Content
Atlantic giant pumpkin is one of the best types of melon crops, which has rightfully earned its place in the hearts of gardeners. In total, there are approximately 27 varieties of pumpkin, which in China is proudly called the “queen of vegetables.” However, three varieties of giant pumpkins attracted the greatest interest from gardeners: Atlant, Sugar Giant and Siberian Giant - due to the unique characteristics of the fruit and the peculiarities of agricultural technology.
Description of giant pumpkin varieties
The origin of this melon crop is associated with South America, but today it can be found in almost any country in the world. Giant pumpkin, or large-fruited pumpkin, is an annual plant with well-developed long and powerful stems on which creeping tendrils grow. The plant has huge dark green leaves on large petioles. The flower stalks of the giant pumpkin are also quite large, bright yellow, with very fragrant petals turned outward.
Atlantic giant
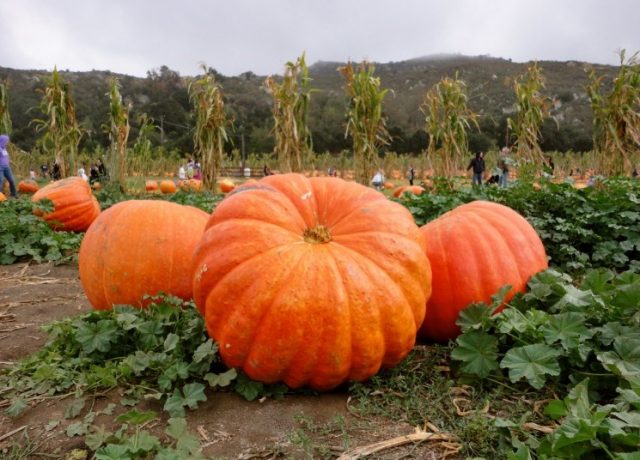
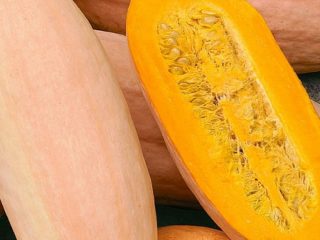
The Atlantic Giant pumpkin variety is a mid-late variety, a climbing plant, with well-developed powerful stems and large leaves.The smooth, wide, elliptical fruits have pronounced segmentation and an orange-yellow skin.
Atlantic giant pumpkin tolerates transportation and long-term storage well. It is popular among gardeners due to its high yield and resistance to common diseases of melons and melons.
Sugar giant
This is a large-fruited, weakly climbing pumpkin variety that reaches maturity 110–130 days after planting. Sugar giant pumpkin is well stored and transported and, interestingly, reveals better taste qualities of the fruit when stored for a long time.
Siberian giant
This is a mid-late variety, characterized by high yield and famous for the good taste of the fruit. Pumpkin ripens 105 - 120 days after sowing the seeds; it requires a lot of space, which must be taken into account when planting. The Siberian giant pumpkin is good both for human consumption and as animal feed, which is why it is often planted for use as silage.
Description of fruits
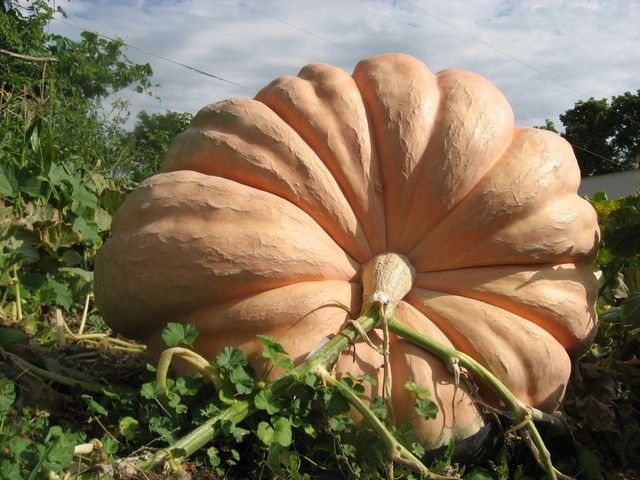
Ripe fruits of the Atlantic Giant variety are round-oval in shape and weigh 50 - 70 kg. Their flesh is bright orange, firm, very juicy, aromatic and sweet. The variety is also characterized by good transportability and long-term storage. This variety is eaten both raw and heat-treated, and, in addition, is used for making juice and various fresh vegetable juices.
Sugar giant pumpkin fruits reach a weight of up to 65 - 80 kg (with intensive care). The pulp, on average, has a thickness of 8 - 10 cm. Its structure is firm, juicy, and bright orange in color. The fruits of this variety are suitable for long-term storage.They are used to prepare various dishes using heat treatment, as well as in raw form (as an ingredient for vegetable salads).
The Siberian giant is distinguished by its richly colored, slightly segmented spherical fruits. Their pulp is loose, creamy-yellow in color, and contains a huge amount of vitamins, mineral salts and organic acids. The variety is considered dietary and is valued for its beneficial properties.
Characteristics of varieties
All three varieties are well adapted for growing in harsh climatic conditions, which is why they are loved by residents of Siberia and the Urals. Since all pumpkin crops are heat-loving, it is recommended to cover young plants with film at night in cold summer conditions.
The large-fruited Atlantic giant pumpkin, just like the Siberian and Sugar giant, has a short growing season, which makes it possible to harvest this crop in regions with short summers.
All three varieties are distinguished by good drought resistance, however, since the fruits of the variety to which they belong are quite large, in order for the maximum weight gain by the fruits, the plant needs to organize regular watering and fertilizing.
Resistance to pests and diseases
Atlantic giant, like the other two varieties, is quite resistant to pests and diseases. But under unfavorable conditions, the crop can be affected by gray and white rot, anthracnose and powdery mildew.
To reduce the risk of diseases, pumpkins are grown in compliance with the rules of crop rotation. Pumpkin is very demanding of its predecessors. The best options for it are planting potatoes, onions, cabbage, root crops and legumes.Cucumbers, zucchini, and squash will be dangerous predecessor crops that can provoke diseases and invasion of pests common to these plants.
In addition to diseases, the crop suffers from pests such as spider mites and aphids. Therefore, the tops and leaves must be regularly inspected for damage by diseases or parasites, and identified diseased areas on the vines must be removed. For prevention, spraying is usually carried out with a solution of laundry soap, ash and onion peel infusion.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Atlantic giant pumpkin has both advantages and some disadvantages. Its advantages include the following characteristics:
- frost and drought resistance;
- ability to withstand sudden temperature changes;
- good yield;
- dietary properties of fruits;
- transportability and keeping quality.
There are few disadvantages:
- special demands of the plant on the composition of the soil;
- insufficient resistance to certain diseases.
How to Grow a Giant Pumpkin
If you follow all the rules of agricultural technology, even an inexperienced beginner can grow any of the three varieties of large-fruited pumpkin.
In addition, when choosing a location, it should be taken into account that all large-fruited pumpkins are characterized by strong weaving, and therefore they need special supports, trellises or a fence.
All three varieties of pumpkins presented are quite demanding on the composition of the soil, so a good harvest can only be obtained when planted in nutritious soil: ideally, if the soil is loamy or sandy loam.In heavy or acidic soil, pumpkin will not produce a good harvest, so dolomite flour or lime must be added.
The beds for sowing pumpkins begin to be prepared in the fall, they are dug up and fertilizers are applied: humus or compost at a rate of 4 - 5 kg per 1 m2, as well as 30 g of superphosphate.
The giant pumpkin is usually grown using the seedling method to guarantee time to harvest in the harsh climatic conditions of Russia. Seeds for seedlings are sown in April. To improve germination, they are pre-soaked in any growth stimulant and germinated in a damp towel. After this, the germinated seeds are planted to a depth of 5 - 6 cm in individual peat pots.
Seedlings are planted in a permanent place towards the end of May-beginning of June, when the ground has warmed up to a depth of 10 - 12 cm. By this time, the young sprouts already have 3 - 4 true leaves. The planting pattern should be such that the plants have freedom, since all large-fruited pumpkin varieties need space. Usually leave 1 to 1.5 meters between each bush, both in length and width.
The giant pumpkin needs feeding twice during the entire season: when planting seedlings in a permanent place and during the period of active formation of vines. As fertilizers, use a diluted infusion of mullein (1:10) or bird droppings (1:20), as well as mineral complexes, for example, Nitrophoska.
To grow a giant pumpkin, it is important to form the bush correctly. Usually one main lash is left, on which no more than 2 - 3 ovaries are allowed. All other lashes and ovaries are removed. After the fourth leaf appears from the ovaries, the main lash is also pinched.
Throughout the season, all care comes down to regular watering, loosening and weeding.It is important to avoid waterlogging and water the plant as the top layer of soil dries out. In order for the pulp to be sweeter, the giant pumpkin should be watered sparingly during the fruit ripening period.
Conclusion
Atlantic giant pumpkin is one of the most favorite large-fruited varieties among gardeners, along with the Siberian and Sugar giant. All three varieties are easy to care for, have high yields and excellent taste. The only small disadvantage of these varieties is their low resistance to pests and diseases, however, timely preventive measures make this disadvantage insignificant.