Content
Petunia is a favorite of many gardeners, as it blooms lushly throughout the season. But in order to achieve maximum decorativeness and preserve it, you need not only to provide adequate care, but also to protect the plant from negative factors. To do this, it is necessary to study the main diseases and pests of petunias with photos in order to be able to recognize warning signs at the initial stage of damage. Only timely measures taken will help restore the plant to a healthy appearance.
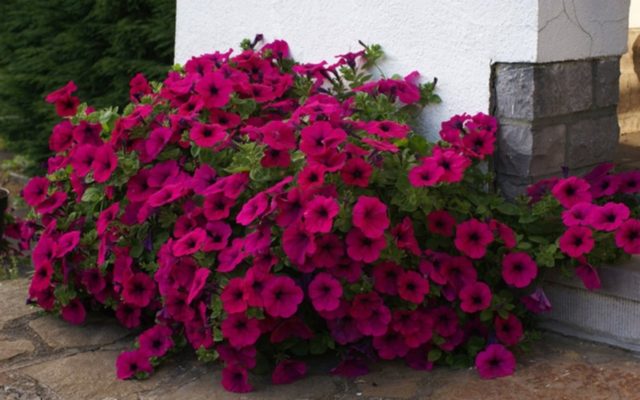

Petunia blooms continuously with proper care
Diseases of petunia flowers
This culture is characterized by high natural immunity. But since growing conditions do not always meet the requirements of petunia, this reduces its stability. Therefore, the plant can be affected by fungal diseases, which is especially dangerous at the stage of growing seedlings. Therefore, you need to familiarize yourself with what problems a gardener may encounter when growing it.Knowing the common diseases of petunia seedlings (photo below), and having studied their treatment methods, you can provide timely assistance to the sick plant.
Blackleg
This disease manifests itself at an early stage of seedling development, when they are not yet able to resist infection. The development of blackleg is caused by several types of soil fungi. The provoking factor of the disease is an increased level of acidity, high humidity and temperatures of more than +25 degrees. Under the combination of these conditions, sporulation in the substrate is activated.
A characteristic sign of the disease is a dark constriction on the stem of the seedling at the base at the initial stage of development. 2-3 days after its appearance, the petunia shoot in this place becomes thinner, which disrupts metabolic processes in the tissues. Subsequently, the stem softens and breaks. This leads to the death of plants.
If conditions are favorable, the fungus continues to spread further in the substrate, covering ever larger areas. In the absence of adequate measures, it will not be possible to save petunia seedlings. The causative agents of the disease persist in the soil and organic residues, so it is important, when affected seedlings appear, to remove them along with part of the substrate adjacent to the roots.
To avoid disease of the roots of petunia seedlings, that is, blackleg, experienced gardeners recommend using peat tablets for growing seedlings. The soil in them has already been treated with fungicides, which eliminates the possibility of pathology developing.
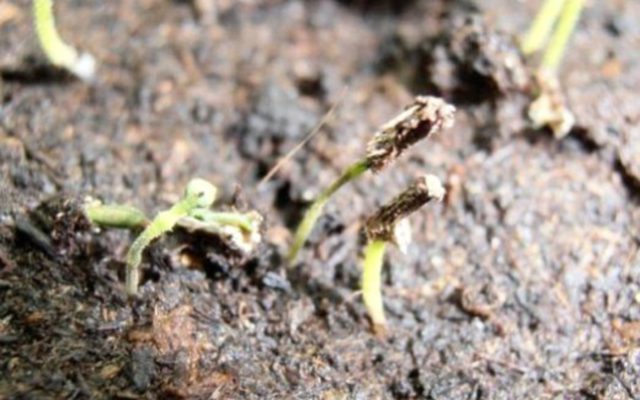

Blackleg can destroy all crops in 3 days
Chlorosis
The disease develops when there is a lack of iron in the soil.Chlorosis in petunia can be recognized by light leaf blades on which dark green veins are clearly visible. Subsequently, the color of the flowers changes; it lacks bright pigment. Against the background of a lack of iron, the development of the bush stops, and the general appearance of the plant becomes dejected.
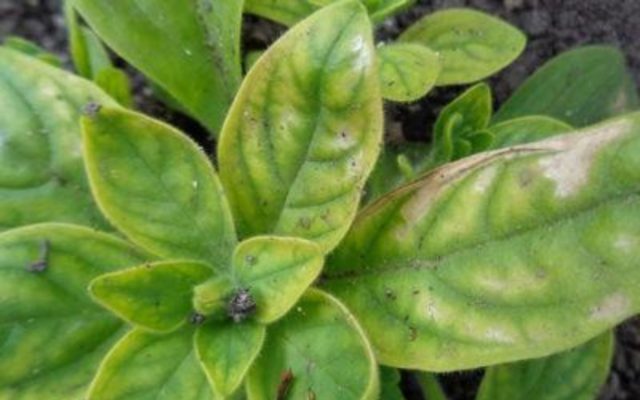

Restoring the decorative appearance of a bush during chlorosis requires a long time
Gray rot
This disease equally affects young and adult petunia seedlings. The causative agent of the disease penetrates the plant tissue through microcracks in the roots and shoots.
The main provoking factors of the pathological process:
- increased humidity of more than 80% of soil and air;
- temperature within +14 degrees and below;
- excess nitrogen fertilizers in the soil;
- lack of sunlight.
The disease can be identified by gray-brown spots on the leaves, which initially appear at the base of the shoots. Subsequently, they increase in size and become overgrown with a fluffy gray coating.
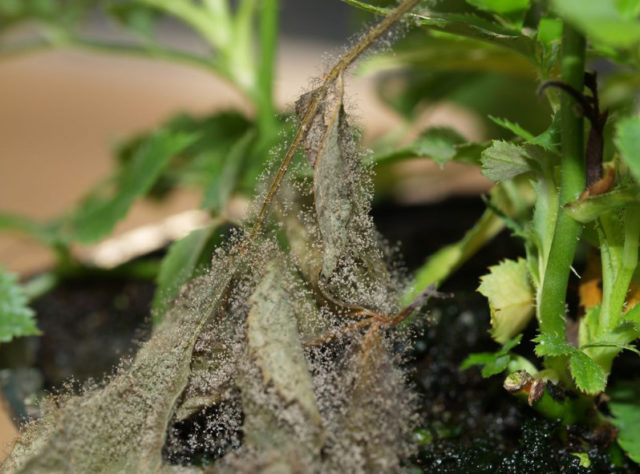

Petunia with gray rot without treatment dies after 3 days
Powdery mildew
Just by the name of this disease one can determine its characteristic symptom. It manifests itself as a thick white coating, which can initially be found on the leaves and then on the flowers of petunia. The disease disrupts the process of photosynthesis, which interferes with metabolism. As a result, the leaves of the plant become deformed and bend upward, and then completely wither.
The disease develops due to a combination of the following factors:
- sudden temperature changes;
- high humidity;
- irregular watering;
- dense plantings.
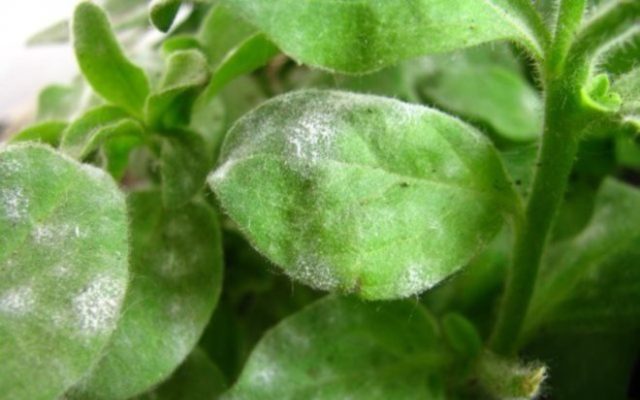

Powdery mildew gradually spreads to the entire petunia bush
Late blight
The disease affects all members of the Solanaceae family, and petunia is no exception. Late blight can be identified at the initial stage by the brown tint of leaves and shoots at the base of the bush. Subsequently, the disease completely spreads to the entire plant.
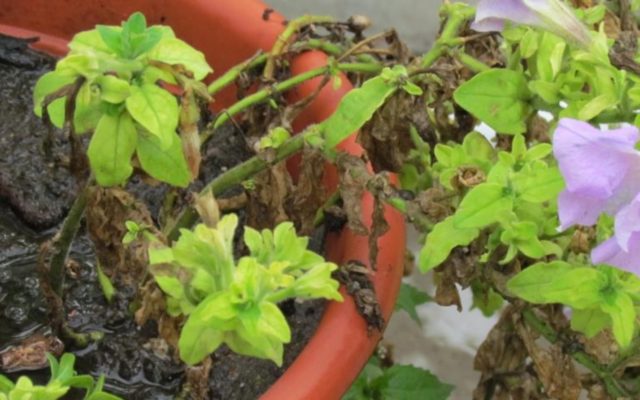

With late blight, the petunia bush first dries out and then rots.
White rot
This disease is caused by a marsupial fungus. Initially, weeping brown spots appear on the leaves and stems of petunia, which are subsequently overgrown with a thick white coating. Damaged parts become soft, so food and moisture do not pass through them. This leads to the tops of the bush beginning to wither. The infection penetrates tissue through mechanical damage on the surface of shoots and leaves.
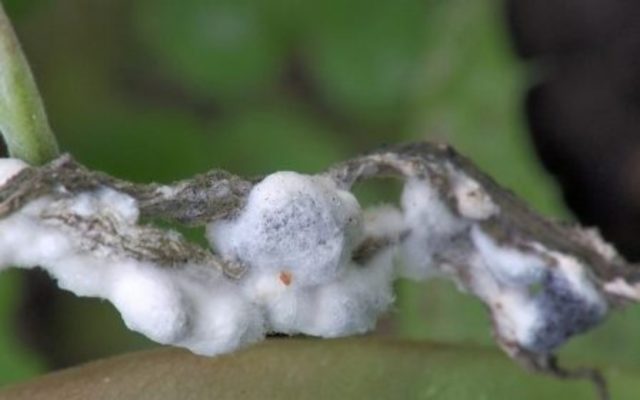

The causative agent of gray rot remains viable in the soil for 3 years
Brown spot
The disease manifests itself as rusty spots that are localized on the leaves and shoots of petunia. Subsequently, concentric areas are clearly visible on them. Initially they have the shape of a circle, and then lengthen. As a result of sporulation of the fungus, light spots form on the affected areas. As a result, the plants gradually wither.
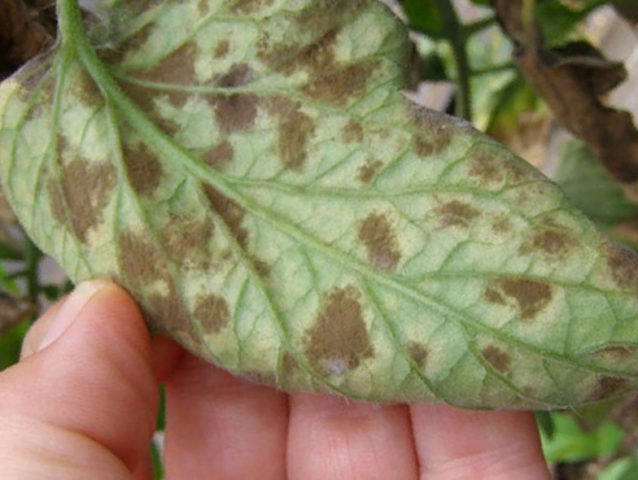

Brown spot develops at high humidity for a long time
How to treat petunia against diseases
Petunia diseases need to be combated comprehensively. To do this, you can use chemicals and folk remedies. This will not only stop the further spread of the fungus, but also prevent its reappearance.
You can learn more about petunia diseases in the following video:
Drugs
Chemical fungicides have an inhibitory effect on pathogens. They must be used according to the attached instructions. In this case, processing should be done in dry, windless weather, observing all personal safety measures.
It is necessary to spray not only affected petunia bushes, but also healthy ones, as a preventive measure. During treatment, treatment should be done 3-4 times every 7 days.
Effective drugs that help fight petunia diseases:
- Ridomil Gold.
- Speed
- Ordan.
- Home.
- Quadris.
- Topaz.
To treat chlorosis you need to use Iron Chelate. The drug must be diluted in water and poured over the petunia. Use the product every 10 days until signs of the disease are completely eliminated.

The prepared solution must be used on the day of preparation.
Traditional methods
These drugs should be used as a preventive measure. If the disease spreads massively, they will be useless. In this case, you need to use chemicals.
Recipes for folk remedies for petunia diseases:
- Heat 5 liters of water to 40 degrees. Add 200 g of wood ash and 40 g of grated laundry soap to the liquid. Leave for 4 hours, stir, peel. Spray the bushes 3 times with an interval of 3 days.
- Dilute 80 g of soda ash and 10 ml of dishwashing liquid in 5 liters of hot water and mix. Cool and use for processing. Spray the bushes every 3-5 days.
- Dissolve 50 g of mustard powder in a bucket of water. Use for spraying and watering petunia bushes every week.
Petunia pests
Not only diseases, but also pests can harm petunias. They feed on the sap of the plant and thereby weaken its immunity. Therefore, you need to study the main signs of pests on petunias (photo below) and ways to combat them.
Aphid
A small pest whose body length does not exceed 0.3-0.8 mm. Forms numerous colonies, which are localized on the tops of young shoots of petunia and on the underside of the leaves. The pest feeds on plant sap, which leads to deformation of the plates. A weakened petunia not only stops blooming, but also stops developing.
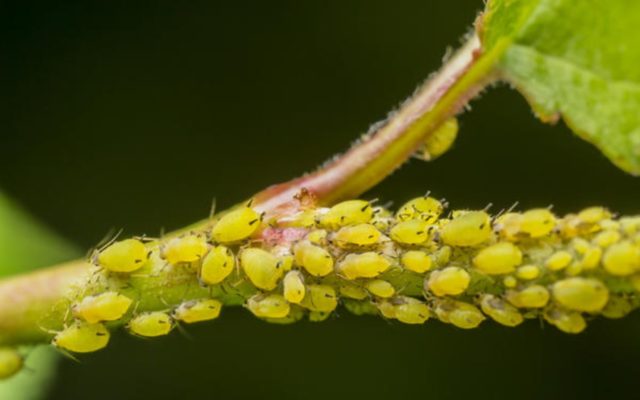

Aphids are a dangerous pest and carrier of viral diseases.
Spider mite
A pest that cannot be seen with the naked eye. When affected, small light dots appear on petunia leaves, which are initially localized along the edges. Subsequently, a thin cobweb appears on the tops of shoots and flowers, which is a characteristic feature of this pest. The plant takes on a dejected appearance and completely stops growth.
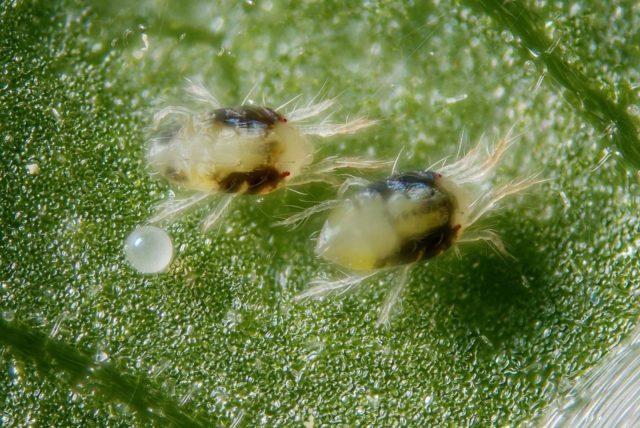

To kill spider mites you need to use acaricides
Thrips
The pest is 1.5 mm in size, with a dark brown body color. Forms small groups that can be seen on the top and back of the leaves. Lesions can be identified at an early stage by light, dry stripes on the plates. At the same time, the petunia begins to wither, and the flowers and buds become deformed.
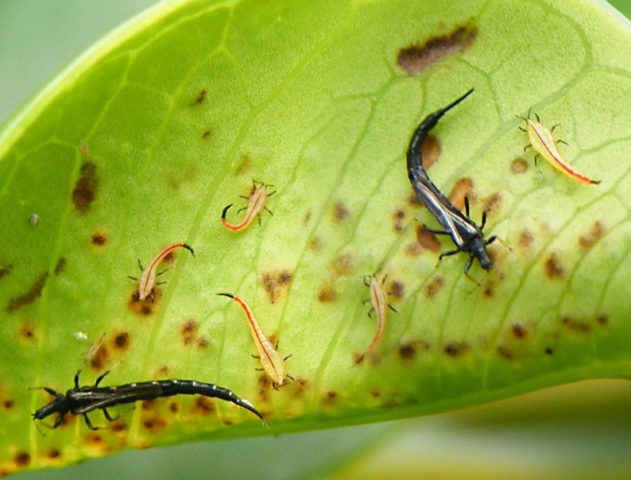

In case of massive damage, green pest excrement appears on the leaves.
Whitefly
A white flying pest in the form of a small fly. The provoking factor is increased humidity and temperature.The whitefly carries sooty fungus, which causes serious damage to petunias. You can identify it by touching the plant. In this case, a white cloud flies up. The pest is localized on the back side of the leaves.

Whitefly mainly appears in the greenhouse
Slugs
This pest causes irreparable damage to petunia. But it feeds on its young, succulent leaves, as a result of which holes appear on them. This negatively affects the decorative appearance of the plant.
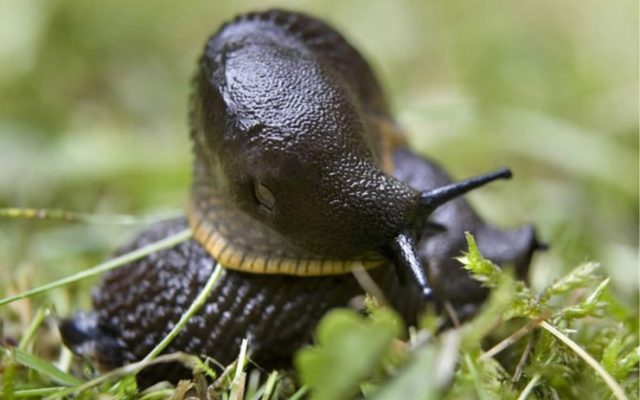

Slugs are nocturnal, which makes pest control difficult
How to control pests
To destroy and repel pests on petunias, you can use chemicals and folk remedies. The former should be used when obvious signs of damage appear, when any delay can lead to serious consequences. The second means are more suitable as prevention.
Drugs
To control pests, you need to use special chemicals that initially cause paralysis and then death of insects. They must be used strictly in accordance with the instructions.
Effective preparations for pests on petunia:
- Actellik.
- Inta-Vir.
- Confidor Extra.
- Aktara.
Folk remedies
This method of controlling pests on petunias is suitable at the initial stage of infection or as a preventive measure. If distributed on a mass scale, it may be ineffective.
Recipes for preparing pest repellents:
- Grind 100 g of garlic cloves until smooth. Pour 1 liter of water, leave for 24 hours. At the end of the waiting period, bring the total volume of liquid to 5 liters and spray the petunia bushes against pests.Repeat every 10 days.
- Finely chop the shoots and leaves of marigolds (200 g). Pour the resulting mass into 5 liters of water, let stand for 6 hours. Then strain and use for processing. Repeat every week.
- Take 100 g of tobacco dust, mustard, liquid soap and wood ash. Pour in 10 liters of water. Leave for 12 hours, peel. Apply to treat petunia bushes 1-2 times a week.
Prevention
To prevent plants from being damaged by pests and diseases, you need to follow simple rules. They cannot completely eliminate this possibility, but they can reduce it to a minimum.
Preventive measures:
- do not allow plantings to become dense;
- disinfect the soil for planting;
- regularly ventilate the seedlings;
- control air humidity and temperature;
- remove plant residues in a timely manner;
- lime acidic soil;
- regularly fertilize with phosphorus-potassium mixtures;
- periodically spray with preparations;
- do not allow overflow.
Conclusion
Knowing the diseases and pests of petunias from the photo, you can determine exactly what to do in each specific case. To do this, you only need to periodically inspect the plants to identify the problem at an early stage. This will minimize damage and quickly restore the plant.