Content
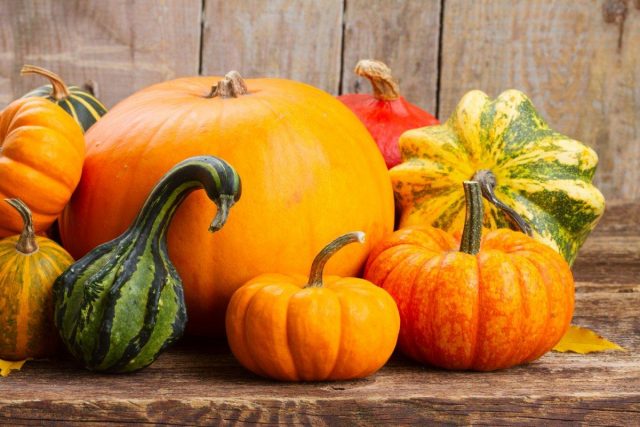
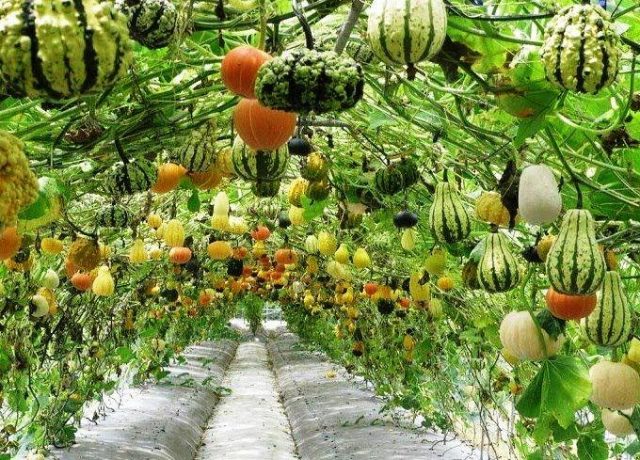
Decorative pumpkin is a real garden decoration. With its help, they decorate arches, gazebos, walls, and decorate flower beds, flowerpots, and verandas. The article presents popular decorative varieties of pumpkin with photos and descriptions that will help you evaluate the variety of colors, sizes, shapes and choose the best option for your site.
Why are decorative pumpkins grown?
Decorative pumpkin varieties are becoming increasingly popular among gardeners. Neat, beautiful, bright, varied in shape and color plants are planted to decorate the garden, design gazebos, and form unusual flower beds. Ripened and dried fruits, coated with varnish or paint, serve as the basis for design work. Vases, boxes, candlesticks, and various vessels are cut out of them.
In addition, gardeners appreciate the agrotechnical characteristics of decorative pumpkins:
- Ease of cultivation. To obtain dense greenery and bright fruits, the crop needs timely watering, fertilizing, and loosening the soil. The green cover is formed naturally and does not require shaping, cutting or pinching.
- High growth rate. Within a month after planting in open ground, the pumpkin vine reaches 5 m, which allows it to be used for vertical framing of fences, gazebos, and walls. Then active flowering and fruit growth begins.
- Form stability. Decorative pumpkin varieties retain their size, shape, and color until late autumn.
Summer residents are also attracted by large, bright flowers that densely dot the vines during the growing season.
Description of decorative pumpkin
Decorative pumpkins are annual climbing melons, bred by cross-pollinating ordinary large-fruited varieties and crossing them with zucchini, squash, and zucchini.
The shoots of decorative pumpkins are thinner and weaker than those of table pumpkins, but they grow very quickly: during the season they stretch up to 4 - 5 m. The foliage cover is denser and thicker, due to the greater number of lateral shoots. The color of greenery varies from emerald to pale green.
Bush varieties of decorative pumpkins are less common. Plants are planted in flower beds, flower beds, alpine slides, flowerpots, and they decorate terraces and garden alleys.
The flowering period of decorative varieties of pumpkins occurs in June. The inflorescences of the culture are velvety: large, bright yellow, sometimes pale or white.
From mid-July the first fruits are formed. Depending on the pumpkin variety, they can be:
- round, pear-shaped, crown-shaped, flattened, bottle-shaped, elongated, turban-shaped, star-shaped;
- yellow, orange, white, red, green, striped, two or three colors, spotted, motley;
- with smooth, ribbed, pimply, bumpy skin.
Varieties of decorative pumpkin
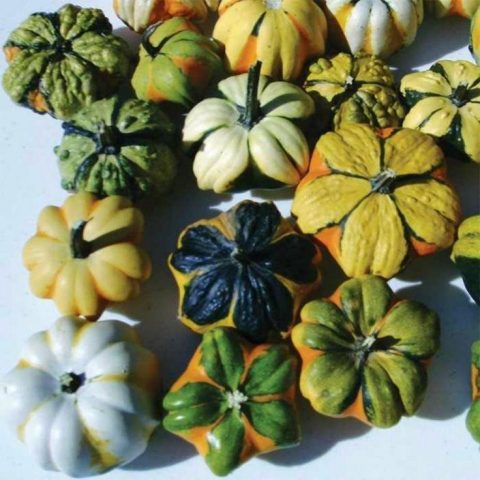
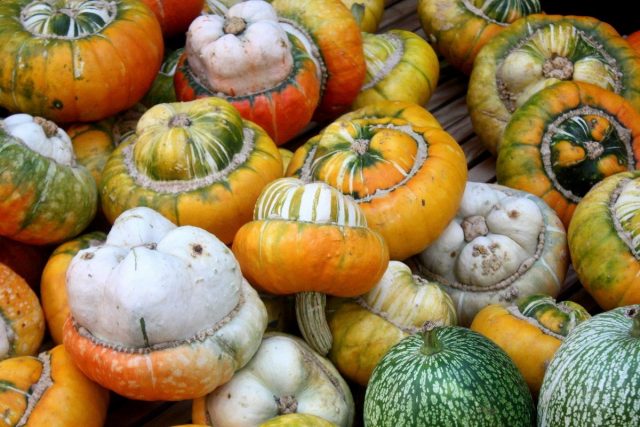
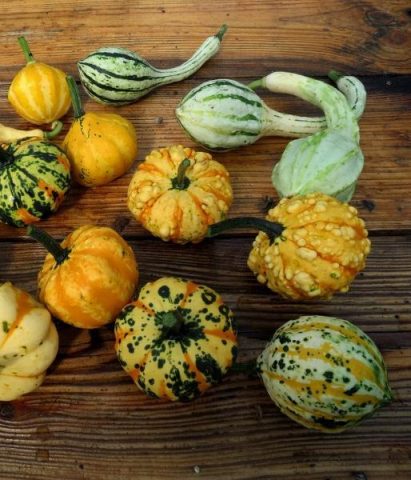
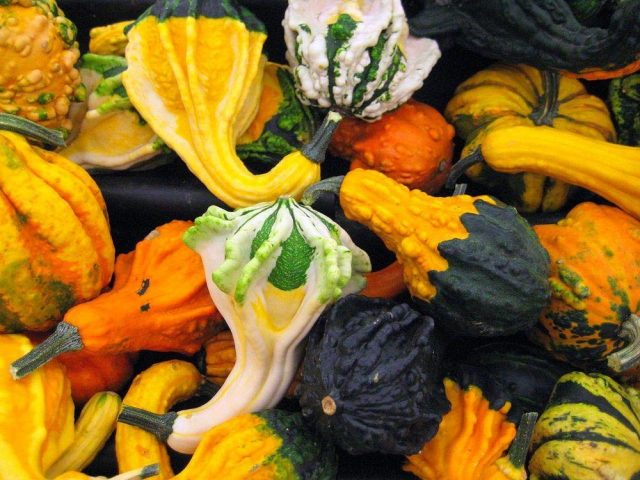
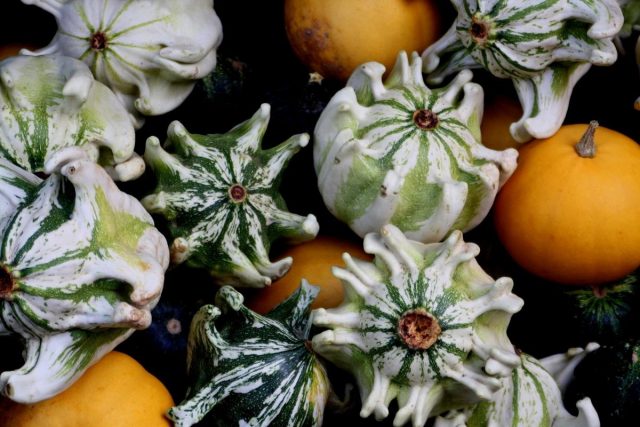
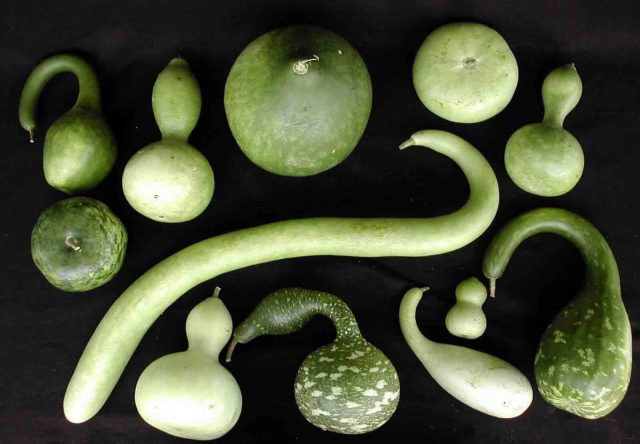
Breeders have bred more than 100 varieties of mini-pumpkins. They differ in color, shape, size. You can evaluate the entire variety of decorative pumpkins from the photo.
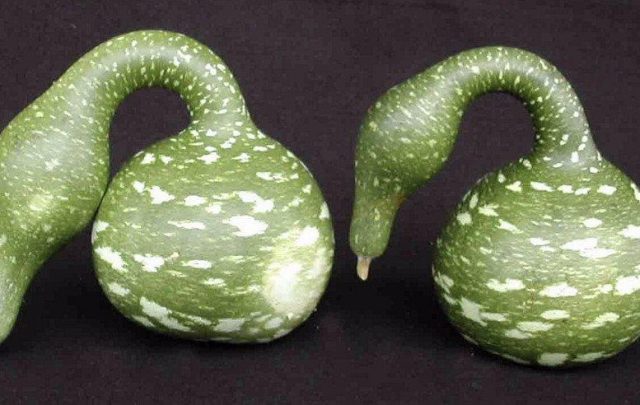
Swan
Decorative pumpkin Swan is one of the varieties of lagenaria. Whip plants are fast-growing with round, large leaves. The culture is demanding of heat, light, and watering. It is better to plant it as seedlings when the air and soil warm up to 17 - 20 degrees.
Of interest are the pumpkin fruits, which look like swans with sophisticated curved necks. The peel of such decorative fruits is dense, dark green with white speckles.
The variety is characterized as fast-growing. If all agricultural technology requirements are met, 8–12 fruits can be harvested from one ornamental bush per season.
Pear-shaped, or pear
The fruits of the pear-shaped decorative pumpkin grow up to 12–18 cm in diameter. Their colors are varied. There are yellow, cream, white, red, green, orange varieties.
Two-colored, variegated or striped decorative pear pumpkins with a clearly defined transverse border (Klein bicolour) look beautiful on the site.
The Texas variety with large, pear-shaped watermelon-like fruits belongs to this subgroup. Their color is dark green and yellow, forming a background on which light transverse stripes are superimposed.
Crown
The Corona variety of decorative pumpkin is one of the most spectacular and unusual. Its bright yellow or yellow-green fruits rarely grow more than 12 - 15 cm in diameter. They come in star-shaped, umbrella-shaped, and crown-shaped.
Pumpkin stems are ribbed, grow 3–4 m in length, ideal for forming hedges and arches. The leaves have a deep, rich emerald hue, which favorably sets off single large flowers.
Fango
Ornamental pumpkin Fango is a fast-growing variety with wrinkled, spiny leaves and large, white, funnel-shaped flowers. Ripe fruits look very attractive, resembling colorful mushroom caps.
For proper growth and a good harvest, Fango pumpkin is planted in sunny areas. It is thermophilic and does not tolerate cold weather or dry soil.
The shoots are used for vertical gardening of a veranda or gazebo, and the fruits are used to make various decorative compositions.
Borovichok
Decorative pumpkin Borovichok belongs to the turban-shaped varieties. Its fruits are shaped like a mushroom with a large red cap and a thick light stalk. This interesting feature is actively used for the design of autumn compositions, children's creativity, and the design of rooms in a rustic style.
The flowers of the plant are large, white, funnel-shaped. They appear in early June. Active flowering lasts about a month.
Boletus - prefers sunny, warm, fertile areas. For successful seed germination, the soil temperature should not fall below 20 degrees. The plant actively responds to fertilization, timely watering, weeding and loosening.
The variety is suitable for horizontal and vertical decoration of flower beds, flower beds, hedges, arches, and garden flowerpots.
Artist
Decorative pumpkin Artist is a mixture of small varieties, different in terms of ripening, appearance, color, and shape.
The vines are fast-growing, reaching 4 m in a season. With sufficient timely watering and fertilizing, they form lush greenery.
In June–July, the plant is covered with large yellow flowers, in place of which small (about 200–400 g) pumpkins appear over time.
The variety is planted for vertical gardening, masking unsightly walls, and decorating openings.
Indie
Decorative pumpkin Indy is a mixture of pear-shaped varieties of different shapes, sizes, and colors.
The lashes of this variety are long, cling well to support, and actively grow. Fruits gain weight quickly and may require additional support.
Shahrazade stars
The color of the fruits of the decorative pumpkin Scheherazade star is varied. They come in yellow, white, milky, green, two-tone, striped or speckled. The diameter of pumpkins does not exceed 10 cm.
Scheherazade belongs to the subgroup of star gourds. Its shape is flattened, oblong, reminiscent of squash - with more pointed, elongated edges.
The variety is suitable for vertical growth.
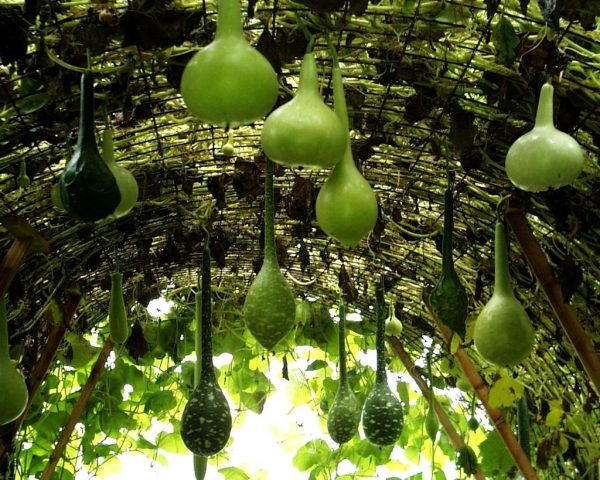
Lagenaria
Lagenaria is the original name for a large group of decorative pumpkins that have a variety of elongated, elongated shapes.
The variety is suitable for vertical cultivation; the vines grow very quickly. In July, pale pink or white large flowers appear on long stems.
The shape of the decorative pumpkin fruits is varied, which can be assessed from the photo.
The peel of pumpkins is very hard, which allows these vegetables to be used for making dishes: jugs, decanters, bottles with a narrow neck and a stable base.
Lagenaria can be eaten. This applies to young shoots no longer than 30–40 cm.
The variety can be grown in open ground, a greenhouse, on a balcony or loggia.
Bottle shop
Bottle gourds are a large subgroup of decorative pumpkins with a narrow, elongated upper part and a rounded bottom. The shape of the fruits can resemble a jug, a swan, or a mace.
Another name for the variety is tableware or gourd pumpkin. Since ancient times, dried, peeled vegetables were used to make light, durable, environmentally friendly utensils: bottles, flasks, jugs.
Mandarin
The fruits of mini-pumpkins of the Mandarin variety are small, about 5–7 cm in diameter, round in shape, and bright orange in color. In appearance they are similar to the fruit of the same name. The foliage of the plant is a rich emerald shade.
The variety is suitable for cooking, but is more often used as a mini-pot, original bowl or cocotte maker.
Fungus
Refers to turban-shaped pumpkins. The upper part of the vegetable is massive, its color is rich orange, red, green. The lower half is smaller, with a white, pale green, mottled coloration.In appearance, color, and ripening time, the crop resembles the Borovichok variety.
The fungus is recognized as the most frost- and drought-resistant variety; it is not susceptible to diseases. The pulp of pumpkins has a fibrous and watery structure and has a bitter taste.
Is it possible to eat decorative pumpkin?
Small-fruited pumpkins are most often grown for decorative purposes, to decorate a personal plot. The pulp of such fruits is also watery, dense, hard, and when cooked it turns out tasteless.
However, some of this variety of decorative pumpkin can be eaten, they are suitable for cooking, and have good taste.
It is important to remember that only young vegetables whose peel has not yet become hard are suitable for food. In cooking, they are most often used as aromatic, edible pots for roasting meat, fish, and poultry.
How to dry a whole pumpkin for decoration
Before using a pumpkin to create a composition or make crafts, it must be properly and efficiently dried.
To do this, select ripe, undamaged fruits with a dried, brown stalk. It is important to have time to harvest before the first frost, otherwise the vegetable will not be stored for long and will eventually rot.
Algorithm for how to properly dry a whole pumpkin:
- The collected fruits should be washed well in warm water with soap or baking soda.
- Then lay them out in one layer in a warm, ventilated room so that they are not exposed to direct sunlight.
- Vegetables should be periodically turned over to the other side, while discarding low-quality, rotting specimens.
- After a week, the top layer of the peel will dry out. Pumpkins are transferred to a dark room with good ventilation. If this is not possible, a place under the bed or in a closet will do. The fruits are placed on a grid at some distance from each other or suspended, providing air flow from all sides.
- Once a week, turn the pumpkins over to watch for any rot or mold.
The process is lengthy and can take 3–6 months, depending on the variety. If, when shaking the fruit, you can clearly hear the seeds rattling inside, this is a sign that the pumpkin has already dried out.
Planting and caring for decorative pumpkin
Planting and caring for decorative pumpkins does not require special knowledge; even a novice amateur gardener can handle it.
Where, when and how to plant decorative pumpkin
Decorative varieties love sunny, well-warmed areas with fertile, loose soil. The best predecessors that increase pumpkin yield are legumes, cabbage, beets, onions, and carrots. On the contrary, potatoes, cucumbers or any melon crops deplete the soil and draw out from it the mineral substances necessary for the full growth of the pumpkin. Ornamental varieties should not be planted in such areas.
Neighborhood with other crops also affects productivity and foliage formation. For example, spinach, beans, onions, and peas attract pests that interfere with the growth of shoots.
In the southern regions and the middle zone, seeds are planted in open ground to a depth of 8 cm. The distance between the roots should be at least 25 - 30 cm. The optimal time for planting is May–early June, when the average daily temperature is no lower than 14 degrees.
To get a harvest, the seeds need to be prepared. For this:
- The planting material is placed in water for a few minutes, the floating seeds are removed: they are unsuitable for growing.
- The remaining seeds are wrapped in gauze and soaked for 2 hours in a manganese solution to disinfect and prevent bacterial diseases of the plant.
- Then the seed is washed and dried.
To speed up germination, the seeds are germinated: wrapped in gauze or flannel, poured with warm water, and left for two days. The main thing is to provide constant moisture to the seeds. After the seedlings appear, the seedlings can be placed in the holes.
In northern latitudes, it is preferable to plant pumpkins in seedlings, for this:
- One seed is placed in small pots (15–20 cm in diameter). The pots are moistened and placed in a bright place under a covering material.
- After germination, carefully monitor the temperature, water the soil with warm water, and periodically add fertilizer (per 10 liters of water: 20 g of superphosphate, potassium sulfide, 1 liter of mullein).
- Young shoots are transferred to a permanent place a month after germination, when the plant has 5 true leaves.
- 2 weeks before planting in open ground, the seedlings are hardened off - taken out to the veranda, outside, and left overnight with the window open.
- Seedlings are planted in holes 10–12 cm deep. Before this, fertilizers must be applied (3 tablespoons of ash, 2 tablespoons of superphosphate) and moistened with warm water.
- The seedlings are sprinkled with fertile soil and mulched with peat or sawdust.
When choosing a place to plant a decorative pumpkin, it is necessary to provide for the installation of high-quality, strong support.Metal or wooden stable structures are suitable. Plastic or bamboo will not support the weight of the fruit.
Growing decorative pumpkin
Even a beginner, inexperienced summer resident can cope with growing decorative varieties of pumpkin.
For rapid growth, flowering, and the formation of full-fledged fruits, the plant requires a lot of sun, abundant watering, and periodic addition of organic additives to the soil.
Pumpkin seeds or sprouted young shoots are planted in open, fertile, well-warmed areas. Complex organic additives are added to the hole during planting, as well as 14 days after it. The next feeding is carried out during the formation of the ovaries. The soil must be mulched with sawdust and dry humus. Further care of the decorative pumpkin consists of timely moistening as the soil dries and loosening it.
During flowering and formation of ovaries, the plant is watered once every 3 days. During the period of fruit ripening - once every 5 days. Use warm, settled water for this.
The next day after watering, the soil is loosened and weeds are removed.
As soon as the main stem of the plant reaches a meter in length, it is pinched to form lush side shoots.
The lashes of the decorative pumpkin easily cling to the support. As it grows and the mass of leaves and fruits increases, additional strengthening and garter may be required.
To preserve young shoots in the spring and extend the fruiting period in the fall, experienced gardeners recommend using covering material.
Pests and diseases
Pumpkin is an unpretentious crop that is resistant to pests and diseases.
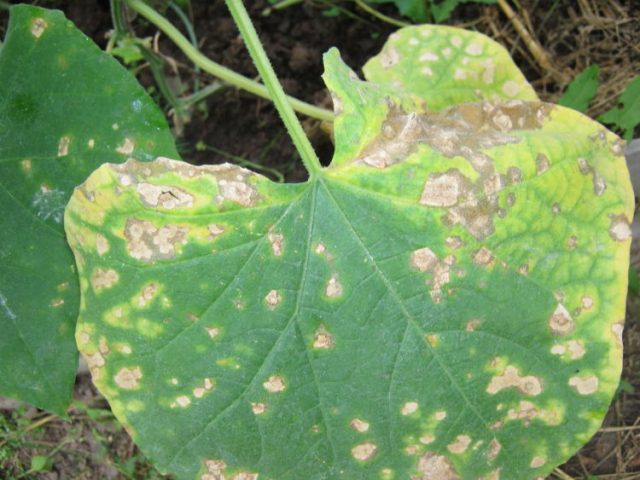
With improper care, waterlogging, and general contamination of the area, decorative varieties face the same damage as all melon types:
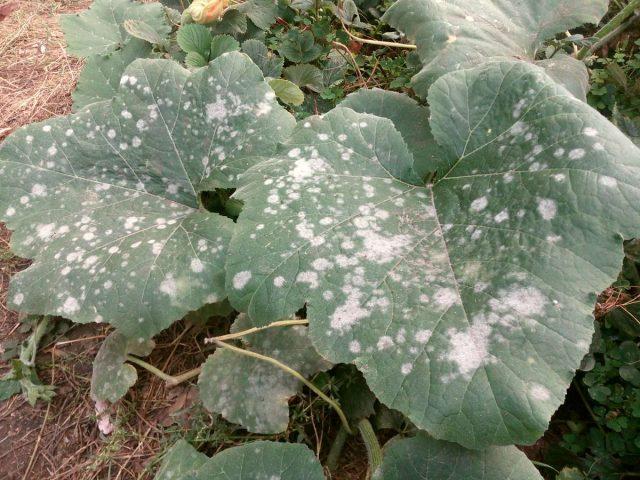
- Powdery mildew - a dense white coating on shoots and leaves, which tends to inhibit growth and spoil ovaries and fruits. It occurs when there is a lack of lighting and sudden changes in temperature. To eliminate it, special drugs are used.
- Root rot (white rot) – the disease is caused by parasitic soil fungi that attack the root system of decorative pumpkins. The plant usually dies. As a preventive measure, before planting, the seeds are soaked in a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and then the root hole is sprinkled with humus or peat.
- Bacterial rot – forms brownish spots on stems or leaves that appear from excessive moisture and frequent heavy watering. Damaged areas of the plant are treated with 1% Bardos liquid.
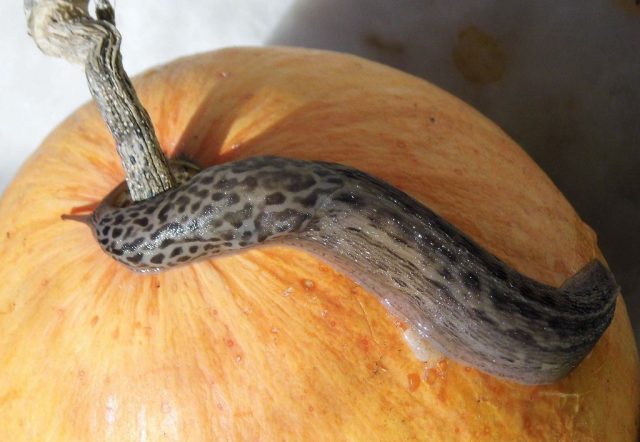
- Slugs – affect the plant during the rainy season, causing significant damage to the leaves, shoots, and fruits of the pumpkin. Scattered ash and slaked lime (1:1) help get rid of them.
If signs of infection are detected, damaged stems, leaves, fruits or the entire plant are destroyed, and the area is treated with appropriate insecticides.
Conclusion
A decorative pumpkin with an unusual appearance will help to refine the design of your garden plot, while adding bright colors to it. An unpretentious plant that is resistant to diseases and pests will not cause trouble even for inexperienced gardeners.