Content
Hosta Autumn Frost is a perennial herbaceous hybrid. Like other varieties of this genus, Autumn Frost is actively used in gardening and landscape design. The shrub attracts with its foliage and is quite unpretentious. For successful cultivation, it is important to organize certain conditions for it.
Description of hosts Autumn Frost
Hosta Autumn Frost has the following characteristics:
- prefers partial shade, but can also grow in sunny areas;
- height 0.4 m;
- Autumn Frost bush is spreading - its diameter can reach 0.5-0.8 m;
- rhizome compact or short-branched;
- heart-shaped leaves on petioles form large basal flowers;
- foliage color is double - the middle is bluish-green, the wide border is cream or yellow;
- the shape of the leaves is varied - they can be narrow-lanceolate, broadly ovate, the edges are straight or wavy;
- possible waxy coating;
- peduncles are practically leafless, height can reach 1.2 m;
- the shape of the flowers is funnel-shaped or funnel-bell-shaped, average size 8 cm;
- the inflorescence is racemose, often one-sided;
- flowers are lilac, less often white or purple;
- Hosta Autumn Frost blooms in July-August;
- no aroma;
- there are no thorns;
- the plant is self-pollinating;
- in one place Autumn Frost can grow up to 20 years;
- It takes 4-5 years for the bush to fully grow; the process is accelerated in a sunny place, subject to agricultural practices.
You can grow Hosta Autumn Frost in most Russian regions. In terms of frost resistance, the plant belongs to zone 4 - ideal for the Moscow region, most of Russia, and the mountainous and northern regions of Scandinavia.
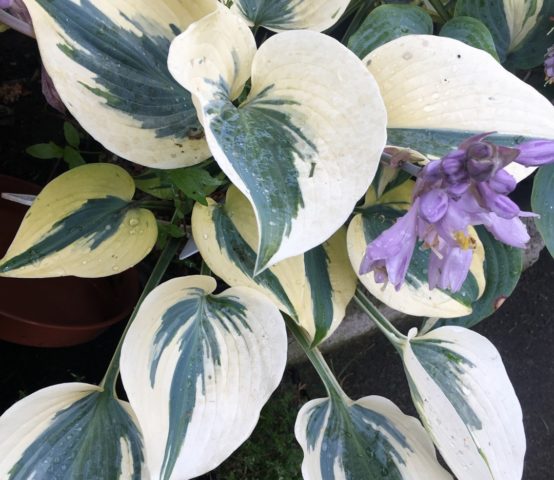

The decorative effect of the hosta Autumn Frost is provided by the foliage; flowering only pleasantly highlights it
Application in landscape design
Hosta hybrid Autumn Frost is grown in open ground. The plant is widely used in landscape design. It can be used in single and group plantings - the view will always be attractive. Hosta Autumn Frost is spectacular in different compositions:
- alpine slide;
- the shore of a pond or other body of water;
- mixborder;
- rockery
From the photo and description of the hosta Autumn Frost, it is clear that its flowering is not lush and not bright, so it can become an excellent background for flowering plants. If you choose a place near a pond, then the combination with marsh iris will be effective. In a shady place, the hosta looks good with morning glory of different shades, astilbe, periwinkle, marigold, liverwort, and primroses. There are other options: gladioli, lavender, lilies, lungwort in bright colors, peonies, Turkish carnations, phlox.
When planting Autumn Frost, you can go in different directions in landscape design:
- create a multi-tiered composition;
- play with contrasts by planting bright flowering plants against the hosta background;
- make edging of paths, borders;
- fill empty space under trees or tall bushes.
There are many artificial background options for hosta. This could be a pond, masonry, stones, border, wooden decor.
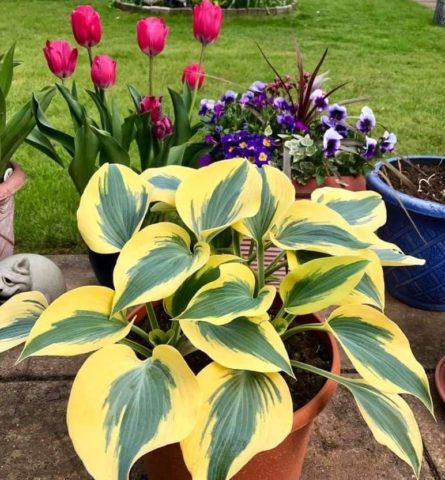

Hosta can be grown in large containers and pots; this option allows you to create different compositions by moving the plant to the right place
Hosta Autumn Frost goes well with almost all plants. The only things not recommended are neighbors whose bulbs need to be dug up every year.
Hosta Autum Frost propagation methods
Hosta Autumn Frost can be propagated by division, cuttings, and seeds. The latter method is used extremely rarely.
It is most effective to divide an adult bush. This method has 2 main advantages - obtaining several hosta bushes at once and quickly restoring decorativeness. Division is carried out in early spring or September.
Landing algorithm
Hosta Autumn Frost should be planted at a specific time:
- early autumn - you can plant the plant in late August or early September so that it takes root before the cold weather and survives the winter;
- early spring, before the leaves bloom.
When growing Hosta Autumn Frost, it is important to choose the right location. The plant can remain on it for many years. The main factors are:
- choose partial shade or a place with diffused lighting; there should be shade during the midday hours;
- the soil is slightly acidic, the acidity is almost neutral - 6.5-7.5 pH;
- the soil is moist and nutritious;
- hosta prefers light soils, the soil should be breathable;
- if the soil is too dense, peat or sand should be added;
- High air humidity is desirable - the plant feels good near bodies of water and responds to this with the splendor of the bush.
To successfully grow hostas, it is important to correctly select planting material:
- roots are dense and hard, healthy white;
- the rhizome should have 2-3 growth buds that are not overgrown;
- development and elasticity of roots, average length 11 cm, mold and rot are not allowed;
- When purchasing a plant, before planting, store it in a dark and cool place, temperature 5-10 °C.
It is better to choose a hosta with a closed root system; it is easier to plant, and the bush takes root faster. With an open root system, there will be no flowering for the first 3 years.
The landing algorithm is as follows:
- Prepare the planting hole. Hosta is characterized by strong horizontal growth of the root system, therefore a large width is important. Depth minimum 0.3 m.
- Fill the hole to 2/3 of the height with a mixture of compost soil, peat, rotted manure and sand. Add wood ash to acidic soil.
- Spill the planting hole.
- Spread the roots of the plant on the ground and sprinkle. Growth buds should be flush with the surface.
- Water the planting.
- Mulch the plant, a layer of 1-2 cm is enough.
If you plant several hosta bushes at once, then you need to leave at least 0.3 m between them.

Hosta Autumn Frost can be planted in large buckets; the lushness of adult plants does not allow them to be seen from above
Growing rules
The secret to successfully growing Hosta Autumn Frost is proper planting care. It includes several stages:
- Water the hosta regularly and in a timely manner, but do not over-moisten the soil.Evening watering by sprinkling is preferable.
- Carry out loosening carefully, do not go too deep. Due to the proximity of the roots to the surface, there is a high risk of damage.
- Feed the host three times per season. First, spring feeding is carried out at the beginning of the growing season, then in the summer during the flowering period, and then at its end. Hosta requires alternating organic and mineral fertilizers. Fertilizing can be both root and foliar. It is better to apply mullein infusion at the root after watering, and embed granular minerals into the soil around the bush.
- Mulching retains moisture and nutrients in the soil and protects plantings from certain pests. It is better to use compost as mulch.
Preparing for winter
Hosta Autumn Frost is characterized by high winter hardiness, therefore it does not require special preparation for cold weather. In autumn, nitrogen fertilizers cannot be used; they activate leaf growth, which is not necessary in winter. The last feeding is carried out in early August.
On the issue of pre-winter pruning of hostas, flower growers have disagreements. The foliage of the plant is soft, so by spring it successfully decomposes, creating good fertilizer. At the same time, refusal to trim is fraught with unpleasant consequences. Some pests and pathogens successfully overwinter on leaves and cause diseases in spring and summer. Timely prevention will help you avoid problems.
In regions with sufficient snow cover, it is not necessary to cover the hosta Autumn Frost for the winter.In areas where there is little snow or frosts are too severe, this event should not be ignored.
Various mulches are used as cover:
- compost;
- sawdust or shavings;
- rotted manure;
- mown grass;
- straw;
- peat;
- needles.
Shelter should be organized in late autumn. A layer of mulch of 5-10 cm is enough. If the leaves are left, then they cannot be covered. If the bush is pruned, you can cover it with mulch.
In regions with harsh winters, non-woven materials such as agrofibre and spunbond are used for covering. Airtight fabrics such as polyethylene film and roofing felt are not suitable for this.
Diseases and pests
Hosta Autumn Frost's main problem is slugs. They feed on young leaves. Because of which the plant loses its attractiveness. A good protection against slugs is mulch. The pest does not like sharp materials:
- wood chips;
- small crushed stone;
- crushed shell rock;
- fallen needles;
- straw.

One slug can lay up to 500 eggs over the summer, individuals of which appear in 2-3 weeks, and after another 1.5 months they begin to reproduce
Hosta leaves are also a treat for caterpillars. You can get rid of them using insecticides. The effect of spraying lasts for a long time and does not harm plants.

Bitoxibacillin, Lepidocid, Monsoon help well against caterpillars of various types
Autumn Frost is not susceptible to host diseases. One possible problem is phyllosticosis, also called brown spot. The disease is fungal. At the very beginning, you can cut off areas with a sharp knife and treat them with crushed activated carbon.
Plantings must be sprayed with fungicides. Instead, you can prepare a solution - add 30 g of laundry soap and 3 g of copper sulfate to 1 liter of water (dilute separately, then mix). To prevent the disease, Fitosporin-M is used.
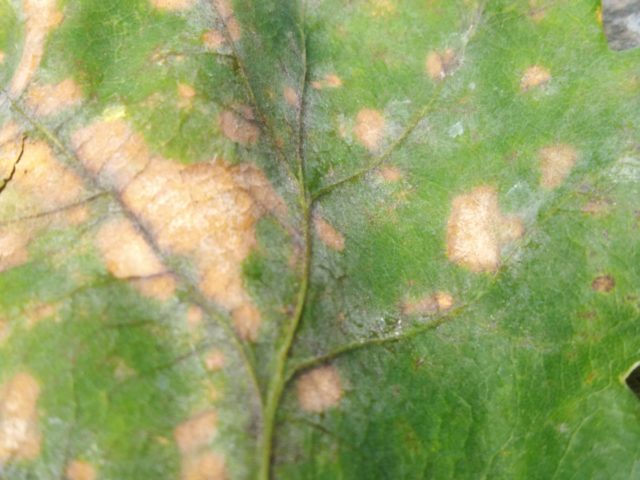

With phyllosticosis, brown spots appear on the leaves, which then cover the entire green mass.
Another problem with hosta Autumn Frost is gray rot. They also fight it with fungicides. For prevention, it is necessary to burn plant residues that contain fungal spores.
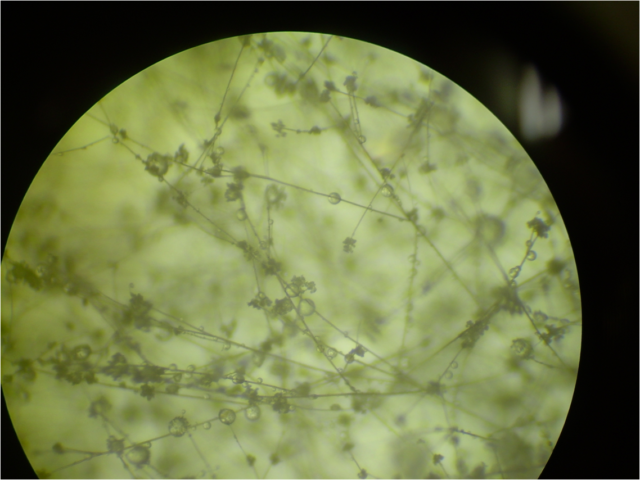
The causative agent of gray rot is the fungus Botrytis cinerea, the disease is dangerous for many plants
Conclusion
Hosta Autumn Frost is a pretty ornamental plant. It is widely used in landscape design, grows in one place for many years and is easy to care for. The hosta is rarely susceptible to diseases, and among the pests it is most often affected by slugs and caterpillars.
Reviews
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G0gGWOWRxO4








