Content
Wherever you and I go, everywhere we will meet people growing on their own weeds or weeds. There are many of them in fields and gardens, next to cultivated plants. They get to our sites thanks to the wind, birds, insects and animals.
The presence of weeds in crop areas leads to a sharp decrease in yield. They draw nutrients and moisture from the ground and are refuges for many harmful insects and diseases. Among them are perennial grass weeds. As a rule, you can fight the enemy successfully if you know him by sight.
What kind of weeds are they?
The diversity of cereal weeds is great due to the ability of plants to adapt to living conditions. There are:
- annuals (juveniles);
- biennial;
- perennial.
There are also differences in the structure of the seed; some are called monocots, while other weeds are called dicotyledons.
Dicotyledons and monocotyledons
The table shows the main differences.
| Plant parts | Dicotyledons | Monocots |
|---|---|---|
| Seed | Consists of two lobules. They contain nutrients. When the seed germinates, dicotyledonous plants develop a stem and two embryonic leaves. True leaves grow later. | One cotyledon.During germination, it does not come out of the ground; real leaves immediately appear on the surface. |
| Aboveground part | Powerful, spreading. | With few leaves. |
| Root | It looks like a rod and can go to great depths. | As a rule, it is fibrous and does not go deep, but wide. |
| Leaves | Located on the petiole | The petiole is missing. |
| Flowers | Structural elements 4 to 5 | Exactly 3 elements each |
Among the wide variety of plants not cultivated by humans, cereals and dicotyledonous weeds.
There are especially many weedy dicotyledonous weeds that accompany cereal crops. Among them there are annual and biennial weeds.
Dicotyledonous annuals
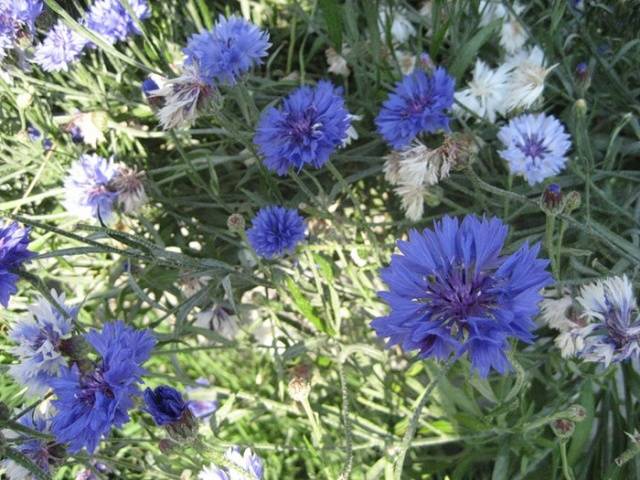
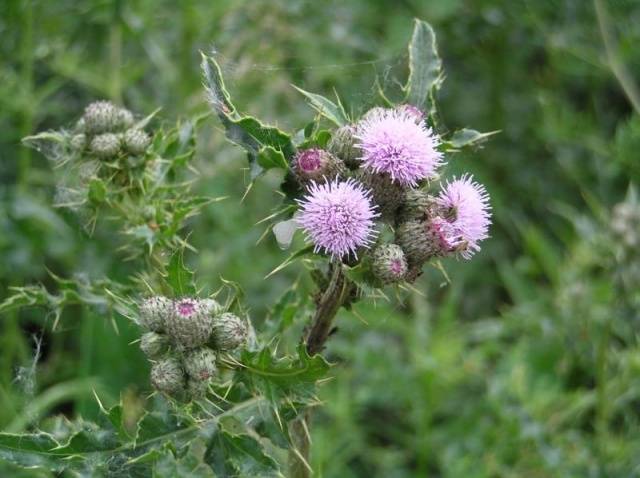
Most often, our crops suffer from annual dicotyledonous weeds that reproduce by seeds.
Some of them are presented in the list:
- mari (quinoa);
- forget-me-not;
- sow thistle;
- nightshade;
- henbane;
- shepherd's purse;
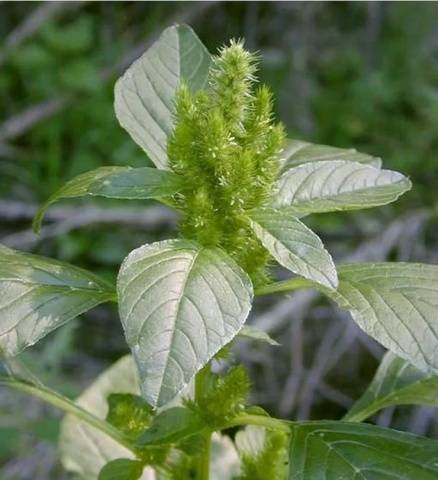
- amaranth thrown back;
- woodlice;
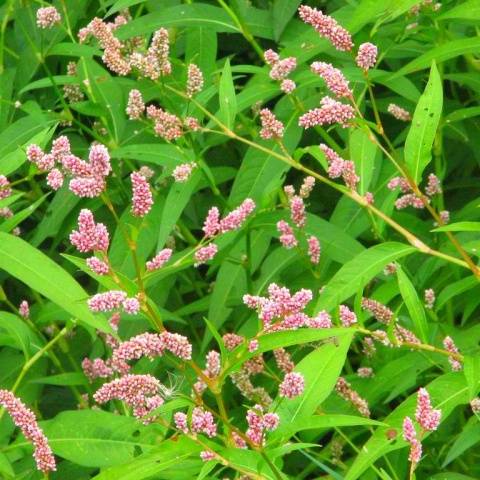
- various highlanders;
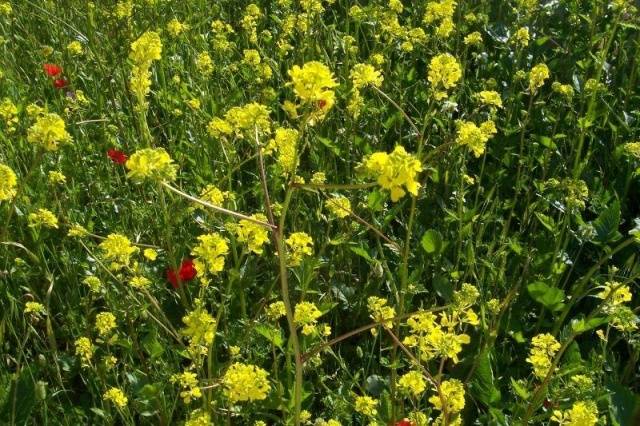
- field mustard (colts);
- blue cornflower;
- wild radish and other weeds.
Perennial dicotyledons
The group of perennial dicotyledonous plants is extensive. They grow everywhere. All plants have a powerful root system that can withstand drought and severe frosts.
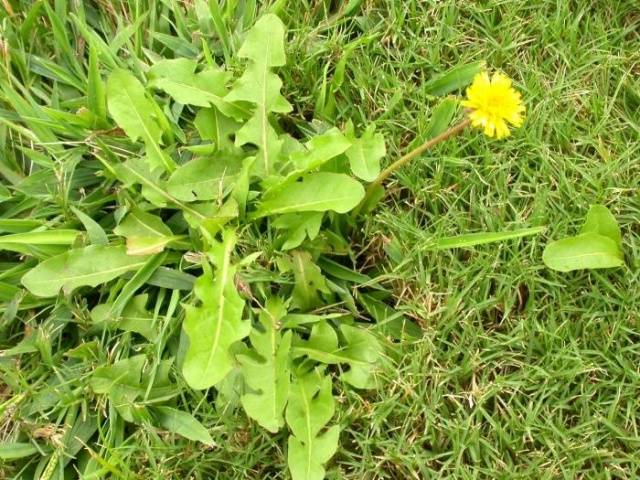
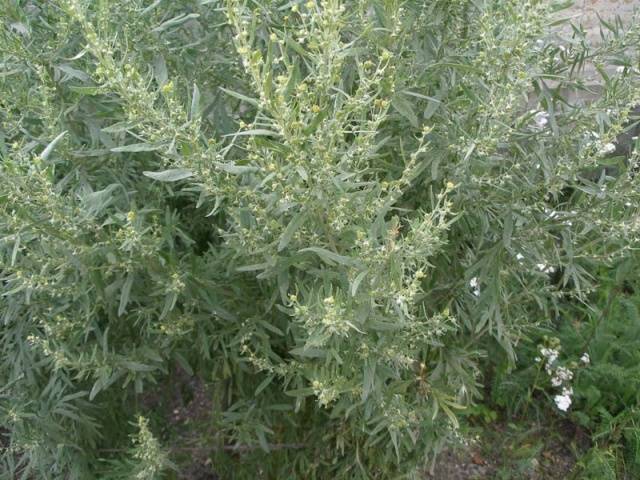
Weeds found in almost all gardens:
- plantain;
- dandelion;
- various types of wormwood;
- field sow thistle;
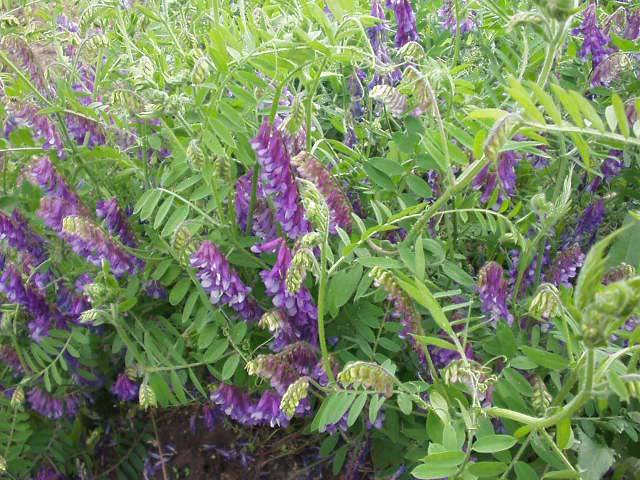
- mouse peas (vyazil);
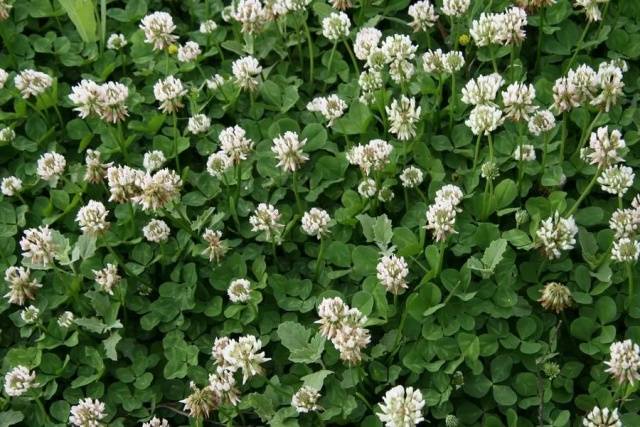
- creeping clover;
- buttercups.
Grass weeds
Perennial and annual cereal weeds are harmful pests of cultivated plants. There are more than 6 thousand of them in nature.
But when plants appear in gardens, fields and vegetable gardens, they become malicious weeds that need to be combated.
These herbaceous plants have a hollow stem-straw with internodes. The leaves are narrow, parallel in arrangement. Inconspicuous flowers are formed in the inflorescence. The inflorescences are in the form of a spike, panicles and sometimes racemes. The fruit is a dry grain.
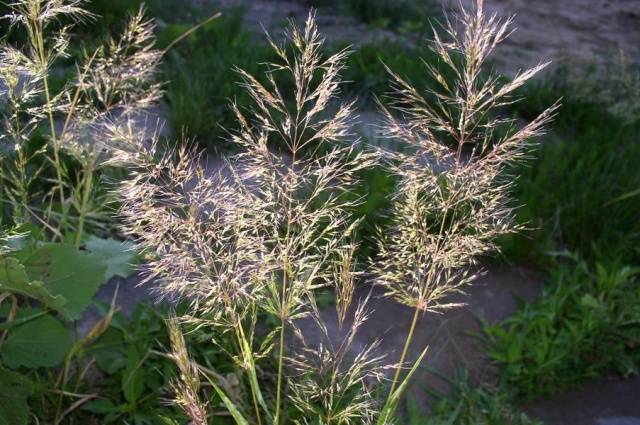
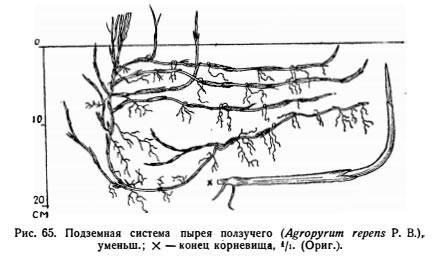
All plants have a well-developed root system. It is fibrous or branched, but is mainly located closer to the surface of the earth. Just imagine how branched the root is of cereal weeds, for example, creeping wheatgrass. Here they are in the photo.
Here are examples of some cereals weed photos and names:
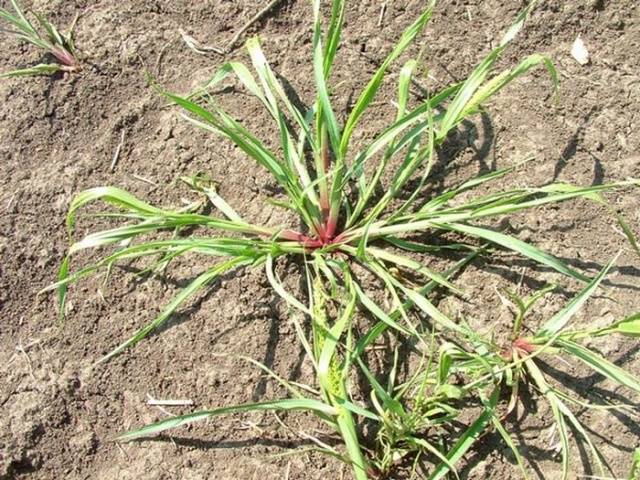
- Creeping wheatgrass. People call it Zhinets, Rzhanets, Dandur. Having settled in the garden, it can crowd out other plants. With its fibrous system it draws juices from the earth, depleting it. The roots grow up to 12 meters. This grassy weed grows especially well on loose, fertile soils.
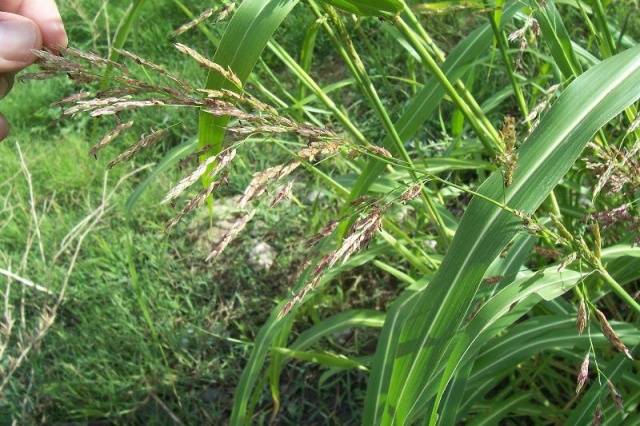
- Chicken millet grows everywhere. The plant is tall, up to 20 cm, spreading. One bush occupies a large area. The wide leaves of this grassy weed require a lot of nutrients and moisture, which it takes away from cultivated plants.
- Blood-red crabgrass feels excellent even on acidic soils. A huge number of small seeds ripen in the spikelets-panicles, germinating already at 2 degrees Celsius.
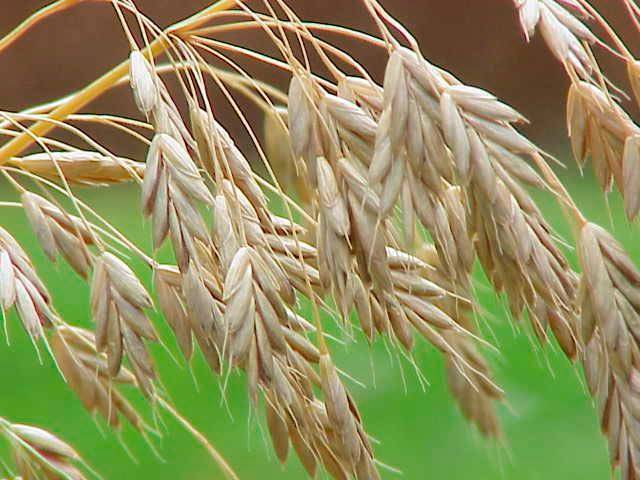
- Rye brome grows in Siberia and the Far East. The plant is winter-hardy and drought-resistant. The seeds ripen in a spikelet. If they go to a depth of 10 cm, they will not be able to germinate. This grassy perennial weed is as tall as wheat by late summer, so brome seed may end up in the combine hopper during harvest. This plant is particularly harmful in reducing the quality of food grains.
The list goes on for a long time. Let's name a few more of the most common grassy weeds in our gardens:
- common broom;
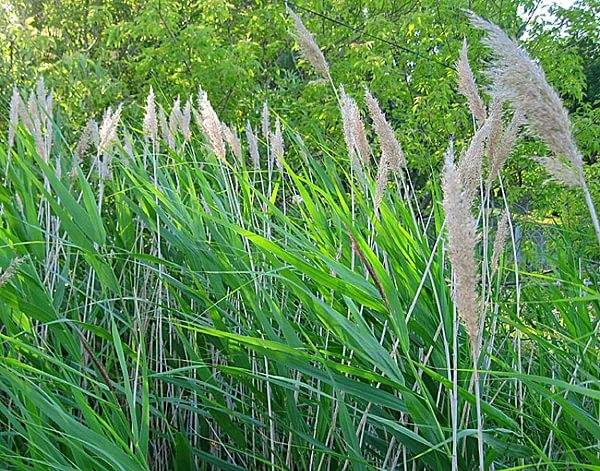
- common reed;
- gumai or wild sorghum;
- turf pike;
- wild oats;
- bluegrass.
How to fight weeds
Regardless of what weeds, annual or perennial, appear in your garden, you need to get rid of them immediately.
There are various ways to combat green pests of gardens and vegetable gardens:
- mechanical or agrotechnical;
- traditional methods;
- use of herbicides.
Agricultural technology against weeds
Firstly, a good gardener never has a single piece of land empty. He will always find a crop that can be planted even on a small piece of land. Therefore, there is no room left for weeds to grow and develop. This is one of the agricultural techniques.
Secondly, regular weeding and loosening prevent weeds from rearing their heads.
Thirdly, mulching of beds and paths on the site is widely used to deprive annual or perennial weeds of light. In this case, already sprouted plants die, and the seeds cannot germinate. You can use available materials as mulch:
- old newspapers;
- cardboard;
- sawdust;
- tree bark;
- pieces of roofing felt;
- old boards;
- dark film.
As a rule, agricultural technology for growing cultivated plants helps to get rid of weeds in dachas and garden plots. But if the desired result is not available, you can use chemical products.
Tough control measures
If it is not possible to get rid of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous weeds using traditional methods, experienced gardeners recommend using herbicides. The choice of drugs today is large. You can use:
- Roundup;
- Hurricane;
- Tornado;
- Lapis lazuli.
The remedy goes through the leaves to the root. After spraying, weeds turn yellow and die. The drugs do not accumulate in the soil. But it is advisable not to plant cultivated plants in the treated area this year so that we can completely eradicate the weeds.
How to fight weeds:
Let's sum it up
It is good to admire flowering plants in a forest or meadow. But when annual or perennial dicotyledonous or monocotyledonous weeds and cereal grasses appear in a plot with vegetables, there is no time for beauty. Delay in removing them can negatively affect the harvest.