Content
- 1 What is the name and appearance of decorative garlic?
- 2 How decorative garlic blooms
- 3 Types of decorative garlic
- 4 Planting and caring for decorative garlic
- 5 Diseases and pests
- 6 When to dig up decorative garlic
- 7 How to propagate decorative garlic
- 8 The use of decorative garlic
- 9 What plants does it go with?
- 10 Conclusion
Ornamental garlic is a dual-use plant. It can be used in landscape design to decorate a flower bed, or in a salad or some other dish. But there is real confusion with the names. And it's all about linguistic traditions.
What is the name and appearance of decorative garlic?
Table garlic belongs to the genus Allium, which has more than 900 species growing on all continents. The word "Allium" means "onion" in Latin. Therefore, one can often observe confusion in names when describing decorative garlic. In the caption under the photo it is often called an onion. From a biological point of view, the latter is true.But the tradition of the Russian language divides the representatives of the genus into garlic and onions. The latter should have a multi-layered bulb and feather tubes. The first is distinguished by a dense, almost monolithic tuber and flat sword-like or belt-shaped leaves.
The color of the corollas among representatives of the genus is very diverse. It happens:
- yellow;
- white;
- lilac;
- pink;
- burgundy;
- dark purple;
- blue.
Also, not all onion inflorescences look like balls. In some species they look more like disheveled umbrellas, in others they look more like a cluster of bells.
When choosing ornamental onion plants, you will have to focus on the first word in the name of the species - “Allium”. And then you need to decide which type of decorative garlic in the flowerbed is preferable. The bow family provides a wide range of choices for the designer.
How decorative garlic blooms
Flowering lasts about 30 days. A mandatory feature of all bows is the peduncle arrow. It is on it that the inflorescence of any type develops.
All bulbous plants are suitable for forcing, and garlic is no exception. Thanks to this, flowers can be obtained at almost any time of the year. As long as the plant is warm enough. Accordingly, by planting garlic heads at different times, you can get flowers throughout the entire growing season. And in a greenhouse or room - even in winter. But normally, onions bloom in the summer: from June to August.
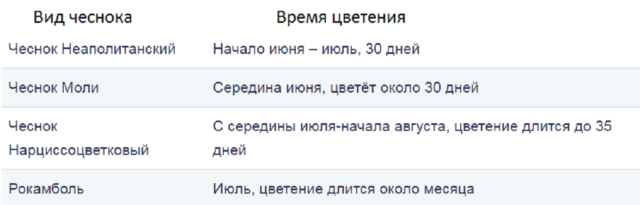
The table shows the flowering times of the most popular ornamental species of the Onion genus, immediately planted in the ground.
Types of decorative garlic
Ornamental garlic can be a biennial or perennial plant. The only rule: there are no annuals. At the same time, for some reason table species are classified as “scenery”.At the same time, among garden ones you can find rather inconspicuous specimens, differing only in the size of the heads. So we must take into account that the division into “edible” and “decorative” species in the case of the Onion genus is very arbitrary. Theoretically, decorative ones include:
- aflatun (Allium aflatunense);
- Dutch (Allium hollandicum);
- gigantic (Allium giganteum);
- bowed (Allium cernuum);
- Christoph (Allium cristophii);
- Karatavi (Allium karataviense);
- daffodil (Allium narcissiflorum).
Another very interesting species is not officially classified as decorative, but it is often grown in a flower bed due to another property. This is Chinese allspice/branching garlic(Allium ramosum).
Aflatunsky
Perennial. It got its name from the Aflatun Pass in Kyrgyzstan. The tuber is ovoid, 2-6 cm in diameter. The leaves are rosette, belt-shaped, up to 60 cm long and 2-10 cm wide. The color is bluish. The peduncle is hollow and powerful. Height 80-150 cm. The base of the stem is surrounded by leaf sheaths. The inflorescences are almost spherical umbrellas, light purple. Blooms in May-June, bears fruit in August.
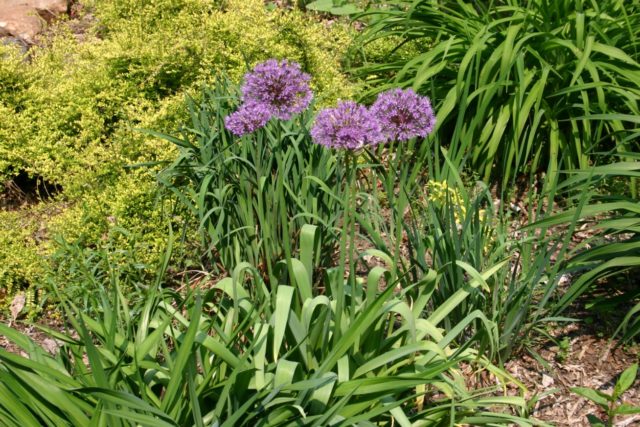

Aflatun onion is often confused with Dutch and gigantic onions
Dutch
Also a perennial from among the large decorative garlics. The number of narrow, but not long, basal leaves can reach 15. The peduncle is very powerful, up to 2 m high. The inflorescence is spherical, densely purple or white in color.

The diameter of the inflorescences of decorative Dutch garlic is 25 cm
Gigantic/giant
Perennial large-leaved species. A native of Central Asia and the Middle East. Grows in soft soil in the lower belt of mountains. The main purpose is to decorate a flower bed.
The leaves of decorative giant garlic can be eaten in the same way as table varieties.If a recipe for a dish calls for green “feathers,” you can use greens from a flower bed.
The diameter of the ovoid bulb is 2-4 cm. The height of the peduncle is 80-150 cm. The width of the strap-shaped leaves of a bluish color is 5-10 cm. The length is usually 2-3 times shorter than the stem. The inflorescence is dense, spherical. The color of the corollas is light purple.
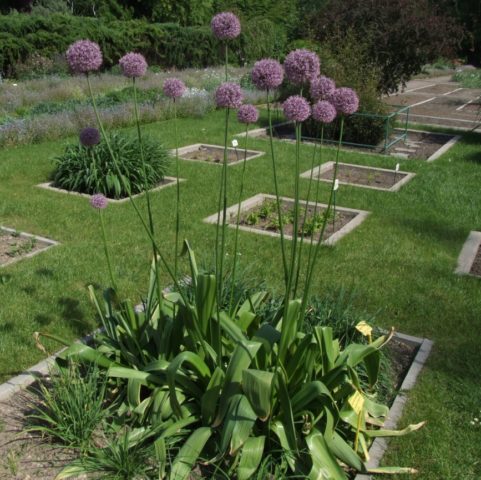

Giant garlic can easily be confused with Aflatun garlic, as they are most likely close relatives
Bowed
Perennial wild plant of North America. Habitats: prairies, dry forests and scree.
In its original state, the plant is very inconspicuous. But breeders took it upon themselves, developing several varieties of ornamental garlic for growing in a flower bed in the garden.
The bulb is conical. With a diameter of 15 mm, its length is up to 5 cm. The leaves are flat and narrow. Width 2-4 cm and length up to 30 cm. Rosette. The length of the peduncle is up to 0.5 m. The stem ends with an umbrella bent down with flowers of white or pink color. Flowering time is July-August.
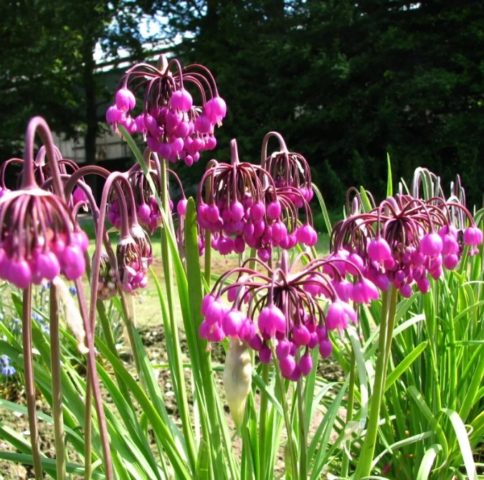

Breeders took up bowed garlic, developing several varieties, including “Purple King”
Christophe's onion/garlic
Powerful, relatively low-growing, perennial plant. The distribution area is mountainous Turkmenistan, northern Iran and Central Türkiye. Grows in the lower mountain zone on soft slopes.
The tuber is spherical, diameter 2-4 cm. The number of rosette leaves is 3-7, their width is 5-25 mm. Flat. The color is bluish-green or gray. There are hard, sparse bristles on the edges.
The peduncle is very powerful. With a height of 15-40 cm, its diameter is 5-15 cm. It is approximately equal in length to the leaves. The inflorescence is 20 cm in diameter. It can be spherical, but more often hemispherical.The color of the flowers is purple or pink-violet. A characteristic feature of this type of decorative garlic is star-shaped flowers with narrow petals. Flowering in June.
Christophe's garlic can be propagated by daughter bulbs or seeds. Its main purpose on the site is to decorate the flower bed.

Christophe's garlic looks good as a border plant if planted fairly densely.
Karatavsky
Endemic to the Pamir-Altai and Tien Shan. The name comes from the Karatau ridge. Prefers to grow on mobile limestone screes of the lower mountain belt.
The bulb is spherical. Diameter 2-6 cm. There are usually two leaves, but there may be three or one. The shape is lanceolate, oblong or almost spherical. Leaf width is 3-15 cm. The peduncle is short: from 10 to 25 cm. It can be half immersed in the ground. The stem is shorter than the leaves. The inflorescence is spherical, dense. The color is white or light pink-violet.
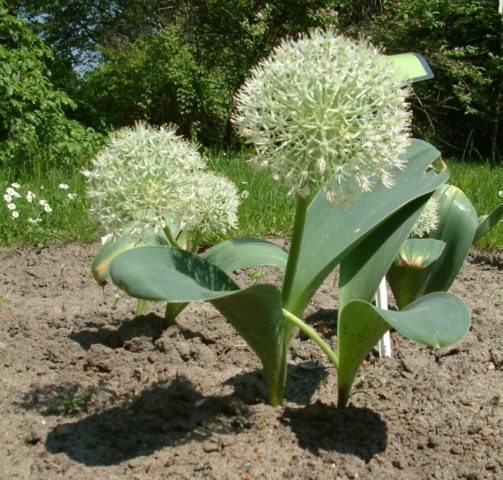

Tulip-like leaves of Karatav garlic in combination with balls of inflorescences create cognitive dissonance
Narcissus flower
Homeland - the mountains of Spain, the south of France and the north of Italy. Herbaceous perennial, only 10-40 cm high. Leaves are lanceolate-linear, bluish in color. The flowers are large: 1-1.2 cm long. The wild form has a pink corolla. The inflorescences are a drooping umbrella of hemispherical or almost flat shape. Both the appearance in the photo and the name of garlic indicate that its main use is decorative.

Brighter decorative varieties have already been bred from the wild form of narcissus garlic.
Fragrant
This species has many names, the origin of which is often associated with Latin names. That is, “tracing paper”. Of the Latin ones, the two most commonly used are: Allium odorum - fragrant onion/garlic and Allium ramosum - branched onion/garlic. Other Russian names:
- wild;
- Chinese;
- odorous;
- Tatar.
There are two more almost forgotten Russian names: lousy onion and steppe garlic.
For marketing purposes, the plant was often called Chinese garlic to add a touch of exoticism. This is partly true, since the mountains of Mongolia and China are considered the birthplace of fragrant garlic. It was brought to Central Asia, Western and Eastern Siberia by nomadic tribes.
This is a perennial frost-resistant plant. Although, in comparison with its “brothers”, Chinese garlic is considered heat-loving. Moreover, even with light snow cover, the bulb can overwinter at a temperature of -45 °C. Jusai is capable of growing both in the shade and in well-lit areas.
The Chinese garlic bulb is not very suitable for food due to its size: 8-15 mm in diameter. It is elongated and goes into the rhizome. The leaves are long, from 35 to 60 cm, but narrow - 8-12 mm. Belt-shaped, fleshy. The color is dark green. There is a waxy coating. The number of leaves per plant is 6-12 pieces. Total weight 35-70 g.
The height of the peduncle is 60-70 cm. The inflorescence is a thick ball. Flowering period July-August. In the photo, Chinese garlic does not look special; it was included in the decorative category not for its flowers, but for its aroma. Its feature, which is absent in other types of onions, is a pleasant floral smell.
Dzhusai is drought-resistant, but beautiful leaves can only be obtained with good watering. Another advantage is that it is undemanding to the soil. He is not afraid of even slightly salted soil.
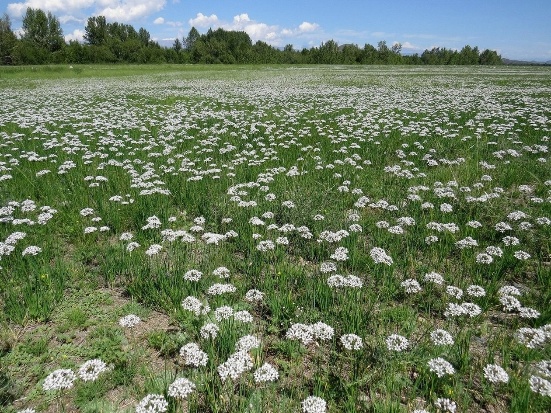

Chinese garlic is cultivated for its leaves, which must be cut 3-4 times during the growing season.
Planting and caring for decorative garlic
Even decorative garlic is in fact a vegetable crop with the same requirements for “neighbors” and predecessors as the table variety. Plants prefer dry, sunny places with loose soil. They are usually undemanding to soil quality and can grow where other flowers die.
When to plant decorative garlic
The decorative variety of garlic, like table garlic, reproduces by seeds and daughter bulbs. The latter will overwinter well in the soil if you do not dig them up. But in the spring you will still have to divide the planting material, since otherwise the garlic will quickly degenerate. Whether or not to dig up bulbs in the fall depends entirely on the wishes of the owner of the site. But it’s better to plant them in a new place in the spring, after the frosts have ended. The advantages of vegetative propagation are that garlic will bloom within the first year after planting.
When deciding to propagate the plant by seeds, planting decorative garlic is carried out in the fall. They are planted 1.5 months before the onset of frost.
When planting seeds in the spring, they are pre-soaked and germinated. Decorative garlic can be planted in early spring, as it is not afraid of frost.
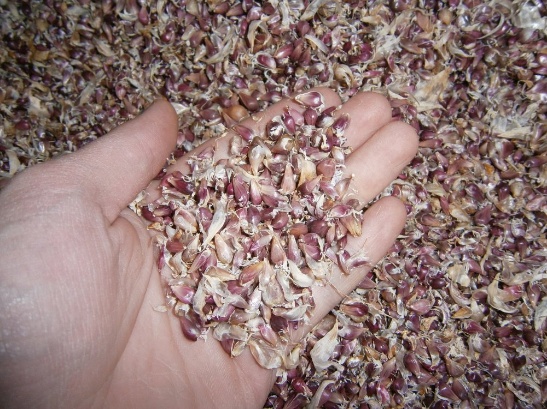

Seeds of ornamental species from the genus Onion can look different: like small heads or black grains
But since garlic is often understood as a decorative onion, the seeds may look different, be dense and black. Such fruits are called “chernushka”.
Requirements for place and soil
Almost all types of onions are steppe plants. The mountain slopes where some of them grow are treeless and differ from the steppe only in slope. Therefore, when choosing a place to plant decorative garlic, you need to take into account the amount of sunlight falling there. These plants can withstand even summer afternoon sun.
Decorative garlic is also undemanding when it comes to soil. But it does not like acidic or waterlogged soil. The soil must be alkaline or neutral. Prefers to grow in loose soil that drains water well. The flower is drought-resistant, and a slight lack of moisture is better for it than its excess.
How to plant decorative garlic
Before planting, the soil must be prepared in order to obtain strong plants with good inflorescences in the spring. The soil is prepared in advance, even in the summer. They dig it up and add nutrients:
- 20 g superphosphate;
- 15 g potassium salt;
- 10 kg of humus.
All standards are given per 1 sq. m.
These plants have too many common diseases.

By selecting species with different colors of inflorescences, you can create interesting compositions
When planting decorative garlic cloves, make grooves about 10 cm deep in the soil. The cloves are “placed” vertically and sprinkled with soil. If garlic is planted in the fall, it will have to be covered with peat during frosts.Planting is carried out no later than 1 month before the onset of cold weather. But it is better to plant daughter bulbs in the spring, since garlic can begin to grow in the fall. Then he will die in winter.
It is better to plant seeds in the fall 1.5 months before the onset of cold weather. They should not be soaked. Over the winter, the grains will undergo natural stratification, and in the spring they themselves will become wet in melt water. Only healthy and whole seeds are selected for planting. They are sown to a depth of 2-3 cm. Shoots appear after a month. “Chernushka” and “vozdushka” grow slowly.
Aftercare
Although decorative garlic is unpretentious, it also requires some care. After sprouts appear, it must be regularly weeded to remove weeds. Watering is required only four times per season, unless the year is dry. Otherwise, you will have to water more often depending on the need for water.
The soil must be loosened regularly, especially after heavy rain. To obtain a strong central peduncle and a beautiful large inflorescence, it is necessary to remove all lateral arrows if they appear.
Otherwise, no special care is required. Only standard pest and disease control for all flowers.

If not properly cared for, the leaves quickly turn yellow and the plant loses a significant part of its attractiveness.
Diseases and pests
Basically, garlic gets sick due to being in an environment that is too humid. In the flowerbed it is affected by powdery mildew. The plant begins to wither, light green spots appear on the leaves and peduncle. Eventually, the garlic dries out. This can be avoided by following watering rules and changing the growing location every 3-4 years. It is also necessary to treat the teeth with a fungicide before planting.
During storage, garlic heads are often affected by neck rot. The cloves first become soft, then mold grows on them, and eventually they dry out. This happens due to insufficient drying of the bulbs before storing. As a preventative measure, the harvested garlic is dried in the sun and only then sent for storage.
Ornamental garlic is attacked by garden pests: spider mites, onion flies and onion moths.
These pests are eliminated using insecticides designed to treat garden crops against insects.
When to dig up decorative garlic
Ornamental garlic ripens in the same time frame as table garlic. Therefore, it should be dug up in early autumn, when the seeds are already ripe and the bulbs have collected maximum nutrients. But if the plant is not intended for the winter table, the heads do not need to be dug up until spring. They overwinter well underground.
How to propagate decorative garlic
Decorative garlic is propagated by seeds and daughter bulbs/cloves. Nigella is harvested after the seed pods turn brown and dry. The inflorescences are torn off, the seeds are husked and dried.
If you choose the method of propagation by daughter bulbs, they must be separated from the mother bulbs in the spring before planting. Otherwise, the small clove will dry out during storage. The head of garlic is dug up, being careful not to damage it. Dry in the sun and lay out in a cool place on straw. Sawdust is not suitable, as too dry ones suck water out of the bulbs. And in damp conditions, garlic can germinate. Another storage method: in hanging bunches.

This is usually how table garlic is stored, but this method is also suitable for decorative garlic.
The use of decorative garlic
Various types of garlic are often used for garden decoration. There is even a separate category of onion garden called “alaria”. Only representatives of the Onion genus are used in it.
Plants look very good on alpine slides. They are widely used in landscape design, where strict geometric shapes are required. Low-growing decorative onions are often used to decorate borders along paths.
The main advantage of decorative types of onions is that they bloom when other similar plants have already completed their growing season. Therefore, they can be used in popular herb and grain gardens. It is even possible to partially “recreate” steppe expanses or alpine meadows.
Peduncles are used as a cut crop. Ball-shaped inflorescences look good in a bouquet in combination with other garden plants. Green leaves can be used in summer salads.
Is it possible to eat decorative garlic?
All species of the genus Onion are edible. They may differ from table garlic in richness and shades of taste, but otherwise they are very similar. In the regions of origin, they are eaten along with regular garlic.
Decorative garlic can be eaten in any dish. Add to taste.
The restrictions are the same as in the case of table varieties. You should not eat whole heads of the spice in an attempt to protect yourself from respiratory viruses. Eating decorative garlic helps against diseases in the same way as in the case of table garlic. That is, no way. But you can burn your stomach lining. So everything is good in moderation.
But since decorative onions/garlic generally mean wild species, you need to remember that these plants have a less pronounced taste and smell than garden crops.
Another reason why ornamental varieties are usually not eaten: it is an expensive pleasure to eat planting material. But you may not get the desired effect in the dish.
What plants does it go with?
Blue, lilac, violet and blue balls of garlic go well with other decorative flowers of similar shades: irises, hydrangeas, delphiniums.
The yellow inflorescences of some decorative onions also go well with these plants.
Conclusion
Ornamental garlic is an unpretentious plant that is well suited for beginning gardeners. Its main advantage is its “dual purpose”. In addition to decorating the garden, ornamental onions can also be used for food. The same cannot be said about many garden flowers, such as delphinium, which belongs to Ranunculaceae.








