not need extra stress. The shrub changes the color of its crown in autumn to bright yellow, so it does not lose its aesthetics. Remove the stems before frost, leaving 5 cm above the ground.
How to prepare loosestrife for winter
Loosestrife is a crop of the Northern regions with high frost resistance; wild species can overwinter without additional measures. Decorative bushes are fed and the layer of mulch is increased. Young seedlings are hilled up, organic matter is added, and covered with straw or peat.
Pests and diseases
Loosestrife is characterized by strong immunity; the plant rarely gets sick. For major garden pests, herbaceous shrubs are of no interest. The only insect that parasitizes the crown is aphids. If a pest is detected, areas of the main cluster are cut off and treated with Calypso.

The effect of insecticide treatment is noticeable after 2 hours
Conclusion
Planting and caring for loosestrife is a simple procedure, the plant is unpretentious, with a high survival rate. The main condition for a full growing season is increased soil moisture, this applies to all varieties and species. The herbaceous shrub is characterized by low drought resistance. When planting a crop, it is necessary to take into account that this is an aggressor plant that will displace all representatives of the flora within a radius of 2-3 m.















