Content
In spring, strawberries begin their growing season and gradually come to their senses after a long winter sleep. They wake up with her and pestswho spent the winter on bushes and in the soil, various diseases become more active. How to properly help plants weakened after winter cope with these troubles? Processing strawberries in early spring is a very important event that helps plants overcome the consequences of winter and devote all their strength to quickly forming a crop.
Spring work on strawberry beds
But before carrying out the treatments, you need to put things in order in the strawberry beds and do some general cleaning.
- Remove cover from strawberry bushes, if any.
- Remove last year's mulch from the beds; it is better to burn it rather than throw it into the compost heap. It can contain many pests and pathogens.
- Clear strawberry bushes of dried leaves; they not only prevent the plants from developing, but also serve as a refuge for pests and can harbor sources of infection.It is better not to pick off the leaves, but to trim them with pruning shears, so as not to accidentally pull out the bushes.
- Inspect overwintered plants, removing diseased and dead ones.
- Plant reserve strawberry bushes, formed from daughter rosettes of last year, in the vacant places. When planting bushes, first pour the planting holes with a solution of phytosporin prepared from 10 g of powder and 10 liters of non-hot water, leave for 2 hours in the shade. You need 0.5 liters of solution per well. Treatment with Fitosporin destroys pathogens of fungal diseases.
- Remove or transplant excess strawberry plants to another bed so that the plantings are not crowded.
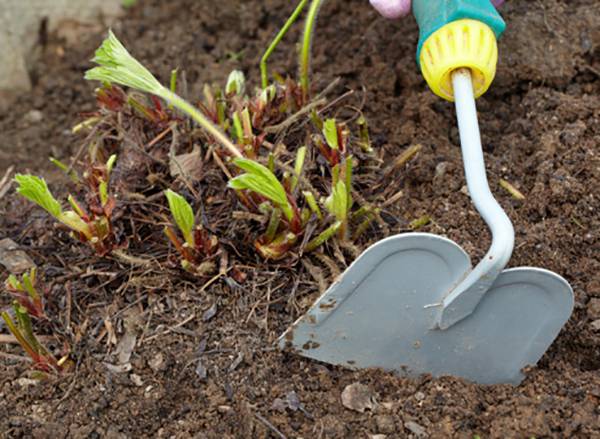
Each strawberry bush requires a certain area of nutrition. If the distance between the bushes is less than necessary for a given variety, this will inevitably affect the quality of the crop and reduce its quantity. - An important step is loosening the soil around the strawberries to a shallow depth. Under the influence of melt water, the soil in strawberry beds becomes compacted, which impairs the supply of air to the roots, which is also necessary for the development of beneficial soil microorganisms. Lack of oxygen reduces soil fertility. Loosening will help the soil warm up faster. If the strawberry bushes have bare roots, they need to be hilled up.
- After winter, the first thing that strawberries begin to grow are young leaves. A sufficient number of leaves through the process of photosynthesis helps to feed the flowers and young ovaries. That's why it's so necessary feed the strawberries in early spring.
Spring feeding of strawberries
Young bushes have enough nutrition provided during planting.
But two-year-old, and even more so three-year-old strawberry plants need nutrition to develop.
If its quantity is insufficient, there will be a shortage of harvest. Oddly enough, the same result will occur with excess nutrition, especially with a predominance of nitrogen fertilizers.
If there is too much nitrogen, strawberries will begin to grow leaf mass to the detriment of flowering and fruiting. With what feed strawberries in early spring? Each type of fertilizer - organic or mineral - has its own advantages.
Mineral fertilizers usually contain macro and microelements in a form accessible to the plant, so they quickly reach them, but are also quickly washed into the lower layers of the soil during watering or rain.
Organic fertilizers contain the same nutrients as mineral ones, but in order for organic substances to become accessible to plants, it takes time to decompose. When organic matter decomposes, a lot of carbon dioxide is released, which is so necessary for strawberries to develop well. Manure, humus, and chicken droppings contain microorganisms necessary for the soil to improve fertility. Mineral fertilizers do not have this feature.
If the soils are poor, it is better to choose organic feeding, but enrich it with ash and superphosphate.
The scheme for feeding strawberries in spring is as follows:
- A special complex fertilizer for berry crops or intended specifically for strawberries is applied according to the norms in dry form directly under the bushes, followed by loosening, provided that there is enough moisture in the soil. If there was little snow in winter and the soil was already dry, it is better to combine fertilizing the strawberries with watering and apply a fertilizer solution under the bushes. It is bred according to the instructions on the package and fed in accordance with it.
- A solution of fermented mullein is suitable as organic matter. Place fresh cow dung in a bucket half full. Fill it with water and let it ferment. To this amount you can add a quarter liter of ash and 60 g of superphosphate. After 1-2 weeks, the fertilizer is ready for use. When feeding 7-9 liters of water, add 1 liter of solution. Consumption – 10 l per sq. m. Bird droppings should be diluted in a ratio of 1 part to 10 parts water for fresh and twice as much water for dry. He doesn't need to wander. When feeding, add 1 liter of solution to 9 liters of water.
Preventive treatment of strawberry plantation
Spring processing of strawberries is an important undertaking that should not be neglected, especially if signs of disease or the spread of pests were observed last season.
Very little time is allotted for preventive treatment of strawberries, since they begin to bloom already in May, and it is undesirable to use chemical protective agents during flowering and, especially, fruiting.
Strawberries, like all other plants, have their own diseases, of which there are about 20, and are affected by pests. Proper processing of strawberries in the spring requires certain knowledge and the ability to understand the signs of various diseases.
Strawberry diseases
Many strawberry diseases are caused by fungal microorganisms.
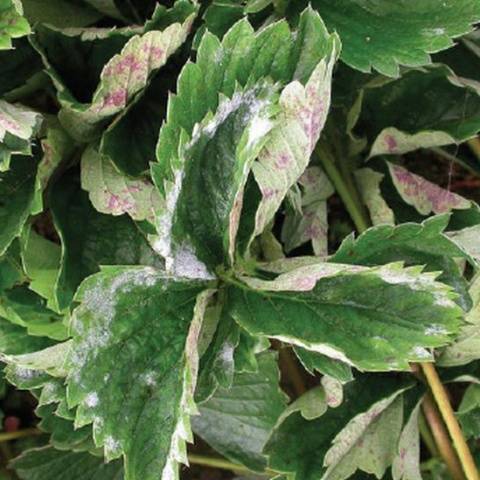
Powdery mildew
A disease that develops most quickly with high air humidity and poor air circulation. Signs of powdery mildew: white spotty coating on all parts of plants. Begins Disease from the petioles and quickly takes over the entire bush. Fungal spores are transmitted from plant to plant and can leave the gardener not only without a harvest, but also without the strawberry itself. Processing strawberries in the spring will help get rid of the powdery mildew pathogen before fruiting.
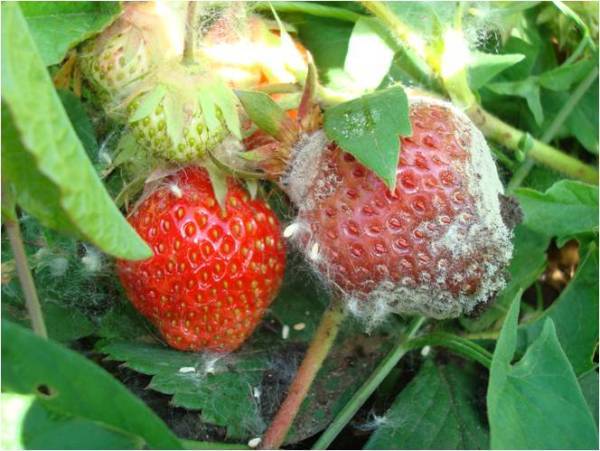
Gray rot
The disease manifests itself when the berries ripen; they rot, becoming covered with gray mold, which is fungal spores. Strawberries should be treated against this disease in early spring. The affected berries are placed in a separate container and destroyed.
White rot
The disease appears in years with low temperatures and high humidity. The strawberry leaves lighten and become covered with a white coating, and the berries rot. The spread of the disease is facilitated by too frequent planting of strawberries and poor weeding of the plantation.
Black rot
The disease only affects strawberries, which become watery and turn black. To prevent the disease, you should not frequently plant bushes and over-moisten the soil.
Various spots also have a fungal nature: white, brown and black or anthracnose, which first affects strawberry leaves, covering them with small spots of different colors, and then affects the entire plant as a whole. It begins to lag behind in growth, and there is no need to talk about getting a harvest.
Mushrooms also cause late blight or late blight rot of strawberries - a dangerous disease, the result of which is the death of the plant. The berries are the first to be affected, and then the whole plant wilts. Treatment for late blight should begin in early spring, without waiting for the disease to develop.
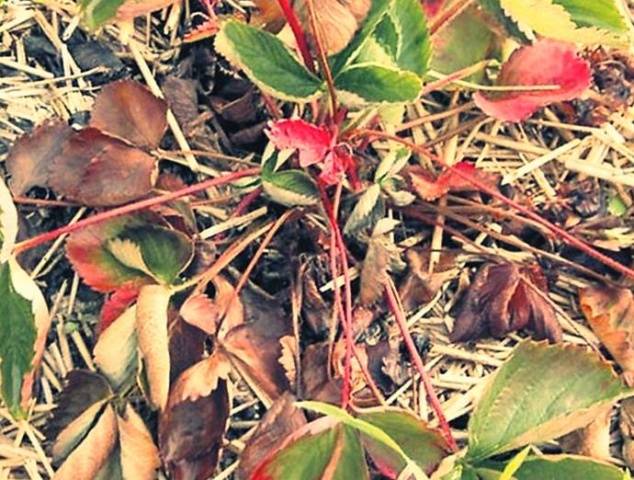
Fusarium wilt leads to the same result. It manifests itself during the period of harvest formation. A distinctive feature is the dark color of the leaves of the plant, which dry out. The disease affects the conducting vessels of strawberries. It is impossible to help a sick plant. It will have to be burned.
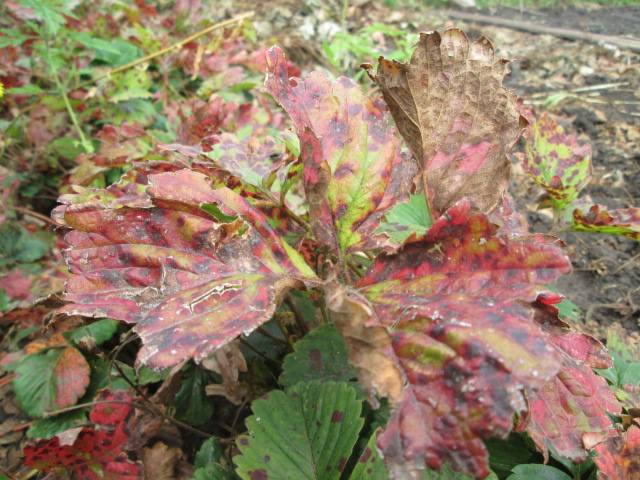
Verticillium wilt of strawberries
The disease begins in late May and reaches its peak after harvest. First, chlorosis appears on the leaves of plants, they begin to lag in growth, and their number decreases. A characteristic feature is the red color of the petioles at the end of the strawberry growing season. On light soils, the disease may progress at lightning speed with the death of plants within 3 days; on other soils, the disease lasts longer, but ultimately still leads to the death of the plant.
Therefore, along with treatments, you should water the strawberries correctly and not plant the bushes too densely so that they can be well ventilated.
Preventive spring treatments
Since the vast majority of strawberry diseases are fungal in nature, you will have to treat strawberries in the spring with products that actively fight various fungi.
Chemicals
Fungal diseases are best resisted by preparations containing copper: hom, Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate.You can use systemic fungicides that have a wide spectrum of action. These are Horus, Topaz - which have hazard class 3 and Fundazol – a very effective drug, but has a hazard class 2. Treatment with foundationazole should be carried out as early as possible, so that by the time the flower stalks emerge, harmful substances have already been removed from the plants.
All these substances are unsafe for humans.
How to process strawberries in order to maintain plant health and grow environmentally friendly berries?
Folk remedies
They may be less effective, but they are definitely safer for humans and beneficial insects.
- Fitosporin is a contact microbiological fungicide that fights well against fungal infections of plants. A significant drawback is that it is quickly washed off during rain and watering, so repeated treatments are required. Fitosporin does not pose a danger to humans; strawberries can be processed at any stage of development.
- Treating strawberries with iodine is a simple but quite effective remedy. Typically, 15 to 20 drops of iodine and a glass of homemade whey are added to a 10-liter bucket. The frequency of treatment is no more than two every 10 days. This method of processing strawberries is also effective against pests.
- Planting onions and garlic in the rows of strawberries.
The phytoncides of these plants repel strawberry pests and help fight diseases. In addition, it is possible to harvest two crops at once from one area. - Pine needles are poured with an equal amount of boiling water. Let it sit for 24 hours, dilute it five times and spray the berry garden.
- Treatment with horse sorrel infusion.Put as much crushed horse sorrel into a plastic bucket as will fit, fill it with hot water and let it brew for 7-14 days. Dilute the infusion ten times and water or spray the strawberry bushes.
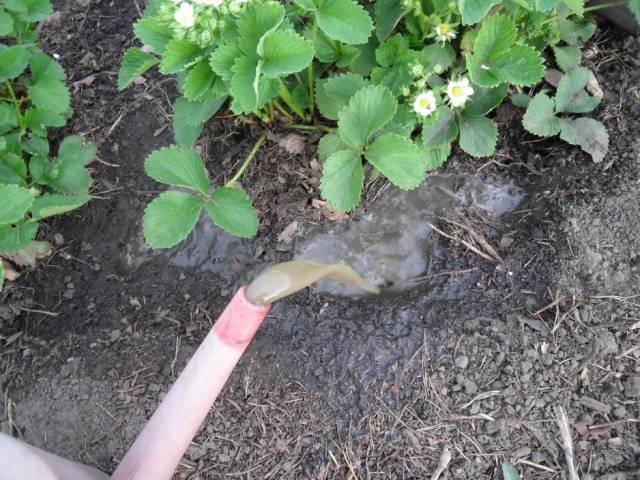
Horse sorrel contains flavonoids and antibacterial substances that are effective against fungal diseases. This infusion is also good for caterpillars on cabbage. - In spring, it is good to treat the strawberry plantation with hot water. This procedure should be carried out while the air temperature is low and the snow has not yet completely melted. Pour water at a temperature of 70-80 degrees into a watering can and water the plants. When watering, the water cools and does not burn the strawberry bushes, but it destroys pathogens and pests.
Often diseases and pests end up in a new place with strawberry planting material. To disinfect it, it is necessary to soak the roots of the seedlings in a phytosporin solution. 10 g of powder are diluted in 5 liters of water. The solution is kept for 2 hours so that Bacillus subtilis, which is the active ingredient of the drug, is activated. The roots of the seedlings must also be kept in the solution for 2 hours. To destroy pests, they can also be kept in water at a temperature of 45 degrees for about a quarter of an hour.
Pests often settle on garden strawberries, which can not only leave the gardener without a harvest, but also destroy the entire berry garden.
Pest Control
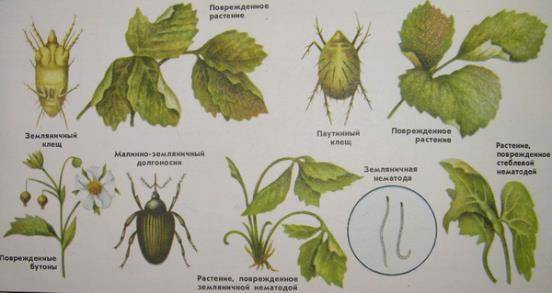
Nematode
Nematodes on strawberries are difficult to control. There is no completely effective treatment for them. All methods used can only reduce their numbers.The drugs piperazine and decaris, which are effective against helminths, can be recommended. But this is a temporary measure, since they only affect adults. Calendula and marigolds repel the nematode, but do not destroy it. Planted among strawberries, they displace most pests from the site. You can treat strawberries with an infusion of these plants.
Spring treatment for nematodes is carried out with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture. You can use the drug Phosfamide, which also destroys ticks. The effect of the drug after treatment lasts 20 days.
A folk recipe for nematodes: pour boiling water over a bucket of nettle leaves. The solution is left to steep for 4 days and water the bushes and the ground around them. When processing, you need to ensure that all leaves are wetted with the solution.
Strawberry mite
Suitable chemicals include karbofos and colloidal sulfur. But treatment with them is possible only at a temperature not lower than 15 degrees Celsius; at lower temperatures it is not effective.
The period from processing to harvest can be as little as 3 days.
The drug Neoron will also work. This is a contact insecticide effective against all types of mites. It has a hazard class of 4 and is non-toxic to beneficial insects. Neoron must not be mixed with other chemicals. The period of protective action of the drug is up to 20 days.
The drug Fitoverm will also help.This is a biological acaricide and insecticide that not only destroys mites, but also fights aphids and weevils.
Among the folk remedies for processing strawberries in spring, an infusion of onion peels is suitable - 200 g per 10 liters. After five days of infusion, the plants are sprayed. Treating plants with infusion of dandelion leaves is also a good and safe way. For 1 kg of fresh leaves (can be replaced with 500 g of roots) you need 10 liters of hot water at a temperature of 50 degrees. The infusion process lasts only 4 hours. We carefully process the strawberry bushes with the strained infusion, not forgetting the underside of the leaves.
The same measures are used to protect against spider mites.
Weevil
In the spring, Inta-vir is suitable for chemicals. Biological drugs Iskra-bio and Nemabact help well.
Folk remedies
Plant onions and garlic in strawberry beds, and place fern leaves under the bushes. There is a very simple way to repel this pest: lightly sprinkle the soil with tooth powder. Ash scattered around the bushes also works. Infusions of hot pepper, tansy and wormwood also prevent the beetle from carrying out harmful activities. The beetle does not like strawberry leaves treated with them. 100 g of mustard powder dissolved in 3 liters of water is an excellent means for processing.
5 g of potassium permanganate, dissolved in 10 liters of water intended for processing strawberries, will not only repel the weevil, but will also help against gray rot and powdery mildew.
It must be remembered that weakened plants are primarily attacked by pests and diseases. Care for strawberries properly, follow all the rules of agricultural technology, take into account the requirements of a particular variety, increase plant immunity with the help of immunostimulants and the number of treatments can be reduced.
Conclusion
Spring treatment of strawberries against pests and diseases is a guarantee of further plant health and a decent harvest of tasty berries.