Content
Peppermint (Mentha piperita) is an interspecific hybrid obtained by crossing Mentha aquatica (water) and Mentha spicata (spike). Only wild plants are found in nature. Kuban mint 6 is one of the few peppermint varieties, especially common in Russia and neighboring countries.
Description of Kuban mint 6
Mint breeding is carried out in several directions. The first is decorative, when they try to make the plant as original or beautiful as possible for growing in flower beds and gardens. Or they release an unusual aroma. All types of mint are involved here.
The second is economic. This is where peppermint comes to the fore. It contains the highest content of substances widely used in medicine, cooking and cosmetology. One group of varieties contains the largest amount of menthol.The other gives a high yield of essential oils, organic acids and carotene in dry leaves, provides a good aroma and taste.
The variety was created by selecting elite seedlings of the second generation by crossing Peppermint and Field Mint. In variety testing since 1971. In 1977, Kubanskaya 6 was accepted by the State Register and recommended for cultivation in all regions.
Description of the plant
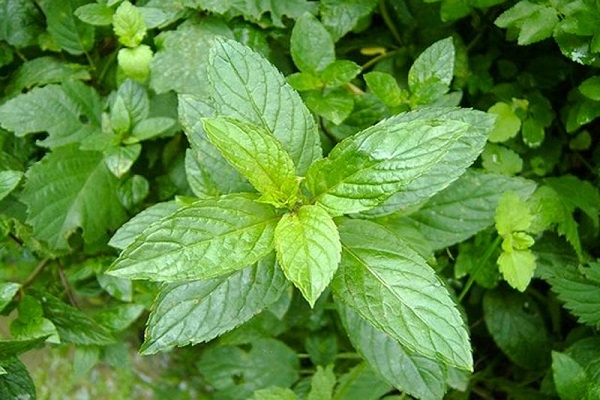
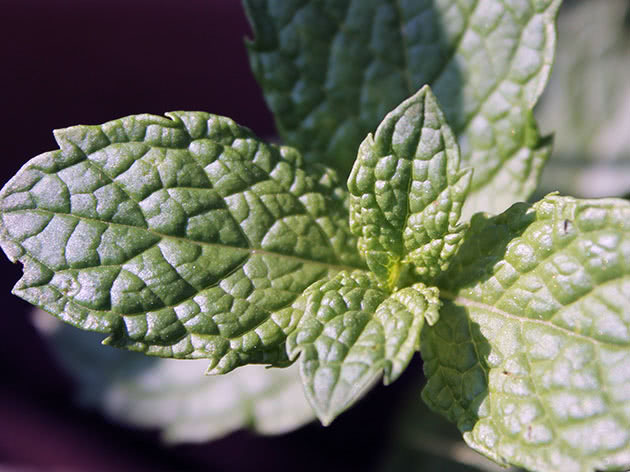
Kuban mint 6 is an erect perennial herbaceous plant about 45 cm high. The stems are tetrahedral, branched, well leafy, hollow inside. The edge of the vegetative organs characteristic of other species is absent.
The leaves of Kuban 6 are opposite, lanceolate, with a sharp tip and heart-shaped base, green, serrated along the edge. The petiole is short. The rhizome is horizontal, branched. The sucking processes are thin and fibrous.
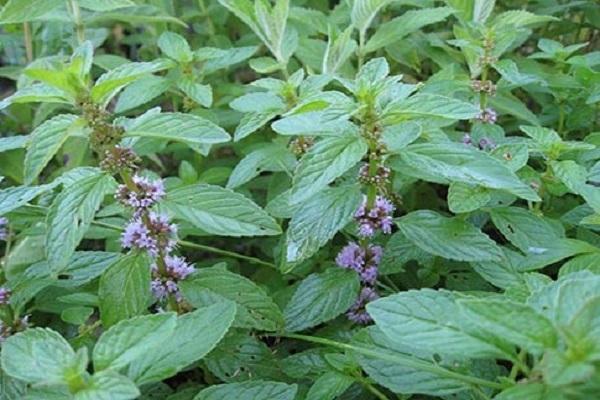
The inflorescence is a spike consisting of false whorls scattered in the axils of the leaves of the upper part of the stem. The corollas are five-membered, irregular in shape, small, pale lilac. Fruits - consisting of 4 zinobia nuts. They are rarely formed and are often sterile, which makes growing Kuban mint 6 from seeds difficult.
The timing of bud opening depends on the region and weather. Kuban mint usually blooms in June-August. The plant can be deceived. If the spikelets are cut off as soon as the buds begin to open, new shoots will grow, at the ends of which inflorescences will form. They will be much smaller than the first ones, but just as fragrant.
Industrial cultivation, yield, essential oil content
On industrial plantations, the Kubanskaya 6 variety reaches a height of 50 to 80 cm. This is explained by the fact that on private farms, peppermint is usually planted somewhere in the backyard. At best, it is watered. Kubanskaya 6 receives fertilizing only if valuable crops grow nearby, the decorativeness or fertility of which must be maintained with the help of fertilizer.
During industrial cultivation, the yield of raw materials must be large, otherwise it simply does not make sense to occupy areas with crops. Kuban mint is watered according to schedule, fed, and combated with pests and diseases.
In response, it produces a yield of 16-20 centners of leaves per hectare. The yield of essential oil is 3.6-5.5%. In turn, it contains from 53 to 60% menthol.
Features of the distribution of nutrients in Kuban mint 6:
- lower leaves contain more menthol;
- The top part of mint is rich in essential oils;
- At low temperatures, fewer aromatic compounds are formed, but they contain more menthol.
The maximum content of essential oils in peppermint variety Kubanskaya is achieved at the beginning of flowering:
- stems – no more than 0.3%;
- leaves – 2.4-2.75%;
- inflorescences – 4-6%.
The use of Kuban mint in cooking
Before using Kuban peppermint in culinary recipes, you need to find out exactly what type is used. Since this is not always written about, it is better to prepare a “test” dish first. The fact is that the aroma and amount of essential oils differs not only between different species, but also from variety to variety.
What is the aroma of Kuban mint?
Peppermint has the strongest smell and spicy taste. Experts call it refreshing, cold, invigorating.Ordinary people primarily smell menthol, diluted with more pleasant herbal notes. The Kubanskaya 6 variety stands out for its content of aromatic oils even in its group.
Where can you add Kuban mint?
Peppermint, including the Kubanskaya 6 variety, is used to flavor vinegar, cheeses, and tea. It is used in canning, and is added to both pickles and compotes. The aromatic leaves are used to prepare desserts and drinks. For example, the famous Mojito owes its unique taste to peppermint. The Kubanskaya 6 variety is perfect for this cocktail.
Peppermint goes well with vegetable and fruit salads and cheeses. Its leaves add a unique taste and aroma to roasts of all types of meat, soups, and marinades.
The British have a popular mint sauce for lamb. Americans add leaves to tomato juice. In Arabic and Mediterranean cuisines, peppermint is included in many spicy preparations. Russians and residents of neighboring countries especially love tea with fresh or dry leaves.
Useful properties of Kuban mint
The smell of peppermint relieves stress and fatigue, invigorates, and stimulates mental activity. Its oils are used in aromatherapy and the perfume industry, in the care of oily skin, for the treatment of dermatitis, acne, and rosacea. Mint lotions reduce bags under the eyes.
Official medicine uses peppermint to treat:
- colds due to antipyretic, antibacterial, diaphoretic, antiviral properties;
- cardiovascular system as a vasoconstrictor, relieving heart pain during angina, arrhythmia and tachycardia;
- upper respiratory tract, mint can even help with loss of voice associated with bronchitis, laryngitis or other inflammatory process;
- Gastrointestinal tract – improves digestion, copes with heartburn, bloating, nausea, colic, increases the flow of bile;
- musculoskeletal system – relieves muscle tension, has a resolving effect;
- in dentistry, it helps relieve pain from stomatitis, caries, and treats inflammation of the gums;
- central and autonomic nervous system - has a therapeutic effect in case of increased excitability, overstrain, anxiety, mood swings, mild depression.
Kuban peppermint relieves spasms during migraines and menstrual pain. Helps with seasickness.
Many widespread and highly specialized medicines are made from peppermint, for example, Validol, Pectusin, Valocordin, Menovazin, Campholin, Anestezol, Bronchosan, DeepRelief, Dolaren, Combigripp, Strepsis, Fanigan, Flamidez, Flukold.
In domestic preparations, peppermint of the Kubanskaya 6 variety, which is grown on industrial plantations, is usually used.
The use of Kuban mint in folk medicine
Herbalists treat the same diseases with mint as conventional medicine. Only they use alcohol and water infusions, decoctions, teas, and not medications. Dry raw materials are used for the preparation of potions along with freshly cut grass.
Landing rules
For peppermint Kubanskaya 6 you need to choose a sunny area with fertile soil. First, they dig it up, remove all the roots of weeds, add humus, peat, and sand if necessary. The crop will not grow on dense clay soils.
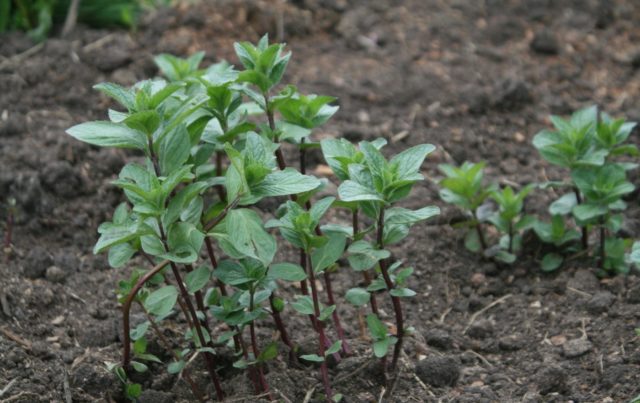
Kuban mint 6 reproduces well by suckers and pieces of rhizome.It easily tolerates division of the bush, quickly recovers and takes root. In regions with cool climates, the best time to plant mint is May-June. In the south, this should be done at least 2 weeks before the onset of extreme heat or the operation should be postponed until early autumn.
It is important that the soil has time to settle after digging, otherwise the mint will become very deep. It will grow only when the part of the stem that is underground is overgrown with new roots. If you don’t have time to prepare the bed in advance, you can roll it out or put a wide board on the ground and carefully walk on it.
When planting mint with suckers or rhizomes, no special tricks are needed:
- Furrows about 10 cm deep are made in the bed. If it is assumed that the mint will grow in a continuous carpet, the distance between the rows does not matter. To form even ridges, the grooves are located 50-60 cm from each other.
- Water generously.
- When the moisture is absorbed, lay out the rhizomes in a line. If by this time the above-ground part has grown more than 10 cm, it is cut off and used in the kitchen.
- Sprinkle the mint rhizomes with soil, compact them well, and water them.
If there are few seedlings, they can be placed in holes. With sufficient watering, Kuban mint 6 will grow quickly. In one place it feels good for 3 years, then it begins to shrink, degenerate, and at the beginning of the next season it may disappear completely.
Growing Kuban mint from seeds is problematic. This is a complex hybrid, it bears few fruits, many of them are sterile. Even if some sprout and look like peppermint, it will not be a pure variety.
Features of cultivation and care
Weeding and loosening Kuban peppermint 6 is difficult.The bushes grow quickly, the rhizomes spread in all directions. If the crop is grown in beds, leave a strip overgrown with mint, and weed out the rest in a continuous line.
Damage to rhizomes does not affect the yield of greenery and flowering. But weeds growing between the bushes are removed by hand. Often they are not touched at all. Carpet plantings of mint are difficult to keep clean. They try to do it not in the garden, but in a berry patch or garden in a sufficiently lit place.
The culture is demanding on watering and does not like the soil to dry out. Many gardeners do not fertilize mint at all. Even without fertilizing, in a tiny area it produces enough greenery to last until the next season. If you still need a lot of mint, you should take into account that even a slight excess of nitrogen causes rapid growth of greenery to the detriment of flowering and the accumulation of essential oils in the leaves. In addition, nitrates provoke many diseases. But phosphorus-potassium fertilizer at the end of the season will benefit mint.
The plant overwinters without shelter. Young greens can withstand short-term frosts. But in a harsh winter with little snow, some of the peppermint may die. Therefore, in the northern regions, it is better to add spruce branches to the garden bed in the fall.
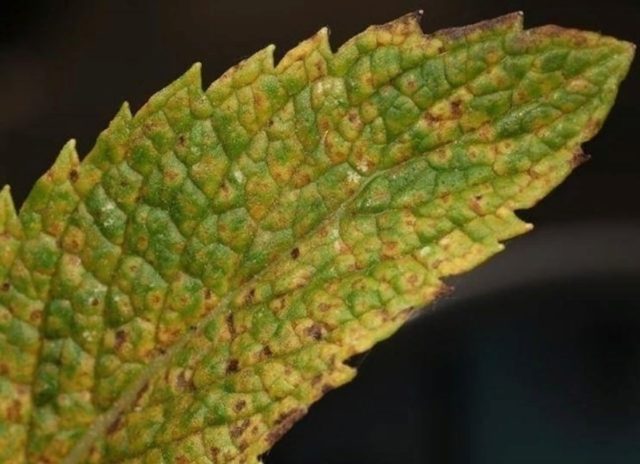
Pests and diseases
Peppermint requires constant vigilance. They grow it for culinary and medicinal purposes, using the above-ground part, so there can be no talk of any chemicals. And mint has a lot of pests. Here is a partial list:
- mint flea beetle;
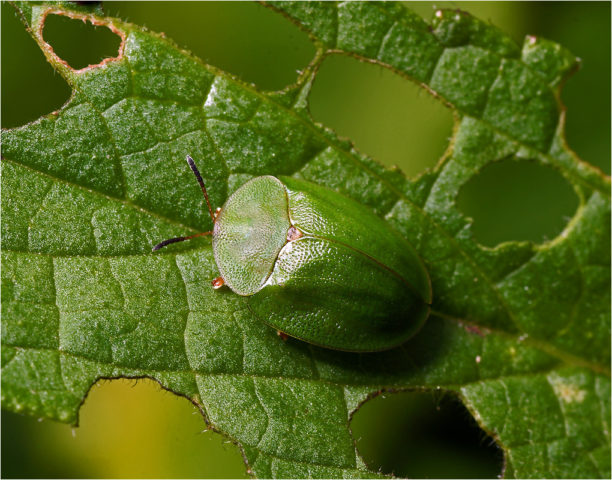
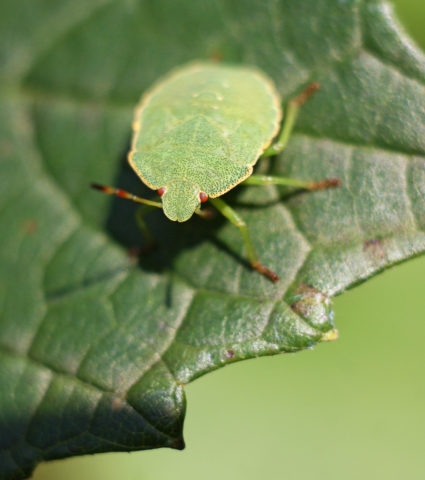
- green shieldweed;
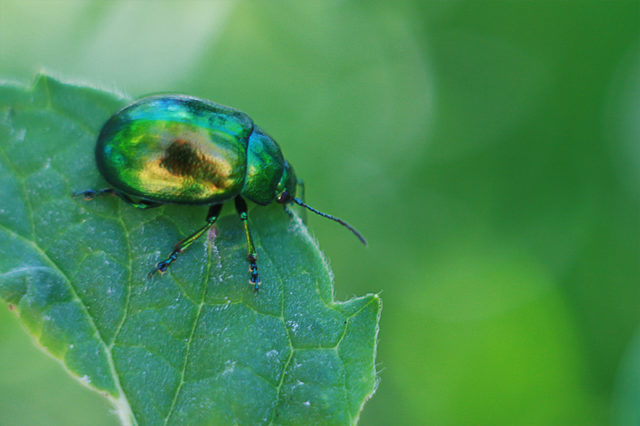
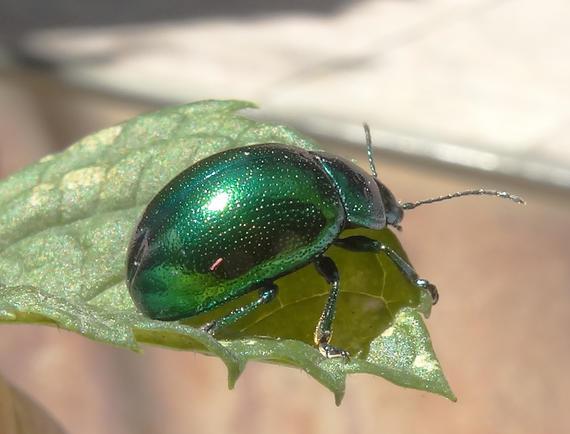
- mint leaf beetle;
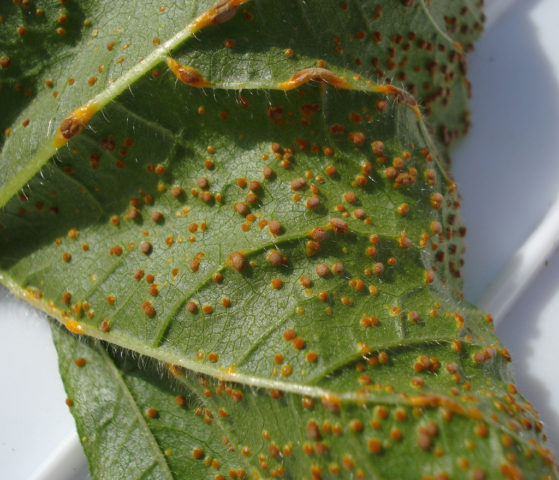
- aphid;
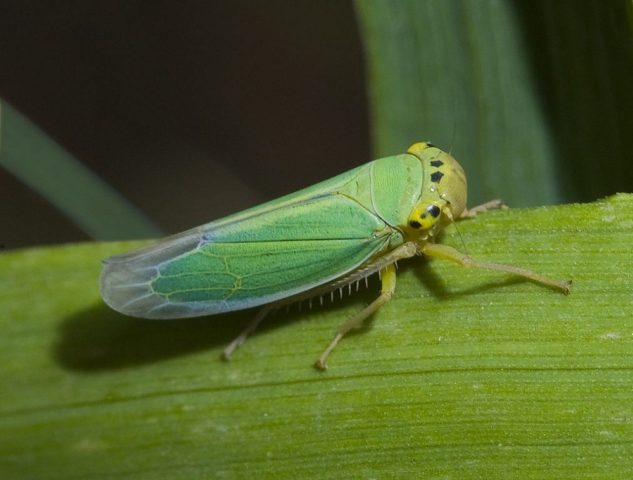
- leafhopper;
- weevils;
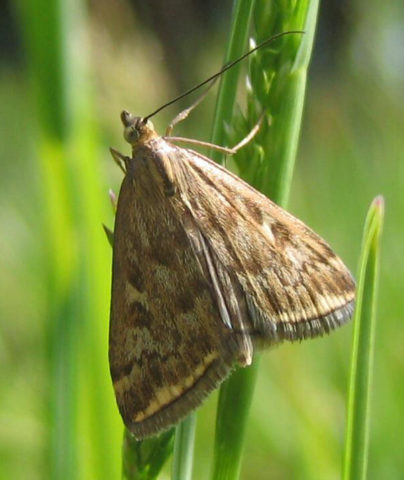
- meadow moth;
- mint mite;
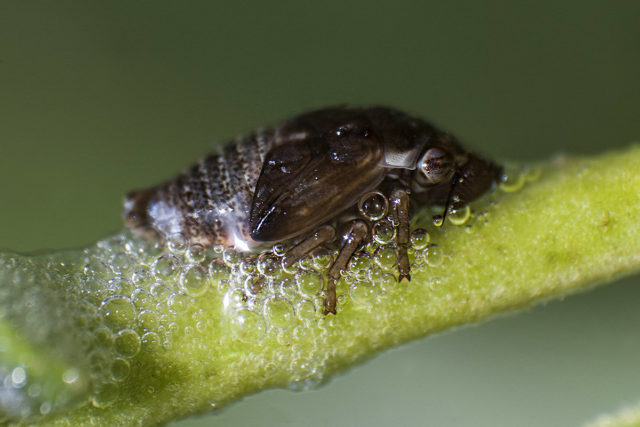
- slobbering pennice;
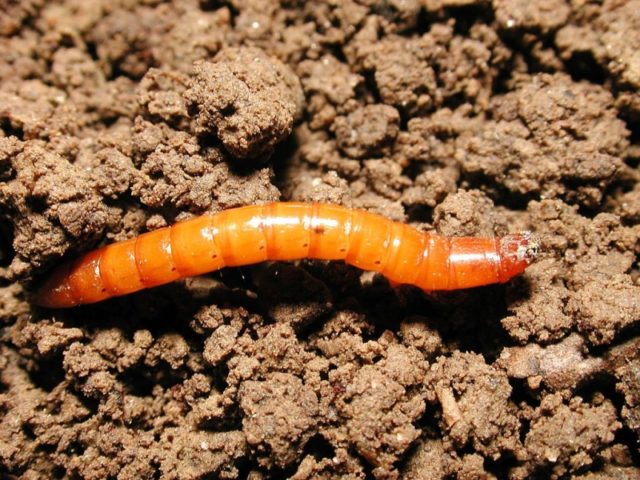
- wireworm
You need to fight pests with folk remedies, for example, infusions of celandine, bird cherry or pine. The earlier a problem is detected, the easier it is to deal with it.
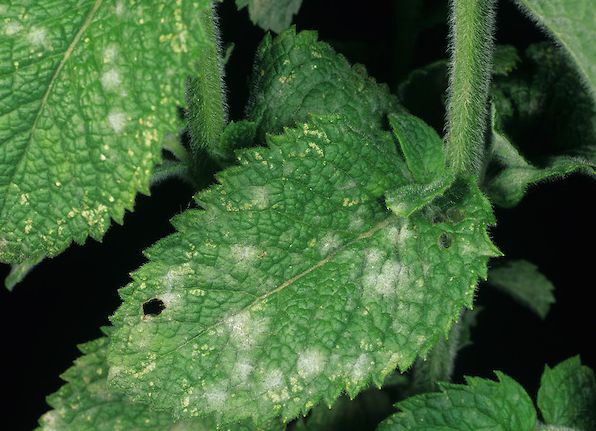
Peppermint variety Kuban 6 is sick:
- rust;
- powdery mildew;
- verticillium wilt;
- anthracnose;
- leaf spotting.
Mint overgrowth is also a disease. It is called microplasma and affects rhizomes. The best way to combat mint diseases is prevention. It needs to be replanted in time, and plant debris must be removed in the fall.
When and how to collect Kuban mint
The largest amount of essential oils in peppermint is found at the beginning of flowering. Then you need to prepare raw materials for cooking and treatment.
The stems contain little useful substances. If possible, only the flowers and leaves at the top of the plant are picked or cut off from mint. The lower ones contain more menthol, but do not have a very pleasant aroma and are bitter.
If you lack time and have enough space to store raw materials, you can cut and dry the mint along with the shoots. But then you will need to pick off the leaves immediately before preparing dishes or medicine.
How to properly dry Kuban mint
Leaves and flowers are laid out on clean paper in a dark, well-ventilated room. When the mint is dry, place it in a glass jar and cover with a lid. The shoots are tied in bunches and hung to dry. Store in cardboard boxes for no more than 2 years.
Conclusion
Kubanskaya mint 6 is a domestic variety, rich in menthol and essential oils. The culture easily takes root and reproduces vegetatively. It will not require much attention if it grows in a bright place, receives enough moisture, and is replanted once every 3 years.