Content
- 1 Composition and release form
- 2 Active ingredient of the herbicide Bazagran
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages
- 4 Preparation of working solution
- 5 Instructions for use of the herbicide Bazagran
- 6 Compatibility with other tools
- 7 Security measures
- 8 Analogues
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Reviews from summer residents about the drug Bazagran
Weeds are one of the main problems both on personal plots and on large farms. To protect cultivated plants from them, special preparations are widely used. These include the herbicide Bazagran, which is used primarily on an “industrial scale” to kill weeds in crops and legumes.
Composition and release form
Bazagran (now its official name is “Bazagran-M”, this is a “corrected and expanded” version of the drug of the same name) is a post-emergence contact herbicide with highly selective action. It is used to control dicotyledonous annual weeds in crops of cereals and legumes. The manufacturer of the herbicide Bazagran is a well-known agricultural company from Germany, BASF.

Initially, Bazagran was not created for amateur gardeners
This is a “highly specialized” drug: it is intended to protect strictly defined crops of agricultural importance from a specific list of weeds.The most common ones are:
- field mustard;
- cornflower;
- bindweed;
- dope;
- plants from the sedge family;
- "Tumbleweed";
- quinoa;
- field buttercup;
- shepherd's purse;
- pigweed;
- field sow thistle;
- chamomile;
- to fill up;
- yarrow.
To protect plantings against all types of knotweed and milkweed, dodder, dandelion, and bittersweet nightshade, Bazagran is useless. It is also not used against monocotyledonous weeds and rhizomatous or root-bearing perennials.
Herbicide Bazagran is available in the form of an aqueous solution, mostly in canisters of 5, 10 and 20 liters. Much less common on sale are 1 liter containers, which are more suitable for amateur gardeners.
Active ingredient of the herbicide Bazagran
The active ingredient of the herbicide Bazagran is bentazone at a concentration of 480 g/l. This substance from the class of benzothiadiazones has a pronounced contact effect. When it gets on the leaves of weeds, the chemical “blocks” photosynthesis by “binding” the electrons responsible for it into stable molecules.

Unable to “breathe” and absorb carbon dioxide, the plant quickly dries out, its above-ground part dies, and the weed dies
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the undoubted advantages of the herbicide Bazagran:
- safety for human health and the environment when following the manufacturer's instructions;
- providing protection for the entire season after a single treatment of plantings;
- long period of validity;
- lack of phytotoxicity, instability in soil, inability to accumulate in soil;
- high selectivity of action;
- Possibility of use in tank mixtures.
The herbicide also has quite significant disadvantages:
- strict “attachment” to the development phases of cultivated plants and weeds;
- a noticeable decrease in effectiveness if treatment is carried out in cool or rainy weather;
- high toxicity to aquatic fauna;
- selectivity of influence;
- high consumption of working solution;
- long period of penetration into weed tissue - if it rains during this time, repeated treatment will be required.
Preparation of working solution
The working solution is prepared no earlier than an hour before the start of treatment. The required amount of the drug is poured into the water and shaken vigorously. Then add the remaining water and mix again.

The solution is immediately prepared in the container from which it is planned to spray the plantings.
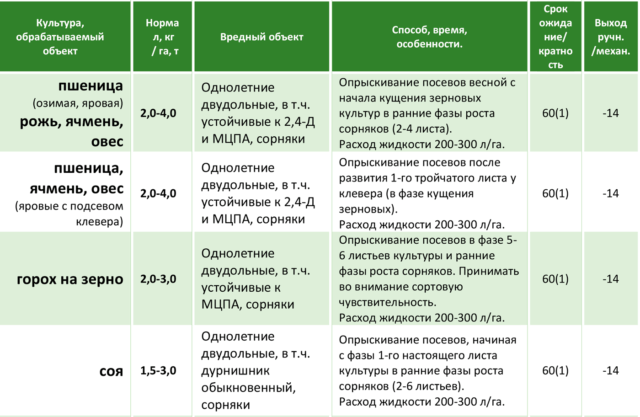
Instructions for use of the herbicide Bazagran
Treatment of weeds with the herbicide Bazagran-M is carried out by abundant spraying. According to the instructions, you cannot save the drug solution; you need to thoroughly moisten the leaf plates and stems of “uncultivated” plants with it.
The most important nuances of working with the Bazagran herbicide that must be taken into account:
- It is used only after the emergence of weeds. The drug is useless against seeds and roots.
- The optimal temperature at which Bazagran is most effective is 15-25 °C.
- Be sure to choose a dry day for processing. If it rains even slightly within four hours after it, the procedure will have to be repeated.
- Spraying must be done before the crops “cover” the weeds.
The application rate of the drug varies depending on the type of cultivated plant:
- 0.2 ml/m² for cereals and cereals;
- 0.3 ml/m² for plants from the Legume family;
- 0.35 ml/m² for flax.
It is best to use the drug when the weeds grow to 10-15 cm (the first stage of stem formation). If you spray them too early, at the stage of active growth of green mass, the weeds will form new, non-poisoned stems. When treatment is carried out too late, its effectiveness is noticeably reduced due to the “protection” provided by the crop plants. In addition, stronger weeds better resist the action of the Bazagran herbicide.
The effectiveness of Bazagran is directly related to the phases of weed development
Herbicide Bazagran for peas
Peas grown for grain are treated with a solution of the herbicide Bazagran in the 5-6 leaf phase. Weeds at this time are still at an early stage of growth. Repeated spraying is unacceptable. The harvest is harvested no earlier than 60 days after the procedure.
Herbicide Bazagran for alfalfa
In the first season after planting, alfalfa is sprayed with the herbicide Bazagran after the appearance of 1-2 true leaves. More than one treatment cannot be carried out.
“Old-growth” plants are sprayed for seeds when they reach a height of 10-15 cm. Here, repeated treatments with the herbicide Bazagran are also prohibited.
Herbicide Bazagran for cereals
Cereals (winter and spring) are sprayed with Bazagran herbicide in the spring, at the time of tillering.They do not yet have time to “cover” the weeds, which by this time have formed 2-4 true leaves. During the season, only one treatment is carried out, and the crop is harvested at least two months after it.
Compatibility with other tools
Bazagran is suitable for preparing tank mixtures. Based on the experience of gardeners and farmers, the best “companions” for it are Pulsar-40 and Pivot.

Bazagran in the mixture enhances the effectiveness of the herbicide, Pulsar prolongs the period of action
With other herbicides, preliminary checking for compatibility is necessary. The active component of Bazagran remains stable only in liquids with a certain pH. Mix 80-100 ml of working solution in a clean container. The composition is suitable for use if no signs of a chemical reaction appear over the next 45-60 minutes.
Security measures
Herbicide Bazagran for humans and bees is classified as hazard class III. However, when working with it, follow basic precautions:
- Use of personal protective equipment (respirator, goggles, rubber gloves).
- Work in clothes made of thick fabric with long sleeves and trousers, waterproof closed shoes, and a hat.
- Prohibition on smoking, drinking, and eating while processing plantings.
- The maximum time of contact with the drug is limited to 4 hours.
- Early removal of children and pets from sprayed areas.
It is also necessary, when treating with the herbicide Bazagran, not to violate the “protection zones”:
- 15 m – to residential buildings;
- 50 m – to people;
- 100 m – to non-residential buildings and structures;
- 150 m – to isolated water supply sources;
- 1.5 km – to reservoirs and apiaries.
If the Bazagran herbicide solution accidentally gets on the skin or mucous membranes, wash it off with a large volume of cool running water, and if swallowed, rinse the stomach, inducing vomiting. If symptoms indicate an allergic reaction or serious poisoning, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. There is no antidote for the herbicide Bazagran; therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms.
Analogues
There are quite a lot of herbicides based on bentazone, in addition to Bazagran. The most popular of them:
- Bazon;
- Baron;
- Benito;
- Garrison;
- Isoben;
- Corsair;
- Sicurs.
All of them are produced in the form of an aqueous solution (AS) or its concentrate (VRC). Herbicides differ in the percentage of active ingredient content, production volumes and the presence of additional components to combat other types of weeds.

Corsair is one of the Russian analogues of Bazagran
The mechanism of action of the drugs is similar to Bazagran:
- Tabezon;
- Flagship;
- Protégé.
These are Russian herbicides that have all the necessary certificates of conformity and are officially approved for use. They are also suitable for personal plots.
Conclusion
Herbicide Bazagran is a selective action drug created to protect fields with cereals and legumes from weeds.It belongs to the category of moderately hazardous; if the manufacturer’s instructions are followed, it does not cause harm to human health, future harvests or the environment. The chemical cannot be called economically consumed, but this is compensated by the one-time treatment of plantings.
Reviews from summer residents about the drug Bazagran








