Content
The cabbage moth is a butterfly belonging to the sickle-winged moth family. It is one of the main pests of cruciferous crops. Distributed throughout the world. The insect causes the greatest harm in steppes and forest-steppe areas.
Why is cabbage moth dangerous?
The butterflies themselves do not pose any danger to cabbage. Their oral apparatus is poorly developed, they practically do not feed. However, their numerous caterpillars can cause significant damage to wild and domesticated plants of the Cruciferous family, which include various types and varieties of cabbage. It is very difficult to predict massive outbreaks of insects, as well as the regions of their occurrence. A photo of the cabbage moth is shown below:

A characteristic feature of butterflies are antennae, sometimes reaching 2/3 of the wing length
In just a warm season, 3 or even 4 generations of the pest can form.Due to their large numbers, they can survive, despite the fact that they themselves are food for several dozen species of animals - from birds and small mammals to insects and ticks.

Caterpillars, several days old, feed on the underside of a leaf.
According to agronomists in the CIS, caterpillars damage to varying degrees:
- early varieties of cabbage - from 15 to 17% of crops;
- average – from 17 to 18%;
- late – from 32 to 47%;
- rapeseed – from 19 to 60%.
Even for people unfamiliar with agriculture, it is clear that cabbage moth larvae cause significant damage to all cruciferous crops currently grown, so control is an important task.
Signs of cabbage moth
Having hatched from the egg, cabbage moth caterpillars penetrate into the pulp of the leaves, where they begin to gnaw winding passages (so-called “mines”) several millimeters long. At this stage, it is almost impossible to detect the pest.
After 2 days, their first moult occurs and after a few more hours they begin to actively feed on the pulp, leaving only a thin skin. On the 4-5th day of life they pierce it and emerge on the lower surface of the leaves. In rapeseed crops, caterpillars at this stage primarily damage the seeds.
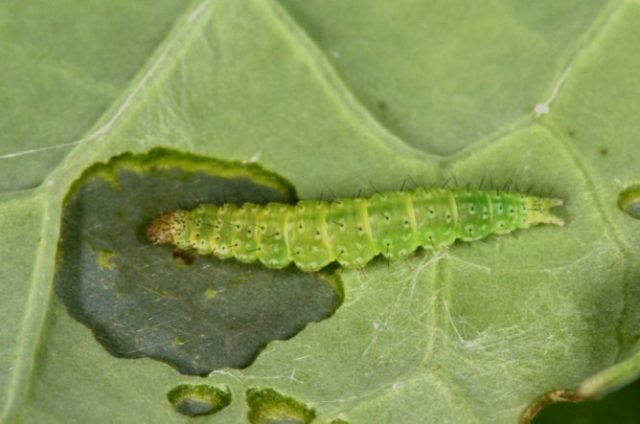

At later stages, the caterpillars are practically no longer hidden
Their protective coloration protects them well from predators, so the population size, despite the change in behavior, practically does not suffer.
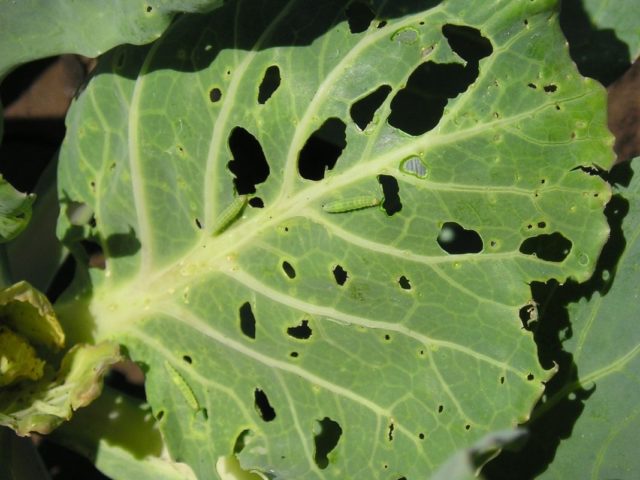

Unlike white moths, which make relatively large holes, the cabbage moth leaves behind leaves with multiple small damage
Mostly the vegetative part of the plant on the periphery is eaten, but in some cases the heads of cabbage may also be damaged.In total, the pest's lifespan in the larval stage is about two weeks. The cabbage moth then pupates, and after 7-10 days a butterfly emerges from the pupa, giving life to the next generation.
How to deal with cabbage moth
Despite the prevalence of the pest and its exceptional fertility, there are many effective methods to combat it. These include both the use of chemicals and folk remedies.
Measures to combat cabbage moth with folk remedies
Folk methods of fighting cabbage moths are very diverse and inventive. Below are the most popular ones.
Attracting Natural Enemies
The most effective insect control agents are wasps or ants. It is relatively easy to attract these arthropods - just place sweets in the area or water the soil with a sweetened solution.
Use of smells
Most insects have an excellent sense of smell, but not all of them are pleasant for arthropods. This feature is actively used. By planting crops that have a pungent or too strong odor near cabbage, you can with a high probability drive cabbage moth butterflies away from the area.
Such plants include garlic or onions, potatoes, tomatoes, coriander, lovage, and calendula.

The recommended distance from the cabbage beds to the planting site of repellent crops is 1 m
If you don’t want to plant plants, you can use various infusions. An effective remedy is a decoction of nightshade tops. To prepare it you will need the following ingredients:
- 3 kg of tomato or potato tops;
- several heads of onion or garlic (you can use onion peels);
- 1 red hot pepper;
- 50 g soap.
The ingredients are mixed in a container with 10 liters of water and infused for 24 hours. Then the cabbage plantings are sprayed with this mixture.
Another effective remedy is acetic acid. It is diluted in an amount of 30 ml in 10 liters of water and also used for spraying.
Application of soda
Baking soda is mixed with flour in equal proportions and the resulting powder is sprinkled on cabbage heads. This method is considered one of the safest.
Using Traps
The flight of cabbage moth butterflies occurs at night. At the same time, insects willingly fly towards light sources. The traps are flashlights pointing downwards. A saucer with vegetable oil is placed at a distance of 10-15 cm from the light source. The entire structure is placed on the ground or suspended from a tree.
Cabbage moth butterflies, attracted by the light, get into the oil and can no longer get out of it. One such trap can kill up to hundreds of insects during the night.
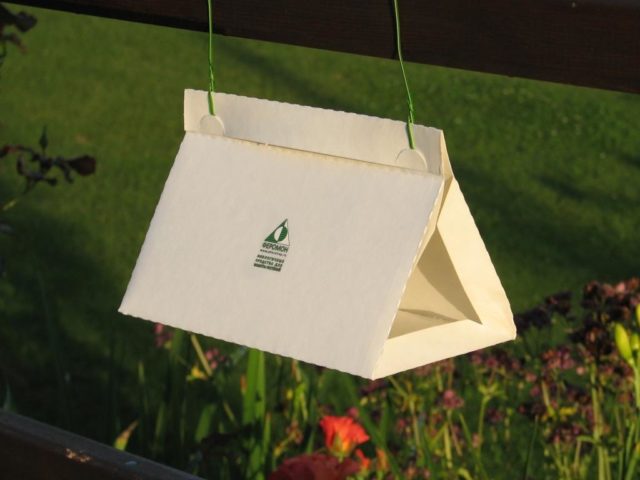

Commercial pheromone traps against butterflies can kill up to a dozen insects per day.
Biological preparations against cabbage moth
Biological or bacterial insecticides are highly effective, but their effect has a certain time delay (from 4 to 12 hours). However, compared to chemicals, they are less harmful because they usually act against specific types of pests.
For cabbage moths, the use of Lepodocid, Bitoxbacilin, Dipel, Dendrobacillin will be effective.
The listed drugs are effective when the pest infestation of plants is from 10 to 25%.
Chemical insecticides against cabbage moths
Chemicals are another option for pest control. Typically, larvae and adults of cabbage moths die 1-2 hours after their use. Most drugs are based on pyrethroids, peritrins or cypermethrins. It is recommended to use such products if the degree of cabbage moth infestation exceeds 10-20%.
The most popular drugs are Butizan, Triflutex, Decis.
If there are a significant number of insects, stronger insecticides should be used: Iskra, Sherpa, Inta-vir.
The use of chemical or biological agents is undoubtedly the most effective way to combat cabbage moths, but one should not forget about their harm to humans and beneficial insects.
Prevention of cabbage moths
In any case, fighting cabbage moths is a rather painstaking and costly task (both in terms of time and money). Therefore, the best way to combat the pest is regular prevention. Below is a list of measures that will help effectively resist the cabbage moth and prevent it from settling on most of the crops:
- Regular cleaning of the soil from plant debris (fallen leaves, branches, tops, weeds, etc.)
- Covering the beds with agrofibre, fine mesh, spunbond and other similar materials to prevent butterflies from laying eggs.
- Planting “repellent” crops around the perimeter of the planting and between the beds: coriander, celery, parsley, lemon balm, etc. The aroma of these plants will reliably protect the crops not only from cabbage moths, but also from many other uninvited guests.
- Installation of birdhouses and nest boxes on the site to attract birds.
- Regular inspection of cruciferous leaves and search for eggs laid on them, followed by destruction.
- Treating seeds before sowing using disinfectants. This measure is especially effective in combating cabbage moths on rapeseed.
- Mulching cabbage beds with fragrant agents (for example, pine needles).
- Combining fertilizing with preventive procedures (for example, using a natural insecticide in the form of wood ash).
All of these methods are quite simple and much less labor-intensive than direct pest control using any means.

Covering beds with a net is one of the effective methods of protection
Conclusion
The cabbage moth is one of the main pests of vegetables in the Cruciferous family. This small parasite is capable of producing up to four generations within a year. Small insect larvae can damage up to 50% of planted crops, significantly reducing the yield and marketability of vegetables. The fight against them is quite complex and time-consuming, so various preventive measures are recommended.