Content
You can save onions if they start to rot. But it’s better not to allow this at all. Rotting occurs due to various reasons. Knowing about them, the owner will be able to avoid a similar situation in the future.
Why do onions rot after harvesting?
The appearance of rot occurs due to damage by microorganisms, which can be fungal spores or bacteria. Even vegetables quickly rot if harvesting deadlines are violated, improper storage, or lack of agricultural technology.
Diseases
Typically, onion rotting is associated with disease before harvest. Unnoticed during the selection process, the bulbs end up in storage, where the fungi continue to actively develop. As a result, neighboring vegetables become infected. Diseases are dangerous because they can lead to the loss of a large volume of crops.
Among them the most harmful are:
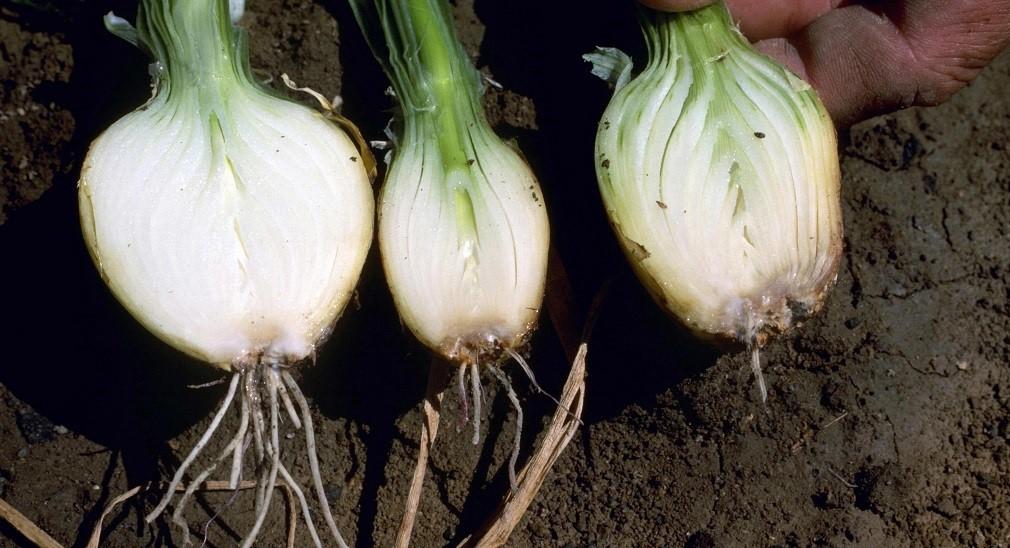
- Fusarium. It is expressed in the appearance of a reddish coating on the onion. The root crop becomes softened and, when cut, has a gray color. As a result of infection, rot occurs.
Onions become mummified during storage.
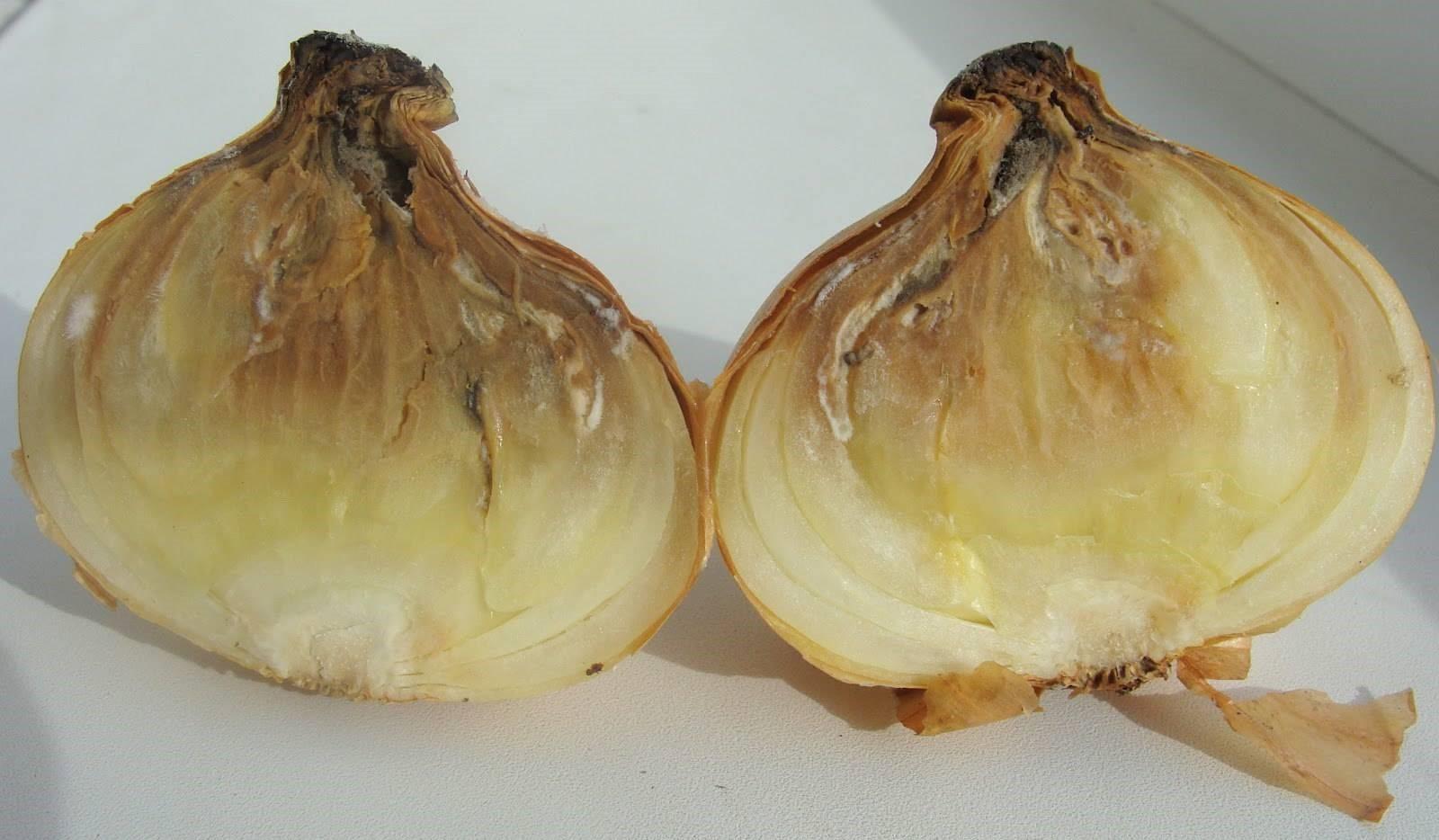
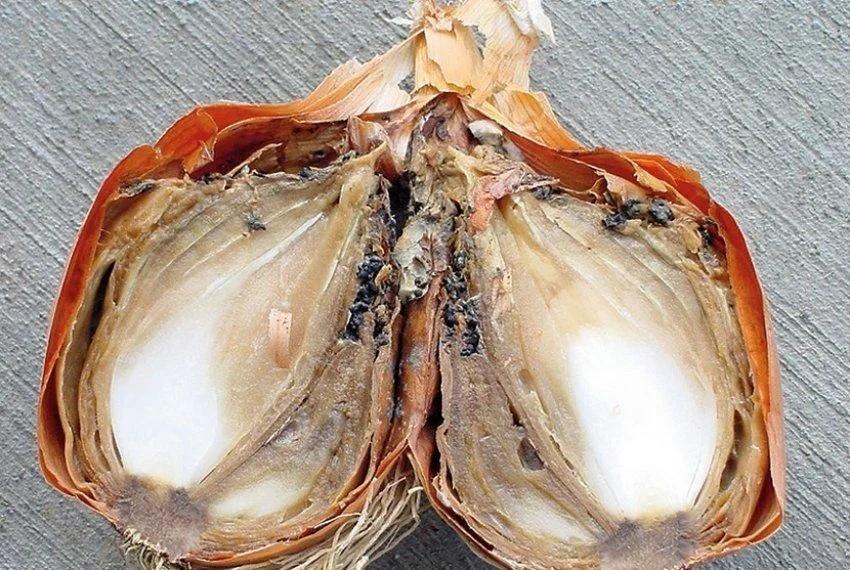
- Cervical rot. In some places mold can be seen, and some areas are darkening.This onion is watery and soft to the touch. Ink-colored dots appear on the scales – a fungus.
Onions rot gradually, and the disease spreads to other crops
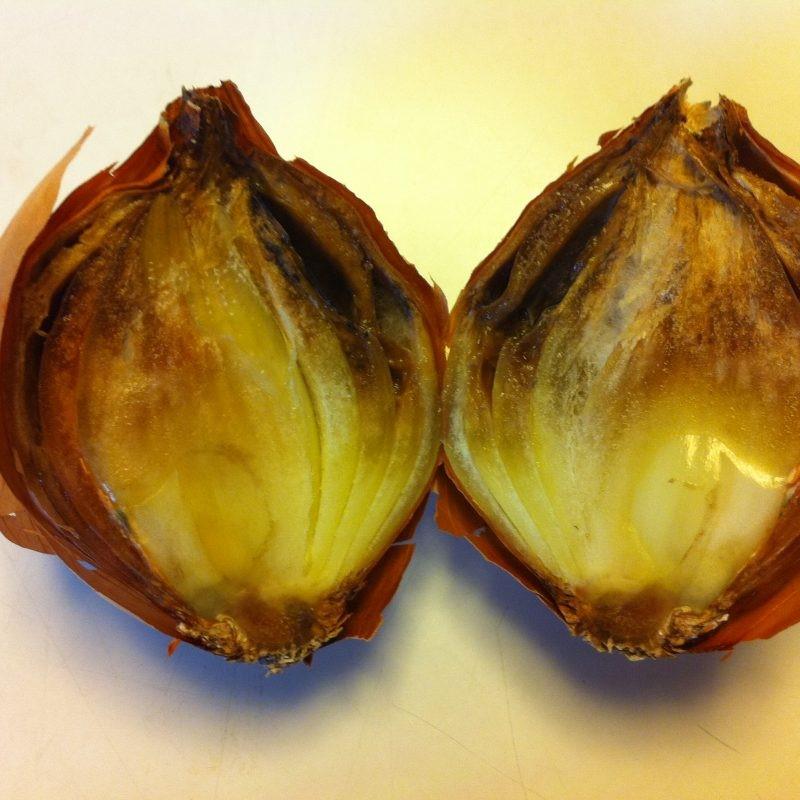
- Black rot. During storage, the middle part softens.
Between the layers, dark colored patches are visible, indicating the presence of black rot fungus
- Bacteriosis. Onions quickly rot during storage; in the middle you can distinguish the alternation of light layers with dark ones. The scales are unpleasant to the touch and have a watery base.
In case of long-term storage, rot takes over the entire head.
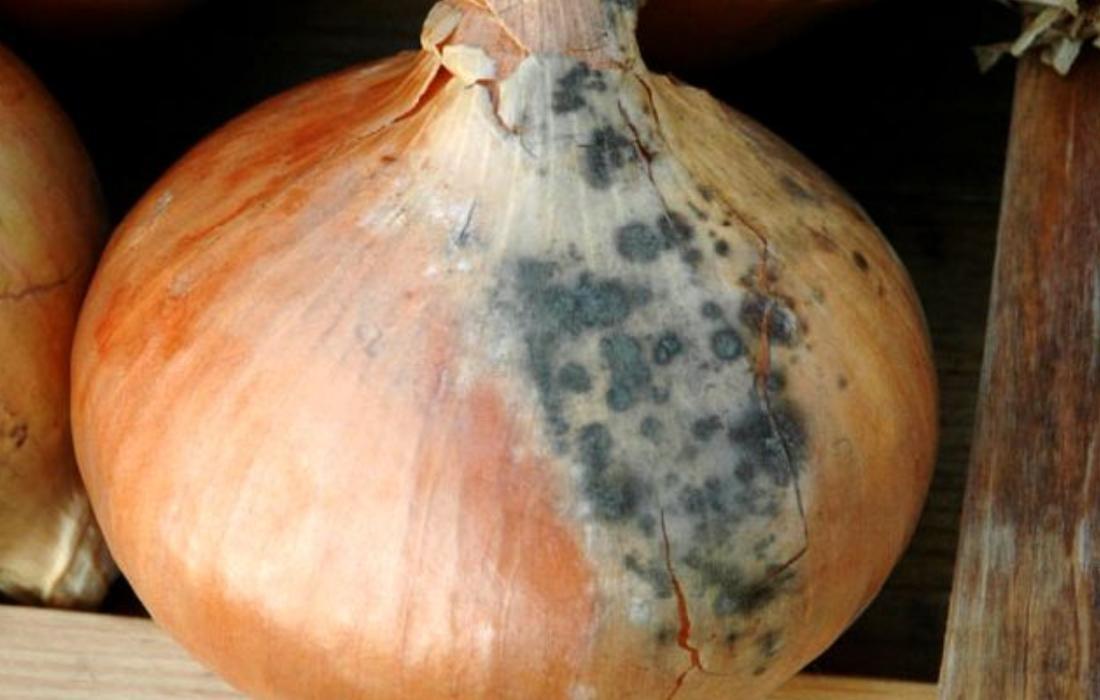
- Blue mold. Unlike previous diseases, the root crop becomes covered with bluish spots.
With blue mold, the lower part becomes dry and rot forms.
Unsuitable variety
Rot on onions can develop on varieties that are unsuitable for long-term storage. Gardeners recommend the hybrids Summit F1, Red Baron and Alonso F1. They have a slightly spicy taste but can last for more than six months.
Violation of cleaning rules
Another reason why onions rot during storage is improper cleaning. An unripe vegetable differs from a mature one in the presence of soft scales. They quickly deform during transportation.
Overripe bulbs also have a fragile structure. Their layer bursts and the bottom is damaged. Incorrectly harvested onions - with obvious signs of deformation - are prone to rot.Microorganisms gain access through cracks.
Poor drying of onions
As is already known, pests can penetrate through the integumentary scales. Due to poor drying, this threat becomes more real. Therefore, initially the onions are ventilated in the open air.

The sun's rays act as a disinfectant and kill some bacteria
Then dry in a room with a temperature of +25 °C. The duration of storage depends on air humidity. On average, this takes 15 days. The onions are turned over and at the same time damaged specimens are removed.
Excess moisture
The root system of the vegetable is capable of absorbing a certain amount of liquid. Due to frequent watering, the underground part of the plant is subject to rot. Onions become unsuitable for storage and consumption.
No sorting of onions
If the neck of the root crop is dry and closed, rot will not bother the onion during storage. Vegetables with signs of destruction, mold, or wet necks will not last long. Such samples are processed.
Diseases can be difficult to recognize in the early stages. They focus on the condition of the head, aroma, and the presence of inclusions. Moldy onions are burned.
Unprepared storage
In order not to create preconditions for the spread of rot, the room must comply with storage standards. The vegetable decomposes quickly in damp rooms. Vegetable debris shall be excluded prior to placement.

Before storing, it is advisable to wash the storage area with disinfectants.
Damage to bulbs by pests
Insects wait out the cold season in the remains of green vegetation. Even if the room is well heated, instincts push pests to choose places abounding in greenery.
Therefore, last year’s garbage must be removed before storing onions. Weediness attracts the attention of winged and wingless insects:
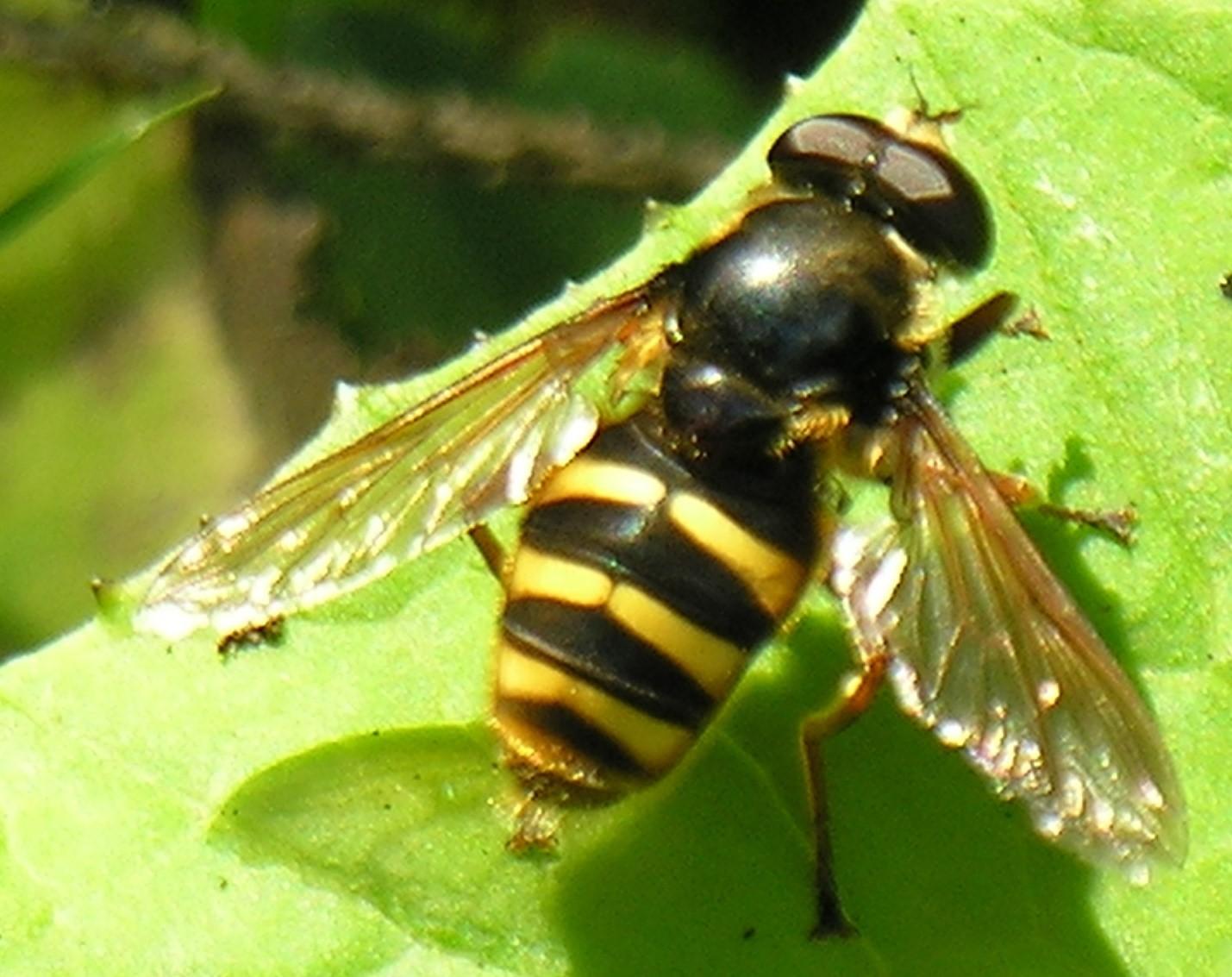
- Hoverfly. The adult insect makes holes in the onion to allow the larvae to enter.
Hoverflies feed on sap, and after a few days they prepare to reproduce
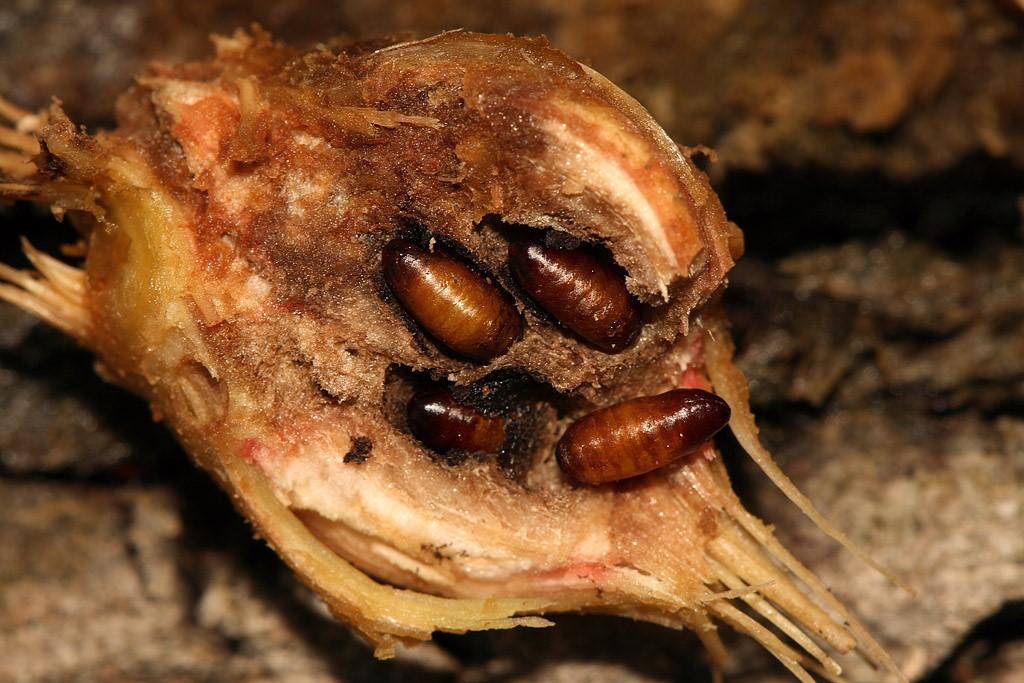
- Onion fly. First, the feathers of the root crop suffer, which are actively eaten by the larvae.
Over time, the fly penetrates the neck, and it begins to rot
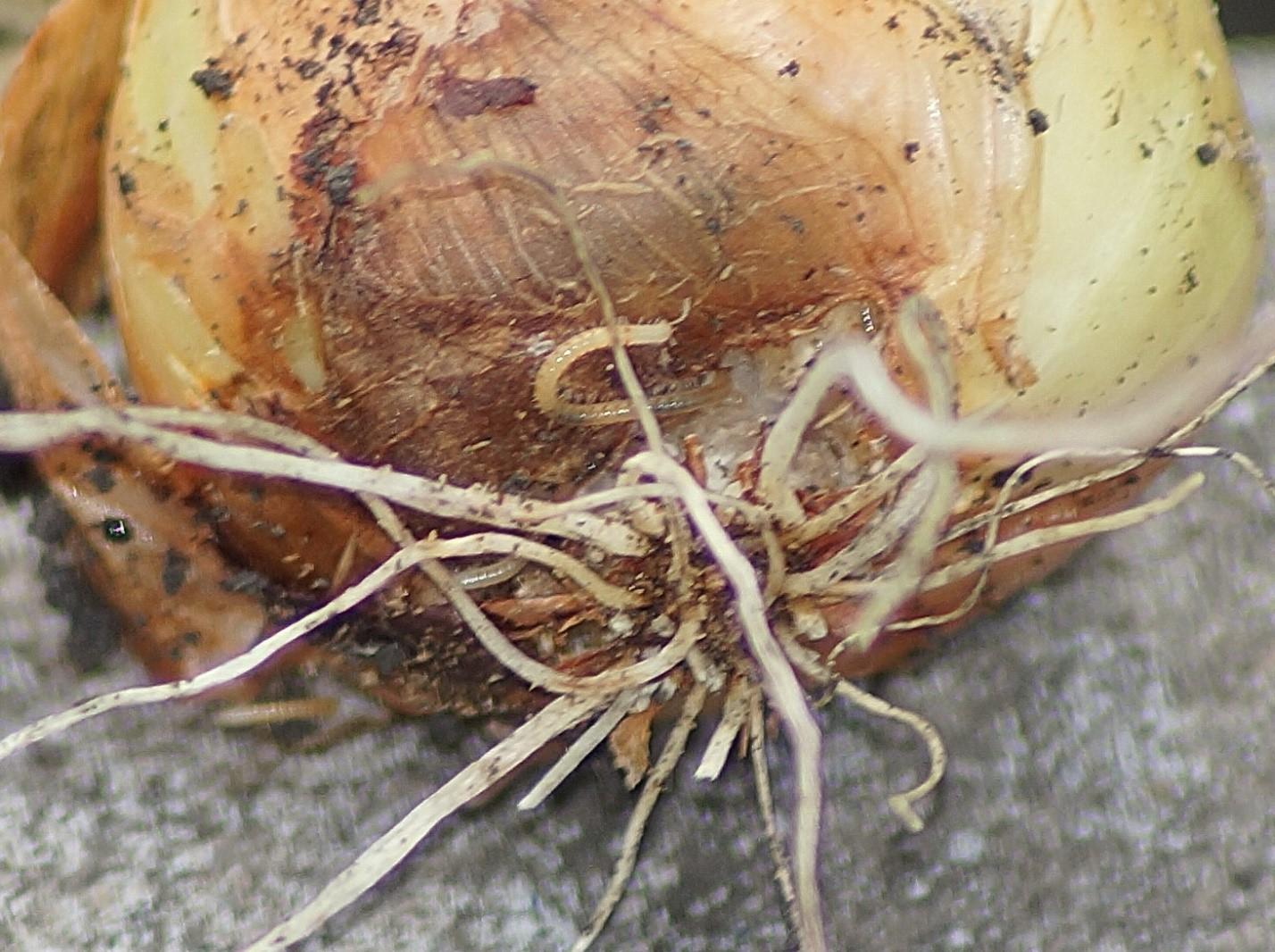
- Stem nematode. They make passages in the lower part of the plant, moving towards the pulp.
Numerous holes cause the onion to become soft
- Onion mite. The parasite is absorbed into the walls of the bottom and feeds on the pulp and juice of the onion.
Onion mites can quickly ruin an entire storage facility.
- Scoop. The larvae prefer greens, while the adults consume the vegetable itself.
The vegetable loses its shape and becomes loose
What to do if onions rot during storage in winter
Before the problem develops into a large-scale one, it is necessary to act quickly and decisively. First, inspect each vegetable. The loss of several bulbs will not be a big loss, because even one low-quality root crop can infect more than 1.5 kg of crop.
Samples with a repulsive odor are immediately discarded.Onions with a soft base or the presence of red and gray inclusions cannot be stored. If mold is detected, the heads are burned.
Vegetables that have come into contact with infected specimens are quarantined. There is a good chance that pathogens and pests are inside them. Externally healthy onions are additionally dried. If the weather is warm and dry, it may be appropriate to place the food items outside.
During winter storage, onions are laid out near radiators and other heat sources. After harvesting, the plant is cleared of soil. It not only spreads dirt, but also serves as a home for spores and viruses. Experienced gardeners recommend powdering the root crop with crushed chalk.
Onions do not store well in polyethylene and rot quickly. The material prevents air circulation, so it is not used. There should be no last year's vegetation left in the room. When stored closely with other crops, in particular potatoes, a large amount of moisture is released. This promotes the appearance of rot.
Temperatures within +12-15 °C are undesirable. In such conditions, fungal pathogens and insect larvae “wake up.” The thermometer should show no more than +10 °C, otherwise long-term storage of onions is out of the question.
Negative temperatures are also avoided, as they provoke the occurrence of rot.
To reduce the moisture level when storing onions, use containers with sand. The material absorbs vapors well. Instead, you can use sawdust of any type.
How to store onions so as not to rot
Onions are stored in a room with a temperature from 0 to +20 °C. The lower the indicators, the longer the vegetable will last. Air humidity must be maintained in the range of 65-80%. In such conditions, the root crop does not lose its original qualities for 5-8 months.
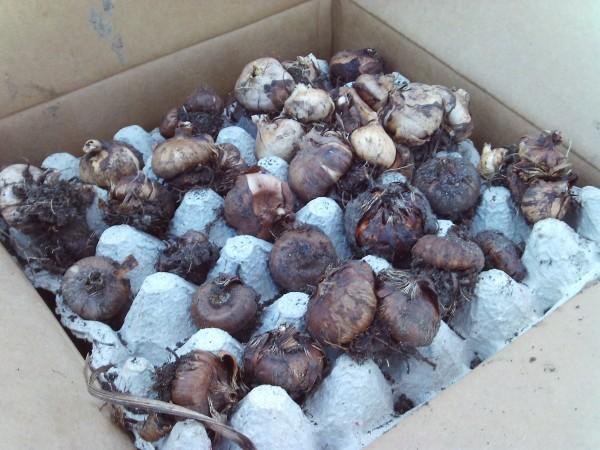
For long-term storage, boxes, containers and baskets are used. Metal boxes are not used. Vegetables are laid in one layer, the optimal thickness of which is 25 cm. The main thing is that the onions can “breathe”. Regardless of the type, many holes are made in the container.
Periodically inspect the premises and bulbs. Damaged samples are removed to avoid loss of part of the crop, and moisture and temperature control are maintained.
When rot affects one root crop, the rest rot after it. It will not be possible to avoid the loss of the party, so attention should be switched to reducing the scale of the threat. Damaged specimens are discarded and the necessary conditions for storage are created.
Conclusion
Preserving onions if they have begun to rot is not an easy task. For successful storage, you need to prepare the room. Disinfection, garbage collection, maintaining dryness are the main tasks. To increase the shelf life, use varieties with a mildly pungent taste.


















