Content
Phlox Genius is an unusual perennial representative of the Sinyukhov family (Polemoniaceae), externally resembling a lush carnation flower. The originator of the variety, bred in 2017, is the Russian breeder V.A. Maslov. Flowers are used in ornamental gardening. They combine harmoniously with other crops, so they can be found in various flower beds.
Description of paniculate phlox Genius
Panicle phlox Genius is a herbaceous bush crop that grows in height up to 60-90 cm. The bush is medium spreading, its diameter does not exceed 40 cm.
The leaves are light green, oblong, pointed at the ends, slightly curved.
The plant is intended for growing in open ground. The frost resistance zone of phlox Genius is 4, i.e. it can withstand temperatures down to -35°C. It can be cultivated in the Moscow region and in other regions of Russia with a temperate climate, including northern and mountainous territories.
Genius is a light-loving variety that grows well in areas with periodic shading. Under suitable conditions it grows quickly. Flowers may fade under the scorching rays of the sun.
Features of flowering
In terms of flowering time, the Genius variety belongs to the group of medium-late varieties.The culture blooms in July-August and pleases the eye until September. The flowers consist of strongly dissected lilac-blue petals.
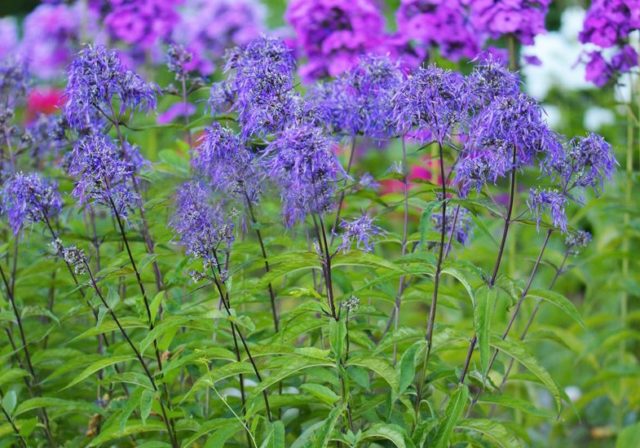

Genius is a chameleon variety, the color of the flowers depends on the degree of illumination
During the day, in sunny weather, the flowers of Phlox Genius are bright blue, and on a cloudy day or in the evening they become lilac-lilac. About fifty flowers are formed on one peduncle, the size of each does not exceed 2.5-3.0 cm. During flowering, this variety creates an airy blue cloud in the flowerbed. The aroma of the culture is weak, barely noticeable.
The flowering rate of the crop depends on the growing conditions. Good air circulation, timely watering and a sunny area are the necessary components for obtaining good flower stalks from Genius phlox.
Application in design
Phlox varieties Genius look great both in single and mass plantings.

An alley of colorful phloxes will unobtrusively divide the territory

Phlox and daylilies will be a wonderful decoration for the local area
Phlox secrete special substances that can protect against fusarium, so they are good companions for asters suffering from fungal pathologies.

The following crops can become good neighbors for phlox: hosta, lungwort, lily, peony, lupine, dwarf wormwood, edelweiss, marigold, roses
Nematodes, which pose a danger to roses and phlox, never appear in a bed with marigolds, so being in the vicinity of them will only be beneficial.
Phlox Genius can be grown at home. It will be a wonderful decoration for a balcony, veranda or glassed-in loggia. The bush is tall and grows well, so a wide pot is needed.The depth of the planting container is not very important, since the root system of paniculate phlox is located in the upper layers of the soil.
Reproduction methods
Phlox Genius is propagated using various methods:
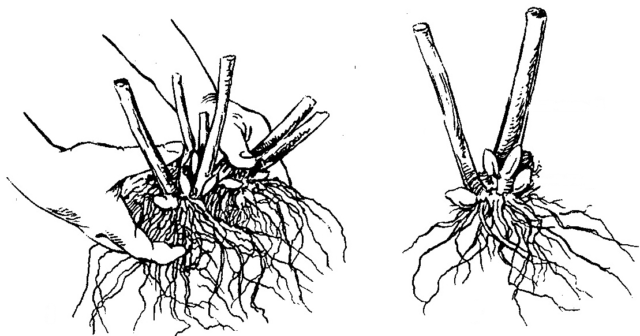
- Dividing the bush. To do this, carefully dig up an adult specimen, shaking off excess soil from the roots. The root collars are separated by hand and the rhizomes are disassembled. If it is not possible to divide manually, use a sharp knife. It is necessary to ensure that there is a growth bud on each separated part, otherwise the seedling will die. The division procedure is carried out in early spring or early autumn;
From one old copy you can get up to 15 new ones
- Stem cuttings. For this, green, well-developed shoots are used. The lower leaves are cut off and the upper leaves are cut in half. Cuttings can be planted in open ground or in a greenhouse. The procedure is carried out in May; it is during this period that the stems planted in the ground take root best. With early planting and proper care, seedlings can bloom in the fall;
There should be two nodes on the cutting
- Seeds bred only at experimental stations, since seedlings grown by this method may not meet the required characteristics.
For adult bushes, division is recommended. This will help rejuvenate the seedlings and increase the number of Genius phloxes on the site.
Landing rules
The best time to plant phlox Genius is spring. Specimens planted during this period will be able to bloom at the end of summer.
To prevent phlox from fading in the sun, experts recommend planting them in partial shade.
If you choose a shaded area, you can get too elongated stems, as well as late flowering of phlox Genius
The culture prefers slightly acidic or neutral soil and grows well on sandy loam. Bushes planted on fertile soils are distinguished by lush flowering.
The planting site for phlox Genius is prepared in advance. It is cleared of debris and weeds and dug up onto the bayonet of a shovel. If the soil is clayey, add river sand, humus, compost, and mineral fertilizers.
When choosing seedlings, pay attention to the following characteristics:
- when purchased in the fall, the bush should have 2-3 thick stems with healthy leaves. Phlox shoots are cut at a height of 5-10 cm. Spring seedlings should have at least 4-5 young shoots about 6-7 cm long;
- Well-developed renewal buds should be visible at the base;
- the roots should not have dried out or rotten areas.
For planting, it is necessary to divide the territory.

Leave at least 50 cm between neighboring phlox bushes.
When placed with peonies, daylilies, hosta, the distance between seedlings is increased, because when planted closely, phlox quickly lose their decorative properties.
Landing algorithm:
- dig a hole, the size of which should be 5-10 cm larger than the volume of the root system. For phlox, it is enough to make a hole with a depth and a diameter of 0.5 m;
- the roots of the seedling are pre-soaked in Kornevin’s solution;
- a turf layer of earth and organic fertilizers are poured into the bottom of the hole;
- watered;
- place the seedling so that the top of the rhizome is buried 3 cm into the ground;
- the earth is compacted by hand;
- watered.
Aftercare
Phlox Genius loves moisture and does not tolerate drought well, so seedlings are watered at least once a week.
Feeding is carried out in stages:
- in spring, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are added to the soil in equal quantities;
- in summer use nitrogen or potassium-phosphorus compounds;
- In the fall, wood ash is suitable as a fertilizer.
Preparing for winter
To prevent phlox Genius from dying out, you need to take care of preparing the crop for winter. This will require the following steps:
- Autumn treatment of the soil and base of the bush with fungicides will help prevent the death of seedlings from pests and diseases.
- The dying parts of the shoots are cut off before the first frost, leaving stumps about 10 cm high.
- To protect the bush from freezing, soil is added to its base. Hilling up is not recommended, as the root system can be damaged.
- A layer of mulch will also prevent the crop from being damaged by frost. You can use peat and humus.
Pests and diseases
If agricultural practices are incorrect, phlox Genius can suffer from viral and fungal diseases and mycoplasmosis.
Fungal diseases of phlox include:
- powdery mildew, manifested in the form of plaque. Treatment with a 1% soda solution is used as treatment. For prevention, spray with a weak copper mixture;
- rust. Damaged areas are cut off and burned, and the ground around the seedling is treated with Bordeaux mixture (1%);
- wilting (wilt) indicates a lack of nutrients. Apply nitrogenous fertilizers;
- septoria (white spot). Damaged shoots are cut off and burned, and the ground is treated with Bordeaux mixture.

Bordeaux mixture helps fight fungal diseases on phlox
Viral diseases cannot be cured. The bushes must be destroyed.Disease carriers are aphids, mites, worms and cicadas, so each seedling is regularly inspected for pests and, if necessary, treated with Aktara and Confidor.
Phlox can be harmed by snails, slugs, aphids, weevils, wireworms, earwigs, thrips, and pennies. To combat pests, they use digging up the soil, as well as treating the soil with chemicals.
Conclusion
Phlox Genius is a beautifully flowering herbaceous shrub used in ornamental gardening. When planted correctly, it grows quickly and creates blue islands that combine well with other varieties of phlox.
Reviews of Phlox Genius
According to reviews, phlox paniculata Genius does not require special agricultural technology, adapts well to growing conditions and pleases with lush flowering every year.