Content
The rose is deservedly considered a “capricious” flower. It immediately reacts to the gardener’s mistakes in choosing a place for planting or care by deteriorating its appearance. Also, if the leaves of a rose in the garden turn yellow, this may be a consequence of the development of a disease or an attack by pests. In most cases, especially when the problem is noticed at an early stage, the bushes can be saved. But you need to be able to correctly identify the cause: the effectiveness of the measures taken directly depends on this.
Why did the leaves of the rose turn yellow?
Many varieties and hybrids of roses are quite “capricious” and “delicate”. When the leaves on the bushes in the garden turn yellow, this is a common reaction to errors in agricultural technology or the wrong choice of planting site. Another very likely option is infection of plants by pathogenic microflora or attacks by pests.
Lack of light
Most varieties and hybrids require bright but diffused light to maintain their decorative properties. Otherwise, the leaves of the rose bushes in the garden become smaller, pale and yellow in the summer.
The lighting requirements of a crop must be taken into account when choosing a location for a flower bed.A deficiency of light manifests itself quite quickly - the leaves on the roses in the garden turn yellow and fall off, starting from the very bottom. Then the shoots unnaturally stretch and thin, turning into a kind of “lashes”. Such bushes form very few buds, or they are absent altogether. The flowers on them are small, the petals are faded.

Not all roses can tolerate direct sunlight, but only a few can grow in the shade
Improper watering
If the leaves of roses turn yellow, this may indicate both a constant “drought” in the flowerbed and regular waterlogging of the soil. In the first case, first the edges of the roses dry out and turn yellow. Then they curl up into a tube, dry out completely and fall off. The development of the bush practically stops; in especially severe cases, the entire above-ground part dies off.
In the second, root rot almost inevitably develops. On the aboveground part of rose bushes in the garden, this manifests itself as follows: first, “wet” brown-black spots appear at the base of the shoots and petioles, then the leaves wither and turn yellow. The stems affected by the pathogen die off, and soon the entire bush dies.
With the correct watering schedule, roses in the garden may gradually turn yellow due to the use of tap water. It is “enriched” with chlorine and fluorine compounds, plants really don’t like these substances. The water must be pre-settled or softened in some other way.

Roses in the garden are extremely sensitive to watering schedules
Temperature change
With a sharp drop in temperature, even for a short period, the leaves on roses turn completely yellow almost before our eyes - within 2-3 days. Then, in most cases, the bush “goes bald”, losing all or most of its foliage.
Substance deficiency
For normal development, abundant and bright flowering, bushes require macro- and microelements. They are quite sensitive to the composition of the soil. If the leaves on roses in the garden turn yellow due to a deficiency of certain substances, as a rule, this is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Nitrogen. First, the leaves on the roses in the garden change their shade to pale green and become smaller, then completely turn yellow and become rough to the touch. The stems become deformed and become thinner.
- Potassium. The leaves of roses in the garden turn yellow only along the edges, and gradually a dry border forms there. New, just budding leaf blades have a reddish-violet tint in color.
- Phosphorus. Young leaves on roses in the garden become very small, the lowest ones turn red. On most of the bush they turn yellow, then dry out and fall off.
- Magnesium. The veins and middle of the leaves turn yellow, the edges retain their natural color. Quite quickly they become covered with reddish “speckles”; the roses in the garden “go bald” by mid-summer.
- Iron. The veins remain green, the leaf blades turn completely yellow. If nothing is done, a reddish tint appears in the color, and the ends dry out.
- Manganese. The oldest leaves on roses in the garden turn completely yellow, while the rest appear with light lemon stripes and spots between the veins.
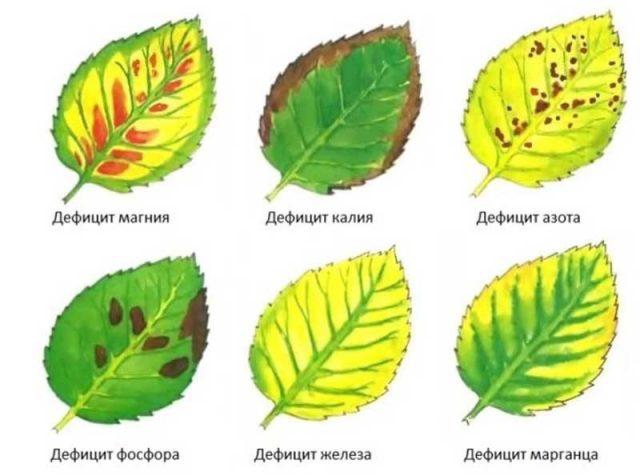
The bushes indicate what exactly they are missing by a change in appearance.
Pests
Among pests in the garden, the rose is a fairly “popular” plant. Most often it affects:
- Spider mite.The plant, especially its most “delicate” parts, are entwined with an almost transparent thin web. Discolored “dots” appear on the underside of the leaf plates. Gradually they completely turn yellow and dry out.
It is difficult to distinguish spider mites on roses in the garden - they are comparable in size to a grain of sand
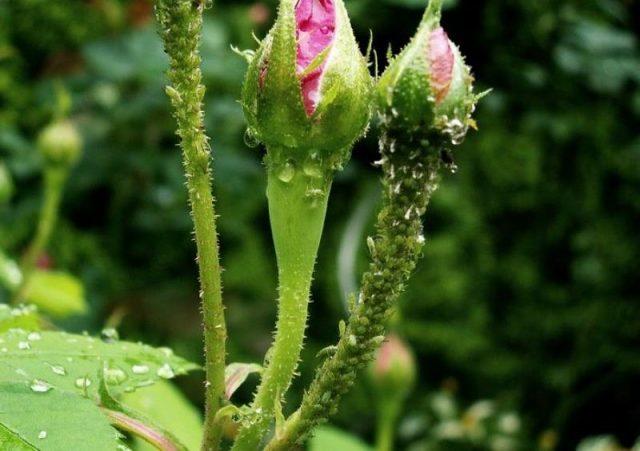
- Aphid. Small insects that “settle” in whole colonies on roses in the garden. They feed on plant sap and cover leaves, stems, and buds in a continuous layer. The affected parts of the bush turn yellow, then completely discolor, dry out and die.
Aphids and ants coexist in a stable symbiosis, so anthills near roses must be dealt with
- Rosen scale insect. Small grayish-brown rounded “growths” on leaves and stems. Gradually they swell, increasing in volume, and the tissue around them turns yellow, then red. The leaves turn brown and curl up, the shoots become deformed.
The scale insect is reliably protected by a durable shell; it is useless to fight it using folk remedies.
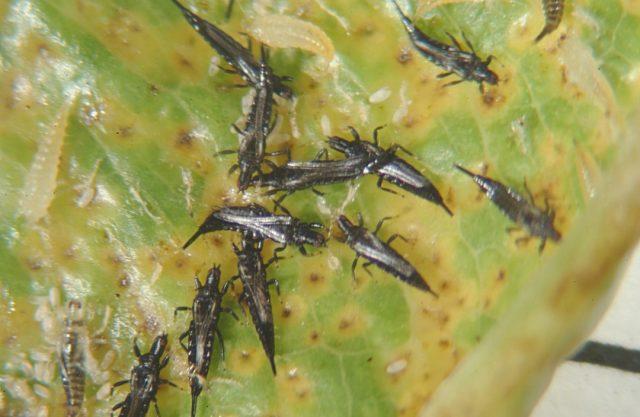
- Thrips. Small black “sticks” on the underside of leaf blades. They suck juice from tissues.
Thrips more often attack indoor or greenhouse roses, but bushes in the garden are not immune from them.
Diseases
Fungi and other pathogenic microflora, if nothing is done, can destroy a rose bush in the garden within a season or even faster. Typical diseases for the culture are:
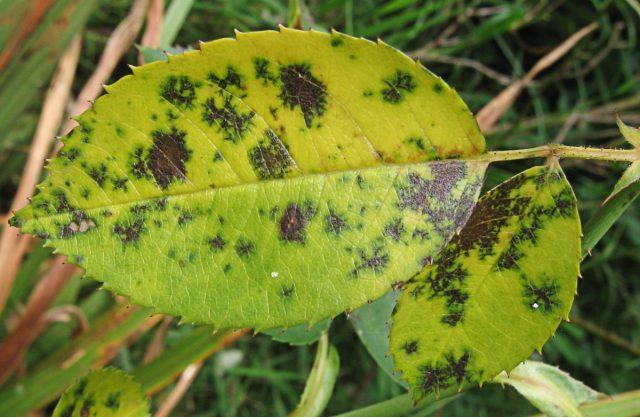
- Black spot. Initially brownish, blurry spots quickly turn black. Rose leaves turn completely yellow, curl up and fall off.
The causative agent of black spot successfully overwinters in the soil, remaining viable for 3-5 years
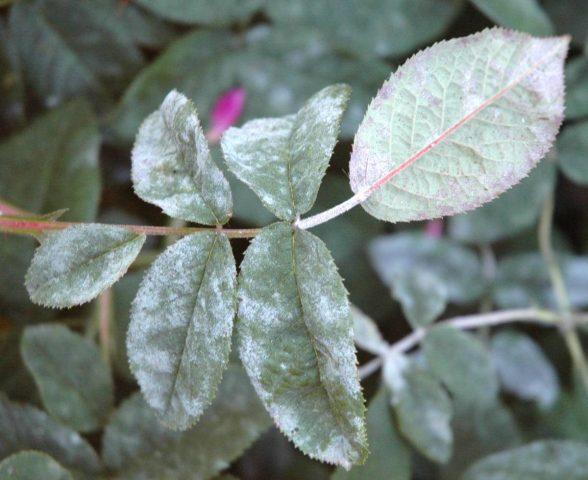
- Powdery mildew. The grayish or whitish powdery coating on the plant gradually darkens and “thickens.”The tissues underneath turn yellow, turn brown and die.
Powdery mildew is dangerous for the vast majority of ornamental and fruit-bearing crops in the garden
- Rust. A “fleecy” orange-yellow coating appears on the underside of the leaf blades, quickly “compacting” and changing its hue to rusty brown. The front side turns yellow.
Roses affected by rust in the garden go bald within a few months.
- "Jaundice". First the veins turn yellow, then the leaf blades turn completely. They curl upward and fall off.
“Jaundice” is a bacterial disease; it is impossible to cure roses in the garden
What to do if the rose leaves turn yellow
The measures taken directly depend on why yellow leaves appeared on the roses in the garden. Therefore, it is extremely important to quickly and correctly determine the cause or set of causes.
If errors in agricultural technology are to blame, it is enough to adjust the care, and the healthy appearance of the bush will be restored on its own. Sometimes, if the leaves turn yellow, you just need to feed the rose or water it.
If the wrong location is chosen, the rose is transferred to a suitable area in the garden in the near future. When the stage of the growing season does not allow replanting quickly, the plant is “supported” using foliar feeding with biostimulants. They do the same if the reason is only the weather, for example, because it is constantly cloudy, the bushes do not receive enough light.
When a rose turns yellow due to disease or pest attack, it is necessary, first of all, to carry out a “haircut”. They get rid of all parts of the bush, even slightly affected by pathogens and insects. All cuts are immediately disinfected, and the resulting plant debris is burned as quickly as possible.
Then specialized drugs are used.Folk remedies, as a rule, are already useless; they will simply be a waste of time. You need to choose from biological products and agrochemicals, taking into account the degree of neglect of the problem and other factors.
If roses in the garden turn yellow due to fungal diseases, use products containing copper - fungicides. There are no drugs to destroy pathogenic viruses and bacteria yet, so all that remains is to dig up the affected bushes and burn them so that the pathogen does not spread further throughout the area.

Treatment with fungicides includes spraying both the bushes themselves and the soil in the flower bed
Universal or “highly specialized” insecticides are used against insects. They will be useless in the fight against spider mites, since they are classified as arachnids. When roses in the garden turn yellow because of it, it is necessary to use acaricides or insectoacaricides.
Any drugs are used in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. You should especially carefully study the instructions regarding the procedure for preparing the working solution, its concentration and frequency of treatments. If you increase the content of the active component or spray roses in the garden more often, counting on a faster and more pronounced effect, you can simply “kill” the plants or cause serious harm to the environment.
All work with chemicals is carried out using a personal protection kit.

Most agrochemicals are not officially considered hazardous to humans, but it’s better to be safe than sorry
Preventive measures
In order not to have to think about why the roses in the garden turn yellow, losing their decorative effect, it is recommended to take care in advance to prevent this unpleasant phenomenon. Simple measures, if you devote time to them regularly, practically guarantee “protection” for the bushes:
- Carefully inspect the roses in the garden at least once a week and a half. This will allow you to notice any problem at an early stage, when it is much easier to deal with than “severe cases”.
- Selection of varieties and hybrids that are resistant to certain diseases or pests. If you have to constantly fight certain pathogens or insects on roses in the garden, it is advisable to choose varieties that provide “innate” protection against them.
- Regular weeding. Weeds, pests and pathogens that cause rose leaves to turn yellow, are used as “intermediate” hosts.
- Cleaning the flower bed at the end of the season from plant and other debris, deep loosening the soil, updating the mulch. Eggs, larvae, adult insects, and pathogenic microflora successfully overwinter in dry leaves, fallen petals, broken stems or shallow soil.
- Choosing a place for planting roses in the garden in accordance with the “requirements” of the culture. Otherwise, the normal development of the bush is impossible; it weakens and becomes more susceptible to any negative external influences.
- Quality care. This is especially true for watering, fertilizing and pruning.
- Planting roses in compliance with the recommended intervals between bushes, without “crowding” in the flowerbed. Otherwise, normal aeration and illumination of all shoots is impossible; a “stagnant” atmosphere is formed, which is very favorable for the development of many pathogens and the activation of pests.
- Disinfect garden tools every time after work. “Transfer” of pathogens and insects from diseased roses to healthy ones in this way is a very common phenomenon.

Regular inspection of rose bushes is a very useful habit.
Conclusion
If the leaves of a rose in the garden turn yellow, this cannot be ignored.This symptom can be caused by a variety of reasons, so there is simply no “universal” solution to the problem. It is necessary to correctly determine the “diagnosis” and only then take action.
















