Content
Strigunovsky onion has been grown in Russia for several centuries. And it still withstands “competition” from new breeding products. The variety has many advantages; gardeners value it for its ease of care, suitability for planting in the vast majority of Russian regions, and high yield. It was not possible to identify any significant deficiencies during the entire cultivation period.
Origin of the variety
Strigunovsky onion (now known as Strigunovsky local or Strigunok) is an old Russian variety grown since the mid-18th century. It was bred in the village of Striguny (now Belgorod region), hence the name.
The “folk selection” variety turned out to be very successful. It was also appreciated by foreign experts (Gold Medal of the World Exhibition in Paris, Great Gold Medal of the Spring Fair in Leipzig).Since 1943, it has been listed in the Soviet State Register of Breeding Achievements under the name “Strigunovsky local”. The variety was actively grown on an industrial scale in the Volga region, the Black Sea region, Belarus, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan.
They also did not exclude him from the Russian State Register. Strigunovsky onion is officially recommended for cultivation in all regions of Russia where gardening is, in principle, possible.

Since the applicant is not listed in the State Register, there are now several agricultural companies producing onion seeds Strigunovsky
Description and characteristics of onion variety Strigunovsky
Externally, Strigunovsky is a classic onion. A non-specialist is unlikely to be able to “identify” it among bulbs of similar varieties.
Appearance
Onion variety Strigunovsky is a fairly compact plant with medium-sized, semi-erect leaves. Sometimes, closer to the top, the “feathers” bend slightly.
The bulbs are of different sizes, the weight varies between 45-80 g. The shape is round, slightly tapering at the bottom and top. The outer integumentary scales are light – yellowish-beige with a pinkish-gray undertone.
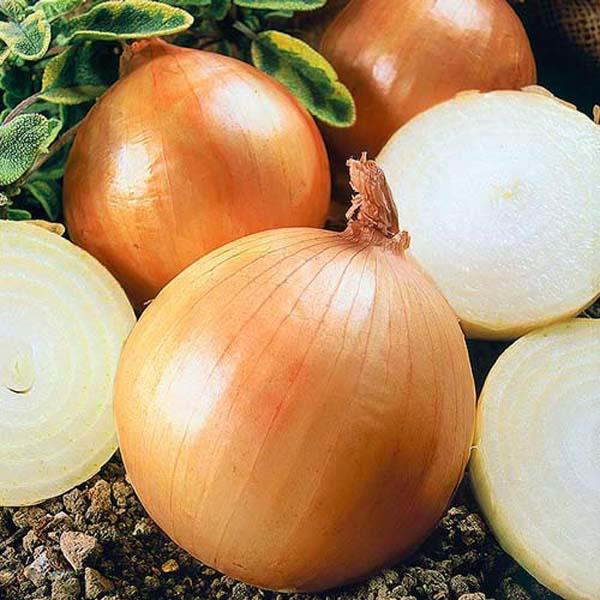

When cut, Strigunovsky bulbs are snow-white
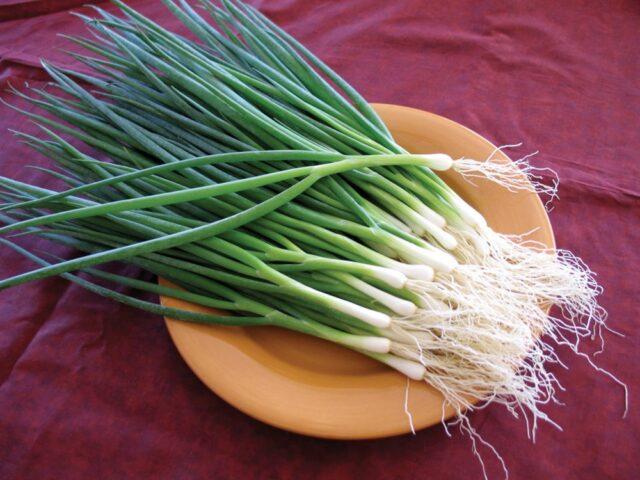

The color of Strigunovsky’s “feathers” is typical of onion greens, there is a light bluish-gray “waxy” coating
Ripening time and yield
Strigunovsky onion is an early ripening variety. Harvesting begins 77-98 days after the seedlings sprout.The percentage of ripened bulbs at this moment is 49-97%. Such a large “scatter” is explained by the climatic characteristics of different regions. The weather during the growing season also matters.
An amateur gardener, with virtually no care for the plantings, can count on 1.18-3.27 kg/m². Competent agricultural technology, combined with warm and sunny summers, increases the yield to 4.8-6 kg/m².

Strigunovsky onion has very good shelf life - without losing its consumer properties, it is stored for 9-12 months
Resistance to diseases and pests
Onion Strigunovsky has “innate” immunity to many diseases typical for the culture. The gardener does not have to worry about protecting the plantings from fusarium, rust, and mosaic virus.
For most pests, hot onions are “inedible” in principle. Among those who still show interest in him, Strigunovsky is also not in great demand. Aphids, spider mites, root nematodes, and onion flies in most cases avoid it.
Composition and properties
Strigunovsky onion contains:
- phytoncides, “natural” antibiotics that destroy pathogenic microflora;
- chlorophyll, useful for strengthening and maintaining the elasticity of the walls of large blood vessels and capillaries;
- essential oils;
- organic acids;
- vitamins A, C, E, almost the entire group B.
This composition provides benefits to the body:
- Beneficial effect on immunity, prevention of seasonal colds, spring vitamin deficiency.
- Improving blood quality, normalizing sugar levels and cholesterol levels.
- Prevention of hypertension, atherosclerosis, varicose veins, blood clots, limb cramps.
- Helps in cleansing the body of waste and toxins, even in removing heavy metal salts.
- Improving the condition of hair and nails both when included in the menu and when used externally, for example, decoctions for rinsing hair, gruel as a mask for the scalp.
Where is it used?
Strigunovsky onion is a food plant, not an ornamental plant. The purpose is universal. It can be consumed not only fresh. In cooking, this variety is widely used in boiled, fried, stewed form. It is added to salads, filling for savory pies, and homemade preparations. This applies to both the bulbs themselves and the feather.
After heat treatment, the Strigunovsky onion loses its sharpness a little. Light sweetish notes appear in the taste.
Advantages and disadvantages
The popularity of the Strigunovsky onion variety is due to a number of its undoubted advantages:
- early ripeness;
- Consistently good yield, even if spring and summer are not very favorable in terms of weather;
- transportability, keeping quality while maintaining consumer properties;
- a good percentage of ripened bulbs at the time of harvest;
- general ease of care;
- suitability for landing in Russia almost everywhere;
- resistance to heat, drought, cold, temperature changes;
- good immunity, resistance against pests;
- versatility of bulbs;
- Possibility of propagation by seeds and sets.

Onion variety Strigunovsky is a very successful combination of ease of cultivation with “stress resistance” and taste
The disadvantages of the Strigunovsky variety are exclusively subjective. Not all gardeners like the relatively small size of the bulbs and the distinctly pungent taste.
Methods of planting Strigunovsky onions
Strigunovsky onion can be planted either by seeds or sets. The experience of gardeners shows that in the second case, the bulbs ripen longer, but they turn out larger.
Growing from seeds
Before planting Strigunovsky onion seeds, they must be checked for germination. You need to soak them in a solution of table salt (about 50 g/l). “Empty” seeds that do not contain an embryo immediately float to the surface.
Next, it is recommended to use products to improve germination. The simplest option is any purchased biostimulant (Epin, Zircon, Heteroauxin). You can also carry out “hardening” by first soaking the Strigunovsky onion seeds in hot (45-50 ° C) water for half an hour, and then in cold water for 12-15 minutes.
Then the Strigunovsky onion seeds are dried to a free-flowing state and planted as seedlings:
- Plant them in relatively shallow, wide containers filled with well-moistened, all-purpose potting soil. Seeds are planted one at a time, leaving 3-4 cm between them, 4-5 cm between rows. They are buried by a maximum of 1 cm.
- Turn the container into a “greenhouse” by covering it with glass or covering it with polyethylene. Place in a dark, warm (24-27 °C) place until seedlings emerge.
- When the seeds germinate, provide good lighting and lower the temperature to 20-22 °C. Constantly monitor the humidity of the substrate, preventing it from drying out.
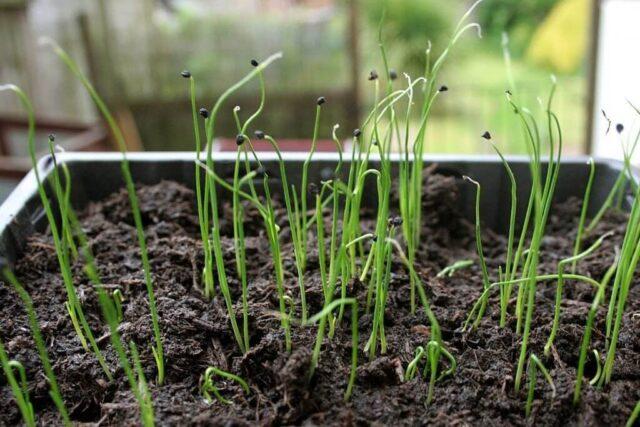

Shoots from seeds appear in 7-10 days
If the seeds are planted directly in open ground, they require similar preparation. Between them leave 5-7 cm, between rows - 10-15 cm. After the emergence of seedlings, the seedlings will have to be thinned out. Until the seeds germinate, it is recommended to cover the bed with plastic wrap or black covering material.
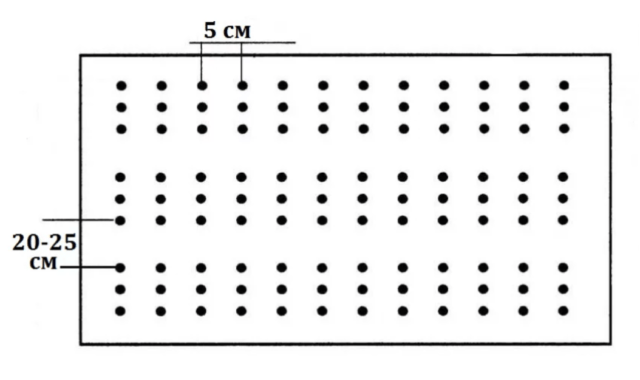
Recommended planting pattern for the Strigunovsky variety – 5-7x20-25 cm
Planting seedlings in open ground
Strigunovsky onion sets also need pre-planting preparation. If it was not stored at room temperature, 3-4 days before planting, the planting material is brought home to warm up. Then the seeds are soaked in a solution of any biostimulant, washed with clean water, and dried.

Before planting, you need to discard onion sets with mechanical damage, traces of rot, or other “suspicious symptoms”
Strigunovsky onions are planted in the bed at intervals of 10-12 cm with a row spacing of 20-25 cm. The most important thing is to leave the top on the soil surface. The soil is well watered before and after planting. When the water is absorbed, it is advisable to mulch the bed.
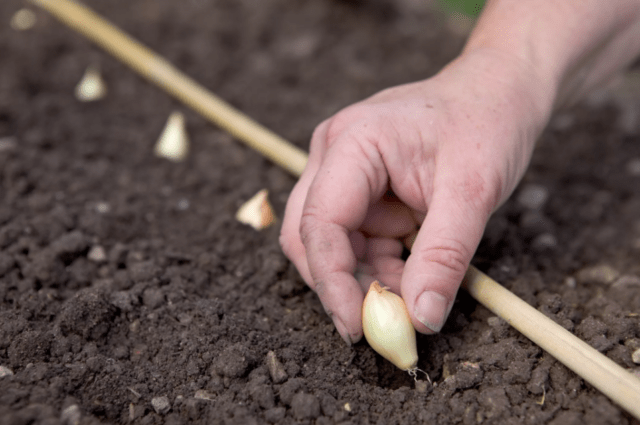

Bulbs are planted no earlier than the soil warms up to 10-12 °C
This variety is also suitable for planting before winter. But then it does not require pre-planting treatment. The bulbs are buried 4-5 cm, the bed is covered with a layer of peat or humus (2-3 cm).
Caring for Strigunovsky onions
Caring for Strigunovsky onions is a standard agricultural technology for the crop:
- Irrigation. In the absence of natural precipitation from May to June, water once every 4-7 days, focusing on the air temperature. The approximate norm is 5-7 l/m².Then watering is stopped completely, otherwise large bulbs will not be produced. An exception is made only if dry, hot weather sets in for a long time (2.5-3 weeks).
- Weeding and loosening. Carry out every 1.5-2 weeks, the next day after watering. An alternative to regular weeding and loosening of the bed is mulching it.
- Feeding. Fertilizers are applied twice per season. The first time (about a week after the second thinning or after the seedlings emerge), natural organic matter or a solution of mineral nitrogen-containing fertilizers is needed. After another 2.5-3 weeks, fertilizing containing potassium and phosphorus is applied.
Onion Strigunovsky reacts positively to both folk remedies and specialized complex store-bought fertilizers.
If Strigunovsky is planted with seeds in open ground, it needs thinning. It is carried out in the phase of the second and fourth leaves, leaving first 4-6 cm between adjacent specimens, then 8-10 cm.
Conclusion
Strigunovsky onion is a variety whose significant advantages and subjective disadvantages have long been well known. For several generations of gardeners they have been choosing it, taking into account the consistently high yield, ease of care, very good immunity, and keeping quality. It can be grown both from seeds and from sets.
Reviews from gardeners about Strigunovsky onions








