Content
Ammon cabbage was bred relatively recently by the Russian company Seminis. This is a hybrid variety that is suitable for cultivation in almost all regions of Russia, except the most northern ones. The main purpose is cultivation in open ground with the possibility of transportation and long-term storage.
Description of Ammon cabbage
Ammon cabbage heads have a round or slightly flattened shape. The diameter can vary from 15 to 30 cm. Their weight reaches 2-5 (less often 4-6) kg. The color of the outer layer of the leaves of the head of cabbage is gray-green. It is slightly whitish inside.
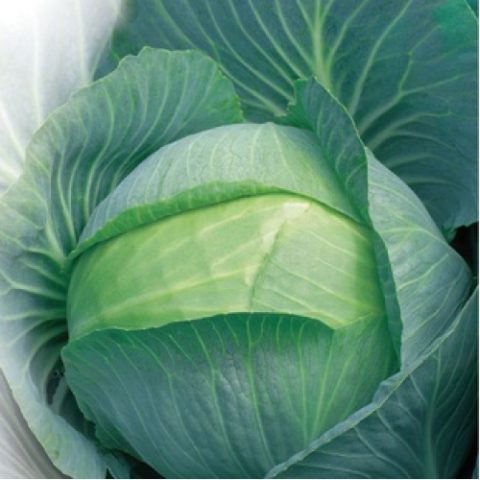

The leaves on the stem of Ammon cabbage are dark green, covered with a noticeable waxy coating.
The leaf plates are thin, tightly adjacent to each other. The stalk is short, occupying approximately a quarter of the diameter of the head of cabbage. The taste is pleasant, fresh, completely without bitterness.
The variety is late ripening. The growing time is 125-135 days from the moment the seedlings hatch. In cold regions, they can take up to 5 months, and the crop will have time to ripen.
Pros and cons of Ammon cabbage
The positive properties of the variety include:
- excellent keeping quality and transportability;
- long-term preservation in field conditions;
- high productivity and a small percentage of non-marketable fruits;
- resistance to fusarium and thrips.
Among the disadvantages of Ammon cabbage, it should be noted:
- the need for frequent watering and fertilizing;
- difficulty in acquiring seed material.
Based on the totality of its characteristics, the Ammon variety is one of the most promising for cultivation throughout almost the entire territory of Russia.
Productivity of cabbage variety Ammon
The yield of the cabbage hybrid Ammon F1 is very high: up to 600 centners per hectare, that is, 600 kg per hundred square meters. Such indicators make it possible to classify the hybrid as an industrial crop that can be grown in agriculture for commercial purposes.
There is only one way to increase the yield of Ammon cabbage - by increasing planting density.

Reducing the distance between heads or rows to less than 40 cm is not recommended, since the crop will be cramped
An increase in fertilizer application rates has virtually no effect on yields.
Planting and caring for Ammon cabbage
Like all cruciferous vegetables, Ammon cabbage thrives in fertile soil of moderate moisture and medium looseness. For planting, choose a sunny area protected from the wind. Preliminary preparations are carried out in the fall of the previous year. Add 500 g of lime and half a bucket of peat and humus to the soil for each square meter.
Seeds are planted in the spring, usually at the end of April. Planting is done in rows located at a distance of at least 50 cm from each other. Seeds are placed in each of the grooves at a distance of 2-3 cm. After sowing, the area is mulched with humus and watered abundantly.
In the future, as soon as the sprouts appear, they are thinned out, leaving the strongest ones at a distance of 40-50 cm from each other.
With earlier cultivation, seedlings are sown in mid-February. Before planting, the seeds are soaked in water for half an hour. You can use regular garden soil as a growing substrate. The seeds are buried into it by 1.5 cm and the container is covered with film or glass, maintaining a constant temperature around + 20 °C. As soon as the first shoots appear, the film is removed and the seedlings are sent to a cool room (not higher than + 9 ° C).
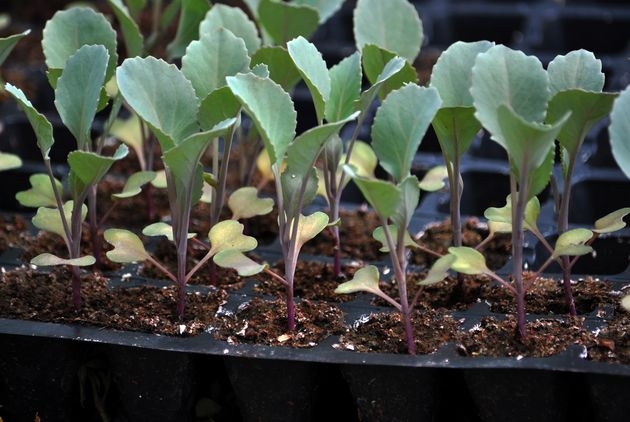

2-3 weeks after germination, seedlings are planted in small individual pots
Planting in open ground occurs in early May. By this time, the seedlings have 6-7 leaves.
Caring for Ammon cabbage requires regular watering and fertilizing. From time to time, plants need hilling (the height of the stem from the ground to the head should not exceed 10 cm).
Watering is carried out once every 3 days, without over-moistening the soil. It is best to produce them in the morning, but you need to make sure that water does not get on the heads of cabbage. After watering, it is advisable to loosen the soil to a depth of 5 cm.
Fertilizers are applied once a month. This can be either organic or mineral supplements:
- humus;
- peat;
- superphosphate;
- nitrophoska, etc.
Organics have a standard dosage - about 2-3 kg per 1 sq. m. m. The application rates of mineral fertilizers range from 20 to 35 g per 1 sq. m. m depending on planting density.
Diseases and pests
In general, the hybrid has high resistance to many diseases, but some of them still appear on the beds with regular intervals. For cabbage of the Ammon variety, this disease will be blackleg. This is an infection caused by a fungus of the Erwinia family.
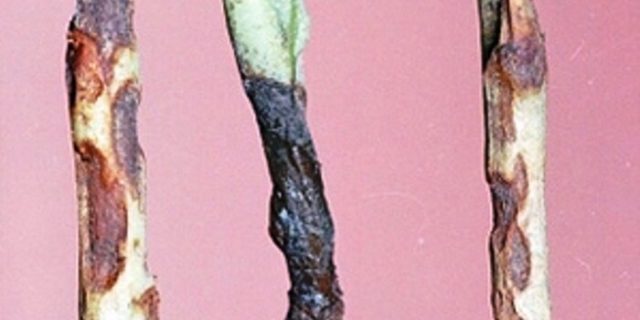
The symptoms of the disease are quite stereotypical - the appearance of brown and then black spots on various parts of the plant
Stems are predominantly affected, most often at the seedling stage.
There is no treatment for the disease. Damaged specimens are dug up and burned. After removing foci of infection, the soil is sprayed with a 0.2% solution of potassium permanganate in water. Prevention of the disease helps well - it is recommended to treat the seeds before planting with Granozan (0.4 g of the substance is enough per 100 g of seeds).
The main cabbage parasites - thrips and cruciferous flea beetles - almost never attack the cabbage hybrid Ammon F1. The only serious pest that remains is the common white butterfly. The second and third generations of this insect (appearing in July and September) can significantly reduce the yield of Amon cabbage.
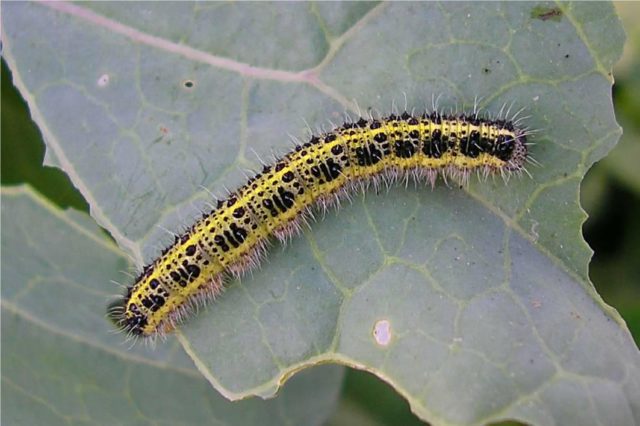

Cabbage white caterpillars infect all parts of the plant - leaves, stems, heads of cabbage
Despite the abundance of external enemies, the population of this pest is very large, and if you miss the moment, you can forget about a good harvest.
Effective remedies against whiteweed are the drugs Fitoverm, Dendrobacillin and Baksin. In addition, plants should be regularly inspected for the presence of clutches of adult butterflies and promptly destroyed.
Application
Ammon cabbage has universal uses. It is consumed fresh in salads, boiled and stewed, in first and second courses and, of course, canned (sauerkraut).
Conclusion
Ammon cabbage has high yields and good disease resistance. This crop has excellent taste and is characterized by high head density. The shelf life of Ammon cabbage, if conditions are met, can reach up to 11-12 months.








