Content
Baltic Rose potatoes are the development of breeders from the German company Norika. This variety is high-yielding and has increased resistance to diseases such as black leg and leaf curl virus. The Baltic Rose variety is one of the first candidates for inclusion in the State Register in 2019. The variety is popular among vegetable growers and can be popularly known as Red Gala.
Description of the Baltic Rose potato variety
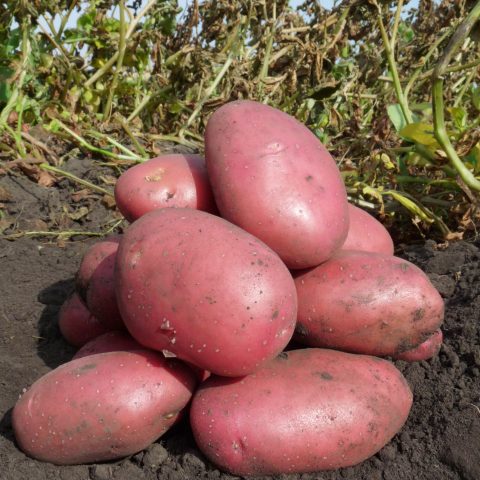
According to the manufacturer’s description and expert reviews, the Baltic Rose potato (shown in the photo) is a mid-early variety with attractive bright red tubers.
Oval-shaped tubers have small eyes. The peel is red, smooth, and the color of the pulp is yellow.
The bushes are medium in height, reaching 50-60 cm. Potatoes bloom with white flowers, of which only a few appear on the bush.
The potatoes sprout together, and large tubers of equal size are formed underground. Due to the early appearance of the harvest, this variety is used commercially.
Taste qualities of Baltic Rose potatoes
According to consumer reviews, the taste of potatoes of this variety is excellent. Based on the starch content in tubers (12.5%), potatoes are classified as medium-starchy. This means that potatoes can be fried and used to make salads; the tubers do not boil over and hold their shape well when cut.
Pros and cons of the variety
Any potato variety has advantages and disadvantages. Before purchasing planting material, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the variety and study the pros and cons of cultivation.
The main advantages of the Baltic Rose variety:
- attractive appearance;
- small eyes;
- approximately the same size of tubers (110-180 g);
- high productivity;
- does not boil over, so it is suitable for frying;
- good transportability;
- long shelf life;
- high resistance to diseases (virus Y, black leg, leaf roll virus, late blight, rhizoctonia).
Disadvantages include low starch content. Some people prefer boiled potatoes, which make delicious soup and mashed potatoes. Baltic Rose is best used for frying and preparing salads.
Planting and caring for Baltic Rose potatoes
To get a high yield of Baltic Rose potatoes, you must follow the planting and care recommendations.
Selection and preparation of a landing site
A site for planting potatoes should be selected in the fall. Waterlogged and swampy areas are not suitable for growing potatoes. Shaded areas prevent the formation of tubers, so well-lit areas are chosen for planting potatoes. The land should be light and fertile. Heavy aluminas are not used for potato cultivation.
If groundwater is located close to the surface, it is recommended to plant potatoes on ridges or ridges.
Autumn soil preparation involves digging up the soil with a shovel or mechanized walk-behind tractor. If the soil is highly acidic, which can be easily detected with special acid meters, lime is added to the soil. It is recommended to add 200-300 g of dolomite flour per 1 m² of area. If the site is fertilized with manure or humus, simultaneous liming is not carried out.
Pre-winter digging improves the composition of the soil and is also one of the methods of controlling insect pests. Many larvae and beetles overwinter in the foliage, in the thickness of the earth, so burning fallen leaves and deep digging lead to the fact that the pests end up on the surface and freeze out.
In the spring, the site is dug up again, breaking up clods of earth. Additionally, mineral fertilizers and organic matter are added. On peat soils, humus and sand are added in equal parts; per 1 m², add 1 cup of wood ash, 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate and 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate.
Preparation of planting material
Preparing tubers for planting is carried out as follows:
- potatoes are sorted and calibrated;
- exposed to heat (germinated);
- treated with pest repellents and growth stimulating substances.
Small tubers selected for planting show no less productivity than large ones. Therefore, for planting, it is best to select small-sized tubers weighing from 50 to 80 g.
It is not recommended to cut tubers for planting, because any wound is a gateway to disease. But if there is very little seed material and it needs to be propagated, the tubers are divided.Potatoes weighing up to 100 g are cut lengthwise into two equal parts. If the tubers are large, they are cut into several parts; it is necessary to ensure that the resulting parts have at least 2-3 eyes. Cutting the potatoes is done immediately before planting, this will help avoid rotting and disease of the tubers. The knife must be treated with formaldehyde after each tuber.
Baltic Rose potatoes begin to germinate 15-20 days before planting in the ground. In this case, the air temperature should be 12-16 °C, humidity about 85%, and illumination 200-400 lux. High light is needed to ensure that the sprouts do not stretch too much.
To prevent tubers from becoming over-infected during sorting, they are treated with the fungicides Ditan, Polycarbacin, Fundazol, and Prestige. At the same time, you can treat with a growth stimulator. The soaking procedure in the stimulating solution is carried out 3-4 hours before planting the potatoes.
Landing rules
Many gardeners make mistakes when planting. Having a minimum area for potatoes, they place the tubers close to each other. Practice shows that the correct placement of beds and the distance between seeds plays a big role in the formation of potatoes.
There are several popular schemes that can increase the yield of Baltic Rose potatoes.
Planting in rows or under a shovel is done as follows:
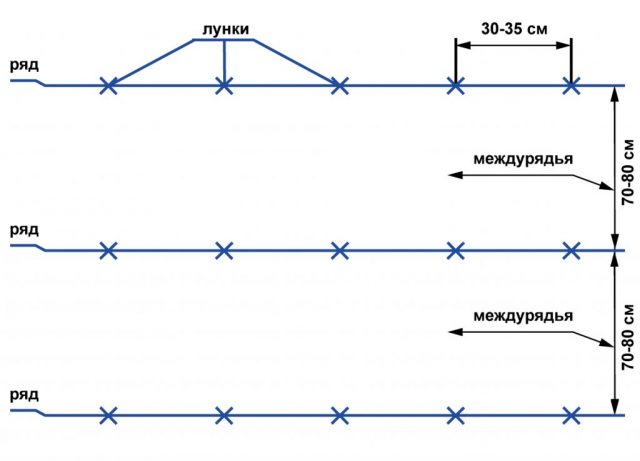
- Limit the area of the site with pegs, the height of which is equal to the width of the row spacing.
- Use a shovel to dig holes, the distance between them should be about 30-35 cm.
- The depth of the hole depends on the quality of the soil. On sandy loam soils, potatoes are deepened to 10 cm; on loam soils, 5 cm is sufficient.
- It is more convenient to plant together.One person digs holes, an assistant pours fertilizer into the holes and carefully places the planting material.
- Sprinkle the potatoes with soil from a neighboring hole.
- The adjacent row is placed at a distance of at least 70 cm from the previous one.
One of the disadvantages of this method is that during heavy rains the potatoes in the ground will suffocate and begin to rot.
In regions with frequent and heavy rainfall, Baltic Rose potatoes are planted in ridges. Tubers located in the ridges do not suffer from stagnant water. During rains, water drains into the rows, so the potatoes do not rot.
When cutting ridges, a plow or cultivator is used. 60-70 cm are left between the ridges, the height of the ridge is at least 15 cm. Holes 5 cm deep are dug in the ridges, the distance between the holes is 30 cm.
On sandy loam and sandy soils, this planting method has one drawback: the ridges dry out quickly and require additional watering in the absence of precipitation.
In regions with rare rainfall, the method of planting Baltic Rose potatoes in trenches is used. In the fall, trenches up to 30 cm deep are prepared, manure, compost, and organic fertilizers are poured into them. Leave at least 70 cm between rows.
In spring, tubers are laid out in grooves, leaving 30 cm between them. The potatoes are covered with earth and mulching materials on top.
Watering and fertilizing
The first watering of Baltic Rose potatoes is carried out after emergence. During the formation of bushes, the need for moisture increases. During budding, watering is necessary, otherwise the ovary will be small. Water the bushes with warm water, previously collected in a container. It is best to water early in the morning or after sunset.
In large areas, the drip irrigation method is used.
Fertilizing helps increase the yield of Baltic Rose potatoes. It is advisable to carry out this procedure three times:
- during the formation of bushes. For 10 liters of water dilute 1 tbsp. l. urea. You can use 0.5 liters of mullein per 10 liters of water. 0.5 liters of nutrient mixture is poured under each bush;
- during budding. It is necessary to dissolve 1 glass of wood ash in a bucket of warm water and pour 0.5 liters of the composition under each root;
- during flowering. For 10 liters of water you will need 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate and 1 cup of chicken manure. This solution is enough to feed 20 potato bushes.
If the plot area is large, fertilizing can be done with dry fertilizers.
Loosening and weeding
During the loosening process, the roots are saturated with oxygen, and small weeds. The procedure is carried out carefully so as not to damage the sprouts or expose the tubers. The first loosening is carried out a week after planting. In the future, loosening and weeding is carried out as necessary: after watering and rain, with strong weed growth.
Hilling
A simple procedure – hilling – allows you to increase potato yields. This event is held 2-3 times per season. It is advisable to carry out the first hilling at the moment when the tops have stretched 15 cm. Wet soil is raked around the bush with a hoe, a small mound is obtained. The second time they hill up no earlier than after 2 weeks. Hill up a third time as needed.
Diseases and pests
The Baltic Rose potato variety is characterized by good resistance to common diseases: blackleg, virus Y, leaf curl virus. To protect against rot and insect pests, pre-planting treatment of tubers is carried out.When signs of late blight appear, spray the bushes with copper sulfate.
When Colorado beetles invade, they are collected manually, and the preparations Fastak, Karate, and Benzophosphate are used for treatment. You can set up a trap for beetles: place potato peelings treated with chemicals in the spaces between the rows.
To prevent the appearance of wireworms, be sure to carry out pre-winter digging of the site.
Potato yield
The yield of Baltic Rose potatoes ranges from medium to high. From 10 to 25 tubers are collected in each bush. The yield of the Baltic Rose variety depends on climatic conditions, as well as on timely application of fertilizers and watering.
Harvesting and storage
Baltic rose potatoes are harvested in late July - mid-August. It all depends on the timing of planting and weather conditions in the region. After harvesting the potatoes, they are left in the shade to dry and chaff, then they are sorted and sent for storage. The temperature is reduced gradually. Small tubers for planting are selected immediately in order to reduce the time spent searching for seed material in the spring.
Conclusion
Baltic Rose potatoes are a high-yielding variety that allows you to harvest up to 2.5-3 kg of crop from each bush. Compliance with the rules of agricultural technology allows you to increase the yield. Preventive treatment of seed material protects against various diseases and pests.