Content
The greatest danger to tomatoes is fungal diseases. They infect leaves, stems, and fruits, as a result of which the growth of the plant stops. Helps correct the situation spraying tomatoes milk with iodine. This combination of components is safe for the environment, however, it prevents the spread of harmful microorganisms. Processing of tomatoes is carried out for the treatment and prevention of viral diseases of tomatoes.
Benefits of milk for plants
Milk contains beneficial substances that have a positive effect on tomatoes:
- copper, phosphorus, potassium, manganese, calcium, iron and other trace elements;
- lactose, which has a detrimental effect on insects;
- amino acids that activate the growth process.
After spraying with milk, a film forms on the leaves of tomatoes, protecting the plant from pests and fungus.
Feeding with milk has a positive effect on plants:
- metabolic processes improve;
- nutrients contained in the soil are absorbed faster;
- compost efficiency increases.
Tomatoes grown using milk supplement, contain many useful substances. When eating them, a person also receives these elements.
The advantage of milk is its environmental friendliness and safety. When working with it, no additional protection for hands, eyes, or respiratory system is required.
Milk is beneficial for tomatoes during growth, when the need for nutrients is especially high. Dairy feeding is also indispensable during fruit formation.
What kind of milk is suitable for spraying?
To spray tomatoes, raw milk is used, which contains a maximum of useful substances. It is possible to use a pasteurized or processed product, however, the concentration of beneficial components in it is not so high.
Tomatoes also benefit from the whey that remains after the product has soured. Usually it is not used in its pure form, but is diluted with water. Thus, the acid-base balance of the soil is maintained.
Whey from milk contains beneficial lactobacilli that can displace harmful microorganisms from tomatoes.
When the milk turns sour, pour it into a saucepan and then heat it over low heat. The liquid that begins to separate is then used for spraying. One liter of milk produces up to 600 ml of whey.
To spray tomatoes, a serum to water ratio of 1:3 is required. Many gardeners add laundry soap to the liquid. If this is not done, the whey will flow down the leaves, which will not receive nutrients.Due to the soap, all the beneficial substances will remain on the foliage.
To improve the properties of feeding, add to low-fat milk iodine. The result is a drug that has a complex effect on tomatoes.
Benefits of iodine for plants
Iodine is a chemical element that ensures the proper development of plants. If there is a shortage of it, tomatoes develop more slowly, which affects the quality and time of harvest.
Additional benefits of iodine include:
- safe for soil, animals, plants, humans;
- performs disinfection functions, destroys harmful microorganisms on tomatoes;
- improves the germination of seed material;
- helps seedlings to take root after transplantation;
- strengthens the immunity of already growing tomatoes, makes them healthier, and increases productivity;
- after treatment with iodine, its content in fruits increases, which brings benefits to human health;
- Due to the increased iodine content, the shelf life of tomatoes increases.
Iodine is especially useful in the spring during the period of plant development.
Tomatoes need time to adapt to new conditions.
Before planting, you can treat the soil with iodine. As a result, harmful bacteria that spread tomato diseases will be destroyed. The procedure is carried out 2-3 days before plant transplantation.
Before fertilizing tomatoes with preparations containing iodine, you need to water the soil well. When the soil is dry, tomatoes are not processed.
To disinfect the soil, one drop of iodine per 3 liters of water is enough. It is allowed to water a week after planting the plants in the ground.
Spraying features
You can process tomatoes growing in a greenhouse or open ground. Spraying tomatoes with milk and iodine is done at a certain time:
- in the absence of bright sunlight;
- in the morning or evening;
- in dry, windless weather;
- at an optimal ambient temperature of 18 degrees.
A fine spray is used to process tomatoes. During the work, you need to ensure that the product covers the leaves of the plants.
Spraying timing
To feed and prevent diseases, tomatoes are sprayed with milk and iodine. The first procedure is carried out two weeks after planting the seedlings. Subsequently, spraying is repeated every two weeks.
If the first signs of late blight or other damage appear, treatment with milk and iodine can be carried out daily.
The optimal time for spraying tomatoes with milk with added iodine is the beginning of July. During this period, plants need amino acids that promote their growth.
Milk and iodine for late blight
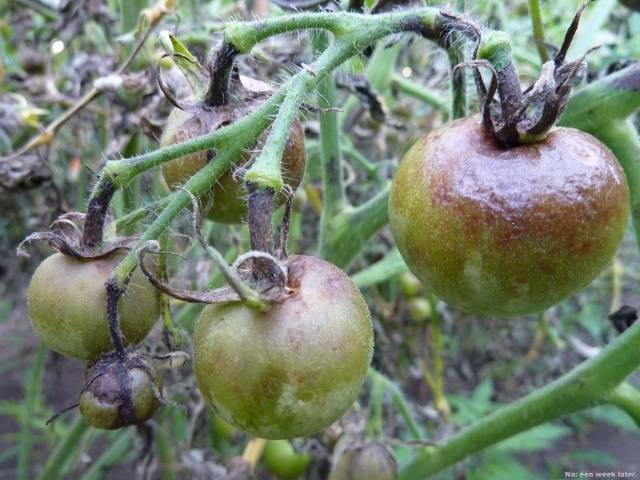
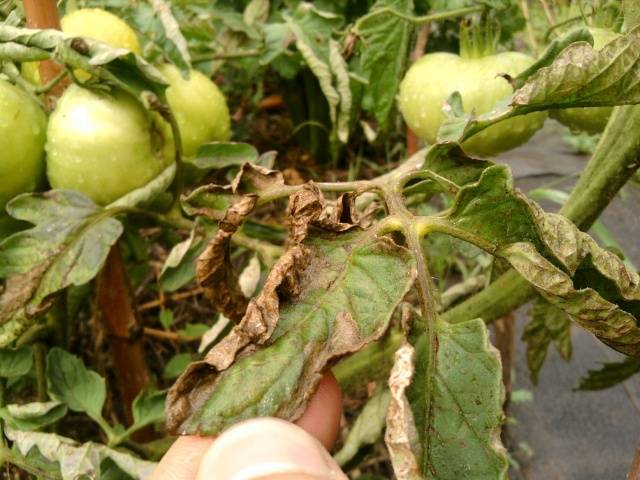
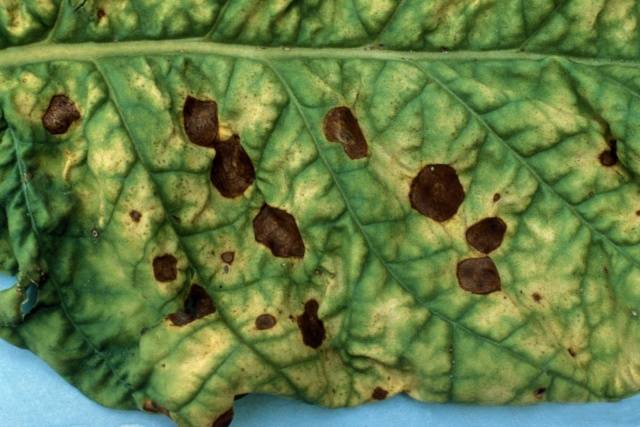
Late blight is a fungal disease that is spread by spores. It is diagnosed by the following signs:
- dark spots appear on the back of tomato foliage;
- leaves turn brown and dry out;
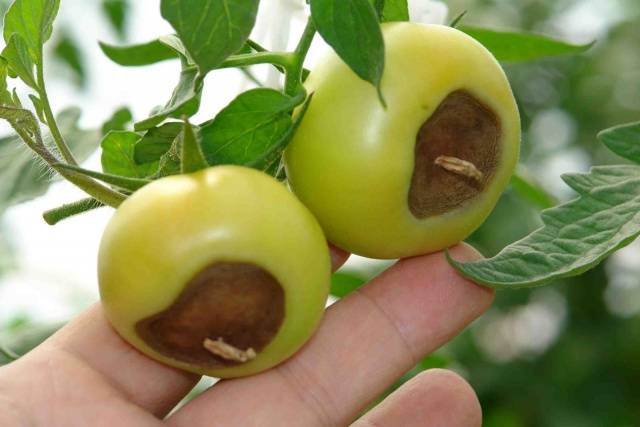
- the fruits turn black.
If the fungus has already begun to spread, then the tomatoes are almost impossible to save. If the lesion affects only certain parts of the plant, they are removed and then burned.
Phytophthora spores spread in calcareous soil with high humidity. If the greenhouse is rarely ventilated, the risk of the disease increases several times. Weakened tomatoes that lack nutrients are especially susceptible to late blight.
Various methods are used to combat late blight. All of them are based on disinfecting the environment where tomatoes grow. A mixture of milk and iodine copes well with this task.
If the disease has already spread, then treatment with iodine and milk should be carried out constantly. Since these are eco-friendly products, they can be used daily.
Only regular spraying will help ensure reliable protection. Otherwise, iodine and milk will quickly be washed off from the leaves after rains and watering. The acidic environment that characterizes whey is detrimental to the late blight fungus. The first treatment with iodine and milk can be carried out from July.
The following mixtures are used to combat late blight:
- whey and water in a ratio of 1:1;
- a bucket of water, a liter of milk and 15 drops of iodine;
- 0.5 liters of dairy product and 10 drops of iodine solution.
Solutions with increased iodine concentrations are necessary to prevent the spread of late blight. It is recommended to alternate this remedy with other methods of combating this fungus:
- a mixture of 10 liters of water, a glass of chopped shoots and heads of garlic and 1 g of potassium permanganate;
- a solution of table salt in water;
- 100 g of crushed tinder fungus per 1 liter of water;
- various chemicals.
Prevention of late blight
Prevention of late blight can begin after planting.To do this, prepare 1 liter of milk or kefir, add up to 10 drops of iodine. The resulting mixture kills harmful microorganisms and does not allow them to develop.
In addition to processing tomatoes, you need to use the following methods to combat late blight:
- peat is added to soil with a high lime content, sand is poured into the furrows;
- plantings are carried out according to certain patterns, maintaining distances between tomatoes;
- plants are watered in the morning so that moisture is absorbed into the soil;
- treatment of seedlings with milk and iodine;
- greenhouses and greenhouses are ventilated, which helps to avoid excessive humidity;
- in cloudy weather, it is enough to loosen the soil;
- tomatoes need fertilizing with potassium and phosphorus;
- do not plant nightshade crops (eggplants, peppers, tomatoes, potatoes) close to each other to avoid the spread of late blight;
- moderation when applying nitrogen and other fertilizers;
- prevent fruits from overripening;
- grow tomatoes after cucumbers, garlic, onions, cabbage, pumpkin, legumes;
- Spray with milk and iodine as a preventive measure.
Milk and iodine for other diseases
A solution of milk and iodine is also effective for other fungal diseases. The spraying rules are identical for any type of lesion.
Brown spot
The appearance of brown spot can be judged by the following signs:
- light spots form on the upper part of the leaves, which gradually turn yellow;
- a brown or gray coating is observed on the underside;
- the affected leaves dry out over time;
- fruits and stems lack nutrition.
If signs of brown spot appear, tomatoes are sprayed with a mixture of 0.5 liters of milk without fat and 10 drops of iodine.
Gray rot
On tomatoes, gray rot appears first on old leaves in the form of a fluffy coating. The pathogen is attracted to broken leaves and stems, cracked fruits. First, the lesion covers the lower leaves, after which it spreads upward to the fruits.
The fight against the disease begins at an early stage. To do this, milk is diluted with water, after which 10 drops of iodine are added. Treatment begins from the bottom of the plant, from where gray rot spreads.
Tobacco mosaic virus
Tomatoes are susceptible to the tobacco mosaic virus, which disrupts the process of photosynthesis in the leaves. The disease can be identified by a number of signs:
- beige mosaic-type stains on the leaves;
- spotted areas on foliage of light and dark shades.
The virus can remain in a passive state for 5 years. Therefore, before planting, the seeds are treated with sodium hydroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate.
To prevent the disease, it is recommended to treat tomato seedlings with milk diluted with water and 10 drops of iodine. If adverse symptoms appear, the plant is removed to avoid the spread of the virus.
Fusarium wilt
The causative agent of this disease germinates with tomatoes through seeds. Wilting occurs after fruit formation, after which the plant weakens and dies. The cause of infection is often damage to the roots, after which the virus penetrates the soil.
Fusarium disease can be controlled by seed treatment. To prevent it, a solution is used that includes 10 liters of water, 1 liter of low-fat milk and 20 drops of iodine.
Recipes for feeding
Even healthy plants require feeding in the form of milk with iodine.This mixture is a source of nutrients and prevents fungal diseases.
- The first feeding of tomatoes is done at the seedling stage. This requires a bucket of water, to which add 1 liter of milk and 15 drops of iodine solution. Watering strengthens plants and increases their resistance to harmful microbes.
- The second feeding is done after the tomatoes are planted in the ground. Pre-prepare a solution consisting of 5 liters of water, 1 liter of milk and 10 drops of iodine. This fertilizing is more concentrated and is necessary for plants before flowering. Each tomato requires up to 0.5 liters of the finished product. The procedure is repeated every 3 days.
- When the fruiting period begins, fertilizing is done twice a week. It is best to combine it with other drugs to provide tomatoes with other beneficial substances. Adult plants are watered before the heat sets in in the morning.
Supplementation with milk and iodine is carried out on an ongoing basis. Its purpose is to provide plants with nutrients.
Conclusion
Milk with iodine helps fight viral diseases that affect tomatoes. Instead of milk, you can use whey obtained from sour milk product. This is a universal drug that helps against most types of fungus. The product is mixed in the required proportions depending on the disease.
Spraying with milk with added iodine should also be carried out for preventive purposes. Due to it, the spread of harmful microorganisms can be prevented.