Content
There is probably no other such labor-intensive operation in the garden as weeding. Standing in a bent position or on your knees for many hours will tire any gardener. But what can you do? Without deletion weed you can’t grow vegetables, berries or fruits. But it was like that before. Progress in the case weed control made the gardener's work much easier. There are many drugs that can destroy weeds with minimal participation from the farmer. Is it necessary to fight them? Maybe there is nothing wrong with the fact that they coexist in the same bed with cultivated plants? Let's look at this in more detail.
What is a weed? The word litter, from which the name of weeds comes, has a synonym - garbage, that is, something that is not needed and is usually thrown away. Therefore, weeds are plants that have every right to grow anywhere, but not in the beds. What is their harm?
Weed damage
- Weeds take away nutrition from garden crops.
- Weeds deprive them of moisture.
- By shading cultivated plants, weeds inhibit their photosynthesis process, thereby delaying the development of garden plants and reducing their yield.
- When large numbers of weeds multiply, they displace garden crops from the beds.
Hardened by the struggle for water, food and sunlight, weeds have great vital potential. Cultivated plants, pampered by human care, are obviously inferior to weeds in the ability to adapt to any circumstances. The job of the gardener is to create conditions under which garden plants will devote all their efforts to producing a harvest, and not to fighting for survival. Therefore, it is necessary to remove weeds from the beds. But there are some subtleties here too. In order to successfully deal with weeds and save your time, you need to know the enemy by sight.
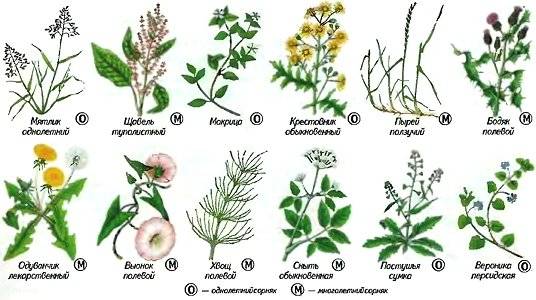
Characteristics of weeds
All weeds differ in the following characteristics:
- duration of growing season;
- methods of reproduction;
- nutritional characteristics.
Weeds are classified as annual, biennial and perennial. Each of these categories requires its own techniques when eradicating weeds.
Fighting methods
There are different methods to control weeds.
- Manual weeding. A fairly effective, but very labor-intensive method, which also has to be repeated many times during the season. Perennial weeds grow back after weeding. Weeds removed from the garden can improve fertility. Don't throw them away anywhere. Build a compost bin without a bottom and with holes on the sides for weeds. After a year, the resulting compost can be used to fertilize garden crops.
- Mechanical method. In addition to traditional hoes, flat cutters and weed root removers have appeared in the gardener's arsenal. For large areas, walk-behind tractors with various attachments can be used.
- Mulching. With its help, conditions are created under which weeds cannot develop.There are a lot of mulching materials: hay, grass clippings without seeds, sawdust, black covering material and a film of the same color, a layer of newspapers or cardboard. If fresh sawdust is used for mulching, be sure to moisten it with a solution of nitrogen fertilizer, such as urea. As sawdust decomposes, nitrogen can be absorbed from the soil, depleting it.
Folk remedies
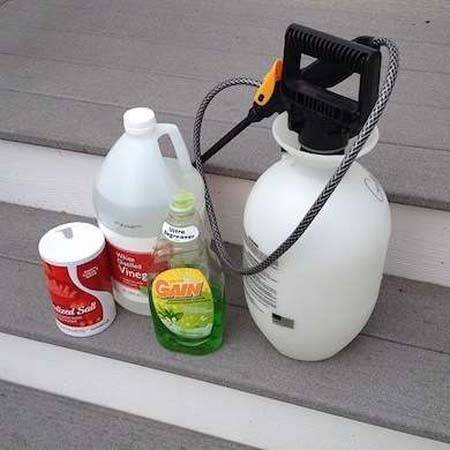
Soda – a strong soda solution will help cope with small grass, especially if it grows between the slabs of paths, where weeding is difficult.
Salt – if you sprinkle a small amount of salt next to the planted crops, the weeds will not only die, but also will not grow in this place for some time.
Vinegar 9% - effective method. It is used to spray weeds.
A mixture of vinegar and salt with the addition of grated laundry or liquid soap, all in equal quantities, is an excellent way to deal with weeds. The product needs to be sprayed.
Vinegar is also used in another mixture to suppress weeds. Its composition: take 2 glasses of water and 9% vinegar, add to them one bag of citric acid, 2 teaspoons of liquid soap and 30 g of alcohol. The precautions are the same as in the previous recipe.
To prevent weed seeds from germinating, feed grain is used. Ground corn or oats are sprayed on the beds. Gluten, which is found in feed grains, inhibits the growth of weed seeds.
If you do this earlier, garden crops may simply not sprout.
Medical alcohol diluted 1:10 will also help fight weeds. If you take one liter of alcohol and dilute it, this amount will be enough for about 2 acres of land. Treatment should be carried out a month before sowing or planting.
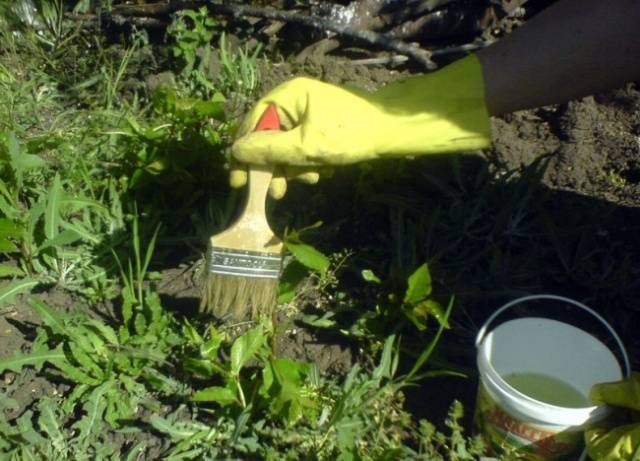
All products listed are suitable for spraying. To treat weeds with certainty without harming garden crops, you can use a small paint brush.
If for some reason all these methods of weed control are not suitable, you will have to resort to chemicals. The modern range of chemicals for combating unwanted vegetation is quite large. They are called herbicides and their effects are as follows.
Characteristics of herbicides
- Selective herbicides. Their use is sometimes called chemical weeding. Such substances act selectively either on one type of plant or only on a certain family of weeds, for example, on dicotyledonous weeds.
- Continuous herbicides. These herbicides destroy all types of vegetation completely. Such substances are used before garden crops appear in the garden beds in the spring or after they are harvested in the fall. Most of these drugs are based on glyphosate.
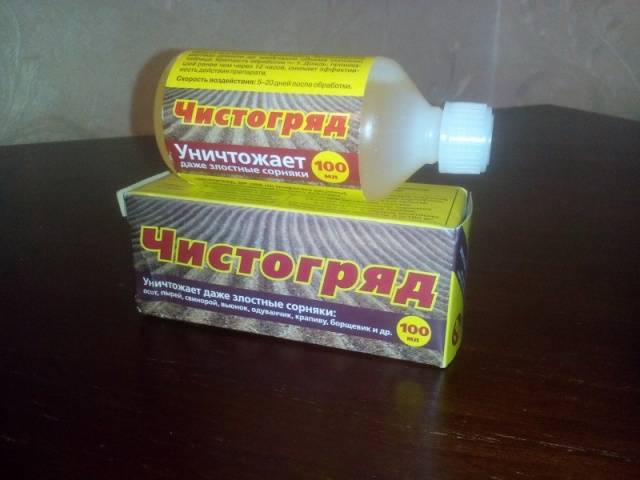
Chistogryad – the latest generation herbicide
A new weed control drug, Chistograd, has recently been created, the reviews of which are encouraging. It is not only a continuous herbicide, but also a desiccant, i.e., a substance that dehydrates plants.
Herbicide Chistogryad is available in tubes of 50 and 100 ml or in a bottle with a volume of 0.5 liters. The active ingredient in Chistogryad is the isopropylamine salt of glyphosate.The mechanism of action of this herbicide on weeds is not fully understood. Some studies suggest that Chistogryad disrupts the process of cellular metabolism in plants by inhibiting the enzymatic process through which aromatic amino acids are synthesized - an important element of cellular metabolism. When it lands on weeds, Chistogryad is partially absorbed by them and, moving through the vessels, penetrates into the roots. The effect of the herbicide will be noticeable within 10 days, and complete death of the weeds occurs after 3 weeks. Chistogryd cannot be absorbed by the roots of plants.
There is evidence that glyphosate-based herbicides reduce plant disease resistance. Once in the soil, they inhibit the development of nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Application area
Chistogryad fights everyone weed species, including the most malicious ones. It is intended for processing areas 2 weeks before sowing cultivated plants and lawn grass. Clean garden can be used to exterminate weeds in vineyards and citrus plantings, provided that the main crop is carefully protected. Clean garden can also be used after harvesting to remove perennial and wintering annual weeds.
How to use
The instructions recommend diluting this herbicide with clean water in a proportion of 100 ml of the drug per 6 or 4 liters of water. A more concentrated solution of Chistogryad is used where there are a lot of malicious weeds, for example, wheatgrass. With this amount of solution, 200 and 130 square meters can be treated, respectively.
To dilute the herbicide, use plastic or enamel containers; metal containers are not suitable. Diluted in stages, first the entire amount of Chistogryad is thoroughly stirred in 1 liter of water, and then the rest of the water is added to the required volume.
Treat the area with a herbicide solution once. The drug is absorbed by weed leaves, so you can’t mow or weed them before treatment. The absorption process lasts up to 6 hours.
If it does not have time to be absorbed into the leaves, it may be washed away by rain, and the effectiveness of the treatment will decrease.
Health Hazard
The main breakdown product of glyphosate is aminomethylphosphanic acid. The period during which glyphosate decomposes by half ranges from a week to 140 days. Glyphosate binds easily to soil and is also easily released from it.
Exceeding the concentration of the drug poses a health hazard. Symptoms of Chistogryad poisoning are as follows.
- Pain and burning in the eyes, blurred vision.
- Burning and itching of the skin, rashes, blisters, eczema.
- Swelling of the face and joints.
- Heart rhythm disturbances, chest pain.
- Headache and increased blood pressure.
- Cough.
If Chistogryad accidentally gets on your skin or eyes, rinse them with plenty of water.
Weeds have no place in the garden. Use any methods to combat them to ensure optimal conditions for the development of garden crops.