Content
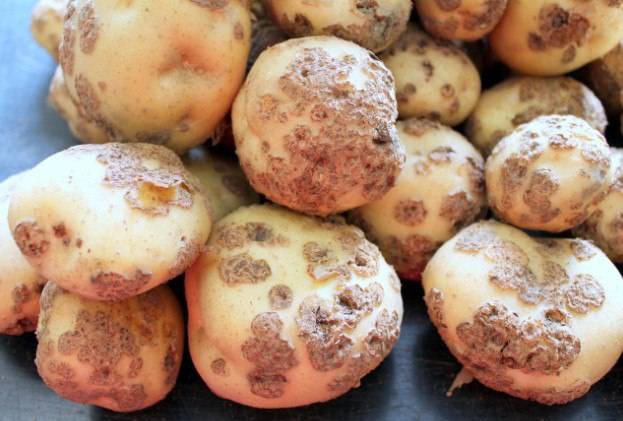
Of all potato diseases Scab at first glance seems the most harmless. In the initial stage of its development, many do not even notice that the potato is sick with something. After all, for example, ordinary potato scab does not manifest itself in any way during the growing season of the bushes. As a rule, it only affects tubers and is not very noticeable to the untrained eye. If you do nothing and continue to plant infected potatoes, you may soon be left without a harvest at all. Moreover, the scab infection mainly lives in the ground and the situation must be corrected with an integrated approach.
Types of scab
Before you think about how to deal with scab on potatoes, you need to understand that disease this has several guises, each of which is characterized by its own characteristics, which are often very different from each other. Accordingly, the measures taken to prevent and get rid of it can be completely different. The following types of potato scab are distinguished:
- Ordinary;
- Powdery;
- Black (also known as rhizoctoniasis);
- Silver.
Most widespread in fields and vegetable gardens common scab. The causative agent of this type of disease is a fungus called Streptomyces scabies.Most often it lives in the soil, preferring dry, sandy soils with a reaction close to alkaline. It develops especially actively at air temperatures above +25°+28°C.
Signs of potato scab infestation are quite varied, but most often the disease begins with small, almost imperceptible brown sores, sometimes with a red or purple tint. Sometimes the surface of the potato becomes rough and barely noticeable mesh-shaped grooves form on it. With severe damage, the ulcers increase in size, harden, cracks appear along them and the tubers begin to rot intensively.
As mentioned above, this type of disease almost does not spread to other parts of the potato; it lives mainly on tubers. Moreover, potatoes are not capable of becoming infected during storage, since under unfavorable conditions (low temperatures) the fungus goes into suspended animation, but does not die. But when adding raw, unrotted manure or significant doses of limestone as fertilizer to the soil, the risk of common potato scab increases. Therefore, it is necessary to treat, first of all, the land itself used for planting potatoes.
To counteract scab, you can use potato varieties that are resistant to this disease: Domodedovo, Zarechny, Yantarny, Sotka.
Powdery scab, unlike the ordinary one, usually appears as a result of prolonged rains on heavy, waterlogged soils.
The disease manifests itself not only on tubers, but also on stems, usually in their underground part. The stems are covered with small white growths, while the tubers have many red-brown warts of varying sizes. Powdery scab spores develop well in conditions of high humidity and at temperatures from +12°C. They can be transmitted both with organic residues and by air. During storage, the affected tubers usually dry out, but if there is high humidity in the storage, they will rot quite quickly. The fungus can survive in soils for up to five years or more.
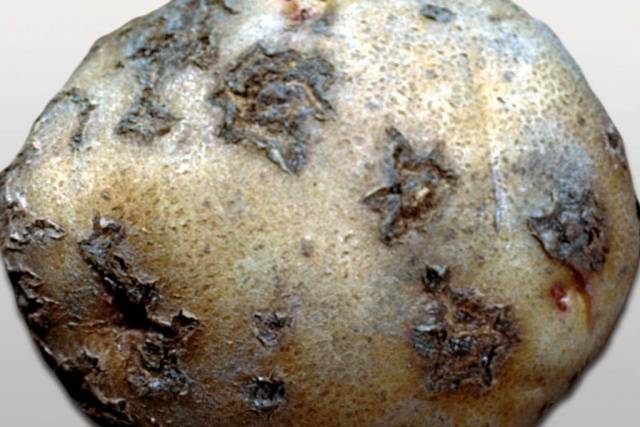
Black scab potato or rhizoctonia blight is one of the most dangerous types of scab. The only thing that makes the diagnosis easier is the fact that the entire potato plant is affected - from tubers to stems with leaves. But as a rule, damage to the above-ground part indicates that it will not be possible to save the plant - it is better to destroy it. The first signs of the disease appear on the tubers and look like small black or brown sores, which often merge into large spots.
This is what black scab on potatoes looks like in the photo.
If such tubers are accidentally used as planting material, the sprouts will be very weak and, most likely, the bushes will not even survive to flower. The causative agent of this dangerous disease is Rhizoctonia solani. The spores of this disease also like high soil humidity (80-100%) and temperatures from +18°C. Soils prefer loamy soils and most often actively develop when the spring is cold and rainy.In this case, black scab spores are able to penetrate the tubers even during the germination period, and such potatoes are doomed to death.
Due to the unpredictability and rapidity of development of the disease, the fight against this type of potato scab should be as serious as possible, including the use of strong chemicals. Moreover, unfortunately, at the moment there are no potato varieties that are completely resistant to this type of scab.
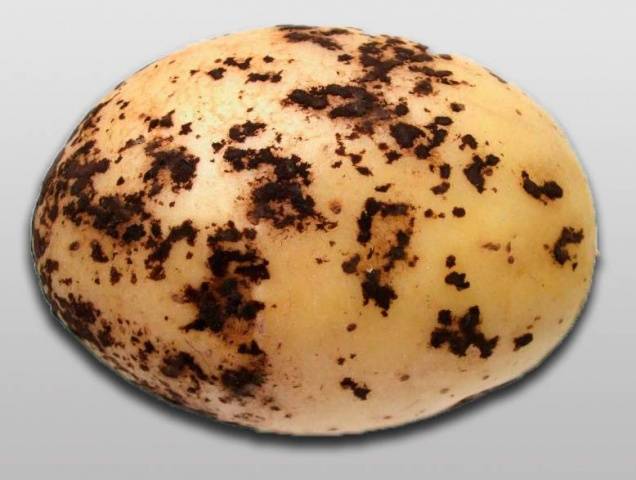
Silver scab potato got its name due to the grayish-silver spots on the tuber, which can occupy up to 40% of the tuber area.
True, such spots appear already at the stage of significant development of the disease. And it all starts with small pale “pimples” with a black dot in the middle. The causative agent of this type of scab is Helminthosporium solani. From the outside, it seems that this is the most innocent type of scab - after all, the affected tubers are stored quite well and practically do not rot. But this appearance is deceptive.
In addition, dehydration quickly occurs during storage, and by spring the tuber may become dry and wrinkled. Due to this, up to 40% of the harvest is lost and such tubers are not suitable for use as planting material.
The silver scab pathogen is undemanding to soils and thrives on both loam and sandy loam soils. Like almost any fungus, it loves high humidity conditions, from 80 to 100%. Therefore, the disease progresses during the period of flowering and tuberization.
Means of prevention and control
Potato tubers affected by all types of scab, except rhizoctonia, are quite suitable for food. It is probably for this reason that gardeners, as a rule, do not pay due attention to the treatment of this disease. But it is necessary to fight it, since both the taste and nutritional value of such potatoes is reduced to a minimum. And if you plant even healthy, but not specially treated tubers on an infected plot of land, they will also be infected and there will be no end to this. So, how can you get rid of scab on potatoes and make sure that it does not appear on the plot again?
Agrotechnical techniques
The main way to combat scab is crop rotation. If you do not plant potatoes on contaminated soil for 4-5 years, the infection may have time to die out. But not everyone can afford to change the land for planting potatoes every year. Moreover, in this area you cannot grow any plants of the nightshade family (tomatoes, peppers, eggplants), as well as beets and carrots. They are also susceptible to the effects of this disease.
What can be done in this case is to sow the area with green manure immediately after harvesting the potato tubers. It is best to use mustard, but both legumes and cereals will play their positive role. When the seedlings reach a height of 10-15 cm, the area is dug up again or at least mowed and green manure is mixed with soil. Being in the soil, the remains of green manure contribute to the formation of saprophytic fungi and bacteria, which are natural enemies of scab pathogens. This is how our great-grandfathers fought against scab and quite successfully.In the spring, before planting potatoes, you can also plant fast-growing green manure, or at least sprinkle the future beds with mustard powder and water them. Mustard significantly reduces the number of fungal and viral infections in the soil, and also protects against many pests: thrips, wireworms, slugs.
Since common scab spores develop especially well in alkaline soils with insufficient manganese and boron content, to combat this type of disease it is especially important to apply the following types of fertilizers in the spring before planting potatoes (application rate per 100 sq. m):
- Ammonium sulfate (1.5 kg);
- Superphosphate (2 kg) and potassium magnesium (2.5-3 kg);
- Microelements – copper sulfate (40 g), manganese sulfate (20 g), boric acid (20 g).
Treatment with various drugs
Other methods of scab control include, first of all, pre-planting treatment of tubers with various fungicides. It is quite effective and safe to use Maxim or the microbiological drug Fitosporin. The latter remedy can be used in different ways. It is not only intended for processing seed potatoes. To consolidate the effect, they are recommended to spray potato bushes three times during the growing season. To obtain a working solution, one packet of the drug is diluted in three liters of water.
There are many chemical preparations for getting rid of scab on potatoes. For example, to destroy black scab, both tubers and the plants themselves are treated with such strong drugs as Mancozeb, Fenoram Super, Colfugo.Treated tubers are able to resist disease even in unfavorable conditions.
In order to cope with other types of scab, it is not necessary to use such strong chemicals. For example, to suppress the development of common scab, various growth regulators, primarily zircon, are suitable. In its description it is noted that the harmfulness of the disease is reduced even with a single treatment with this drug. With twice its use, the disease may recede completely. 1 ml of zircon (1 ampoule) is diluted in 20-30 liters of water and the resulting solution should be treated with potato bushes after germination and at the beginning of flowering.
Conclusion
Scab on potatoes is an unpleasant phenomenon, but it can and should be dealt with if you follow all the recommendations outlined above.